Identify (Z) in the series.
C3H7OHconc.H2SO4−−−−−−−−−→443K(X)Br2−−→(Y)Excess of −−−−−−−−→alc. KOH(Z)
CH3−CH∣NH2−CH2∣NH2
CH3−CH∣OH−CH2∣OH
CH3−C∣OH=CH2
CH3−C=CH
The correct Answer is:D
To identify compound Z in the given reaction series, we will break down the steps involved in the transformations of the starting material, C₃H₇OH (which is propanol), through to the final product.
Step 1: Identify the starting material
The starting compound is C₃H₇OH, which is propanol (specifically, 1-propanol or n-propanol).
Step 2: Reaction with concentrated H₂SO₄ at 443 K
When propanol reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid at elevated temperatures (443 K), it undergoes dehydration to form an alkene. The dehydration of propanol leads to the formation of propene (C₃H₆), which is the compound X.
Reaction:
C3H7OHconc. H2SO4,443K−−−−−−−−−−−→C3H6 (propene)
Step 3: Reaction with Br₂
Next, propene (X) reacts with bromine (Br₂) in a non-polar solvent like carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄). This is an electrophilic addition reaction where bromine adds across the double bond of propene, resulting in the formation of 1,2-dibromopropane (Y).
Reaction:
C3H6+Br2CCl4−−−→C3H6Br2 (1,2-dibromopropane)
Step 4: Reaction with excess alcoholic KOH
The final step involves the reaction of 1,2-dibromopropane (Y) with excess alcoholic KOH. In this case, KOH acts as a strong base, promoting elimination reactions. The dibromopropane will undergo dehydrohalogenation to form an alkyne. Specifically, it will eliminate both bromine atoms and form propyne (Z).
Reaction:
C3H6Br2+alc. KOH→C3H4 (propyne)
Conclusion
Thus, the final compound Z is propyne, which can be represented as:
Z=C3H4 (propyne)
Summary of the Steps:
1. Starting Material: C₃H₇OH (propanol)
2. Step 1: Dehydration to form propene (C₃H₆)
3. Step 2: Electrophilic addition with Br₂ to form 1,2-dibromopropane (C₃H₆Br₂)
4. Step 3: Dehydrohalogenation with alcoholic KOH to form propyne (C₃H₄)
The starting compound is C₃H₇OH, which is propanol (specifically, 1-propanol or n-propanol).
When propanol reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid at elevated temperatures (443 K), it undergoes dehydration to form an alkene. The dehydration of propanol leads to the formation of propene (C₃H₆), which is the compound X.
C3H7OHconc. H2SO4,443K−−−−−−−−−−−→C3H6 (propene)
Next, propene (X) reacts with bromine (Br₂) in a non-polar solvent like carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄). This is an electrophilic addition reaction where bromine adds across the double bond of propene, resulting in the formation of 1,2-dibromopropane (Y).
C3H6+Br2CCl4−−−→C3H6Br2 (1,2-dibromopropane)
The final step involves the reaction of 1,2-dibromopropane (Y) with excess alcoholic KOH. In this case, KOH acts as a strong base, promoting elimination reactions. The dibromopropane will undergo dehydrohalogenation to form an alkyne. Specifically, it will eliminate both bromine atoms and form propyne (Z).
C3H6Br2+alc. KOH→C3H4 (propyne)
Thus, the final compound Z is propyne, which can be represented as:
Z=C3H4 (propyne)
1. Starting Material: C₃H₇OH (propanol)
2. Step 1: Dehydration to form propene (C₃H₆)
3. Step 2: Electrophilic addition with Br₂ to form 1,2-dibromopropane (C₃H₆Br₂)
4. Step 3: Dehydrohalogenation with alcoholic KOH to form propyne (C₃H₄)
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS & ETHERSBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS & ETHERSEXERCISE - Enable
100 Videos
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS & ETHERSBOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS & ETHERSEXERCISE - Efficient
98 Videos
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS & ETHERS BOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS & ETHERS EXERCISE - IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE - L
10 Videos
- ALDEHYDES,KETONES & CARBOXYLIC ACIDS BOOK - VMC MODULES ENGLISHCHAPTER - ALDEHYDES,KETONES & CARBOXYLIC ACIDS EXERCISE - IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-M
10 Videos
समान प्रश्न
Order of boiling point among primary , secondary and tertiary alcohols is :
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions does not form salicylic acid ?
