Standard free energy change for an equilibrium is zero, the value of Kp is
zero
1
2
100
The correct Answer is:B
To solve the problem, we need to find the value of Kp when the standard free energy change (ΔG0) for an equilibrium is zero. Here’s the step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Understand the relationship between Gibbs free energy and the equilibrium constant
The relationship between the standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG0) and the equilibrium constant (Kp) is given by the equation:
ΔG0=−2.303RTlogKp
where:
- R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
- T is the temperature in Kelvin
Step 2: Substitute the given value of ΔG0
According to the question, ΔG0=0. We can substitute this value into the equation:
0=−2.303RTlogKp
Step 3: Simplify the equation
Since −2.303RT is a constant and cannot be zero, the only way for the equation to hold true is if:
logKp=0
Step 4: Solve for Kp
To find Kp, we need to eliminate the logarithm. Recall that if logKp=0, then:
Kp=100
This simplifies to:
Kp=1
Conclusion
Thus, when the standard free energy change for an equilibrium is zero, the value of Kp is:
1
The relationship between the standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG0) and the equilibrium constant (Kp) is given by the equation:
ΔG0=−2.303RTlogKp
where:
- R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
- T is the temperature in Kelvin
According to the question, ΔG0=0. We can substitute this value into the equation:
0=−2.303RTlogKp
Since −2.303RT is a constant and cannot be zero, the only way for the equation to hold true is if:
logKp=0
To find Kp, we need to eliminate the logarithm. Recall that if logKp=0, then:
Kp=100
This simplifies to:
Kp=1
Thus, when the standard free energy change for an equilibrium is zero, the value of Kp is:
1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMEXERCISE - Illustration
24 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMEXERCISE - SOLVED EXAMPLES
19 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMEXERCISE - EFFICIENT
50 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING-I & IIBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING-I & IIEXERCISE - JEE Advanced (Archive)
98 Videos
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - JEE Advanced (Archive)
51 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Free energy change for a reversible process is
A>0B<0Cequal to zeroDunpredictableThe free energy change for a reversible reaction at equilibrium is:
zero
small positive
small negative
large positive.AzeroBsmall positiveCsmall negativeDlarge positive.
The free energy change the due to a reaction is zero when
View SolutionPhysical and chemical equilibria can respond to a change in their pressure, temperature, and concentration of reactants and products. To describe the change in the equilibrium, we have a principle named Le Chatelier's principle. This we can define in terms of energy, as the free energy change in equilibrium is zero means the system is stable. So if we are doing some changes in equilibrium, then the system having a tendency to reestablish the equilibrium by undoing the effect we brought. Consider the following equilibrium.
Three sparingly soluble salts A2B,AB, and AB3 are given. If all the three having the same value of solubility products (Ksp), in the saturated solution, the correct order of their solubilites is
View SolutionStandard Gibbs free enegry change ΔGΘ for a reaction is zero. The value of the equilibrium constant will be:
View SolutionThe free energy change for a reversible reaction at equilibrium is
View SolutionA reaction is spontaneous if free energy change ΔG , for the reaction is negative .
The question arises, how we can explain , the spontaneous reversible reaction taking the example of dissociation equilibrium ,N2O4⇔2NO2(g).
the variation of free energy with the fraction of N2O4 dissociated under standard conditions is shown in the figure below.
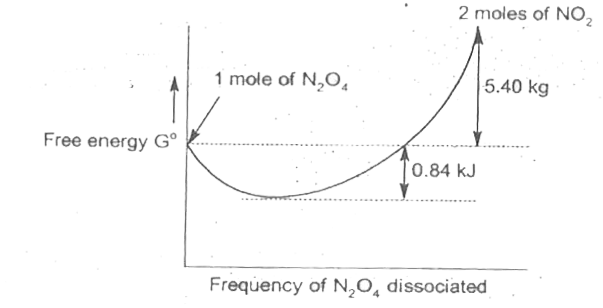
The standard free energy change for the conversion of 1 mole of N2O4 into 2 moles of NO2 is
View SolutionThs standard free energy change ΔG∘ is related to K (equilibrium constant ) as
View Solution