View Solution4-chloro-3,5-dimethyl phenol is called :
View SolutionLiAlH4 is used as :
View Solutioncomplete the missing links in the folloiwng :
(i)C2H5Na−−→[X]C2H5I−−−→Heat[Y]Cl2(hv)−−−−→[Z]
(ii) C2H5ONaC2H5I−−−→[X]Excess of HBr−−−−−−−→(373K)[Y]KOH(alc.)−−−−−−−→[Z]
(iii) CH3CHBrCH3KOH(alc.)−−−−−→[X]HBr−−−−−−→(Preoxde)[Y]CH3ONa−−−−−→[Z]
(v)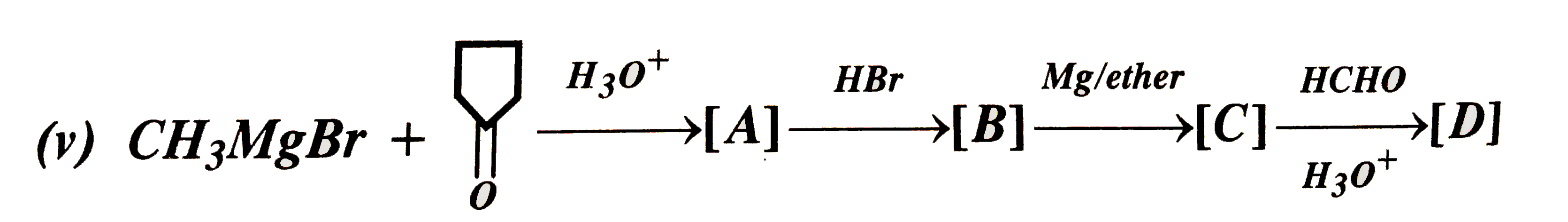
View Solution2ClCH_(2)CH_(2)OH("excess") underset(415K)overset(Conc. H_(2)SO_(4))rarr X underset("Fuse")overset(KOH)rarr Y The compound Y is
View SolutionIdentify Z in the series C_(3)H_(7)OH underset(160^(@)-180^(@))overset(conc. H_(2)SO_(4))rarrX overset(Br_(2))rarrY overset("excess of alc. KOH")rarr
View SolutionThe acid S obtained through the following sequence of reactions is : C_(2)H_(5)Br overset(Alc. KOH)rarr P underset(C Cl_(4))overset(Br_(2))rarr Q underset(("excess"))overset(KCN)rarr R overset(H_(3)O^(+))rarr S
View SolutionIdentify (Z) int eh following reaction series : Etahanol overset(PCl_(5))(rarr)(X)overset("Alc. KOH")(rarr)(Y) underset(H_(2)O,"heat") overset(H_(2)SO_(4),"r o om temp.)(rarr)(Z)
View SolutionIdentify (Z) in the series.
C3H7OHconc.H2SO4−−−−−−−−−→443K(X)Br2−−→(Y)Excess of −−−−−−−−→alc. KOH(Z)
View SolutionIn the following series of chemical reactions identify Z C_(3)H_(7)OH underset(160-180^(@)C)overset(Conc. H_(2)SO_(4))to X overset(Br_(2))to Y underset(Alc. KOH)overset("Excess of ") to Z
View SolutionMSO_(4)overset(NH_(4)OH)rarr underset("White")(Xdarr)underset("Excess")overset(NH_(4)OH)(rarr)Y overset (H_(2)S)(rarr)Zdarr Here, M and Z are
View SolutionIdentify Z, in the following reaction.
C2H5lalc. KOH−−−−→XBr2−−→YKCN−−→Z
View SolutionIdentify Z in the following series:
C2H5IAlcoholic−−−−−−−→KOH X Br2−−→ Y KCN−−→Z
View SolutionIdentify Z in the following series:
C2H5IAlcoholic−−−−−−−→KOH X Br2−−→ Y KCN−−→Z
View SolutionC_(2)H_(5)Cl overset(KCN) rarr X overset(H_(2)//"Catalyst")rarr Y overset(CHCl_(3)) underset(alc, KOH) rarr Z What is 'Z' in the above sequence of reactions ?
View Solution

