The half cell reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH=5 will be :
0.29V
−0.29V
0.059V
−0.059V
The correct Answer is:B
To find the half-cell reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH = 5, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Understand the Nernst Equation
The Nernst equation relates the reduction potential of an electrochemical cell to the standard reduction potential and the concentrations of the reactants and products involved in the half-reaction.
The Nernst equation is given by:
E=E∘−0.0591nlog((products)(reactants))
Step 2: Identify the Reaction
For the hydrogen electrode, the half-reaction is:
2H++2e−→H2
Here, n=2 (the number of electrons transferred).
Step 3: Calculate the Concentration of H+
Given that pH = 5, we can calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+):
pH=−log(H+)
(H+)=10−pH=10−5M
Step 4: Substitute Values into the Nernst Equation
Since the standard reduction potential E∘ for the hydrogen electrode is 0 V, we can substitute the values into the Nernst equation:
E=0−0.05912log(1(10−5)2)
Step 5: Simplify the Logarithmic Expression
Calculating the logarithm:
log(1(10−5)2)=log(1010)=10
Step 6: Calculate the Reduction Potential
Now substituting back into the equation:
E=−0.05912×10
E=−0.2955V
Final Answer
The half-cell reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH = 5 is:
E=−0.2955V
---
The Nernst equation relates the reduction potential of an electrochemical cell to the standard reduction potential and the concentrations of the reactants and products involved in the half-reaction.
E=E∘−0.0591nlog((products)(reactants))
For the hydrogen electrode, the half-reaction is:
2H++2e−→H2
Here, n=2 (the number of electrons transferred).
Given that pH = 5, we can calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+):
pH=−log(H+)
(H+)=10−pH=10−5M
Since the standard reduction potential E∘ for the hydrogen electrode is 0 V, we can substitute the values into the Nernst equation:
E=0−0.05912log(1(10−5)2)
Calculating the logarithm:
log(1(10−5)2)=log(1010)=10
Now substituting back into the equation:
E=−0.05912×10
E=−0.2955V
The half-cell reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH = 5 is:
E=−0.2955V
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROCHEMISTRYExercise:ENABLE
Explore 50 Videos
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROCHEMISTRYExercise:EFFICIENT
Explore 46 Videos
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ELECTROCHEMISTRYExercise:JEE Advanced (Archive)
Explore 74 Videos
- CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES Book:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES Exercise:JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE)
Explore 30 Videos
- ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRYBook:VMC MODULES ENGLISHChapter:ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRYExercise:JEE Main (Archive)
Explore 39 Videos
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
The most convenient method to protect the bottom of the ship made of iron is
View SolutionThe Nernst equation E=E∘-RT/nF in Q indicates that the Q will be equal to equilibrium constant Kc when:
View SolutionThe standard reduction potentials at 298K for the following half cells are given :
ZN2+(aq)+2e−Zn(s), E∘=−0.762V
Cr3+(aq)+3e−Cr(s), E∘=−0.740V
2H+(aq)+2e−H2(g), E∘=0.000V
Fe3+(aq)+e−Fe2+(aq), E∘=0.770V
which is the strongest reducing agent ?
View SolutionThe energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom is called……….of atom.
View SolutionWhen rain is accompanied by a thunderstorm, the collected rain water will have a pH value
View SolutionFor the half cell
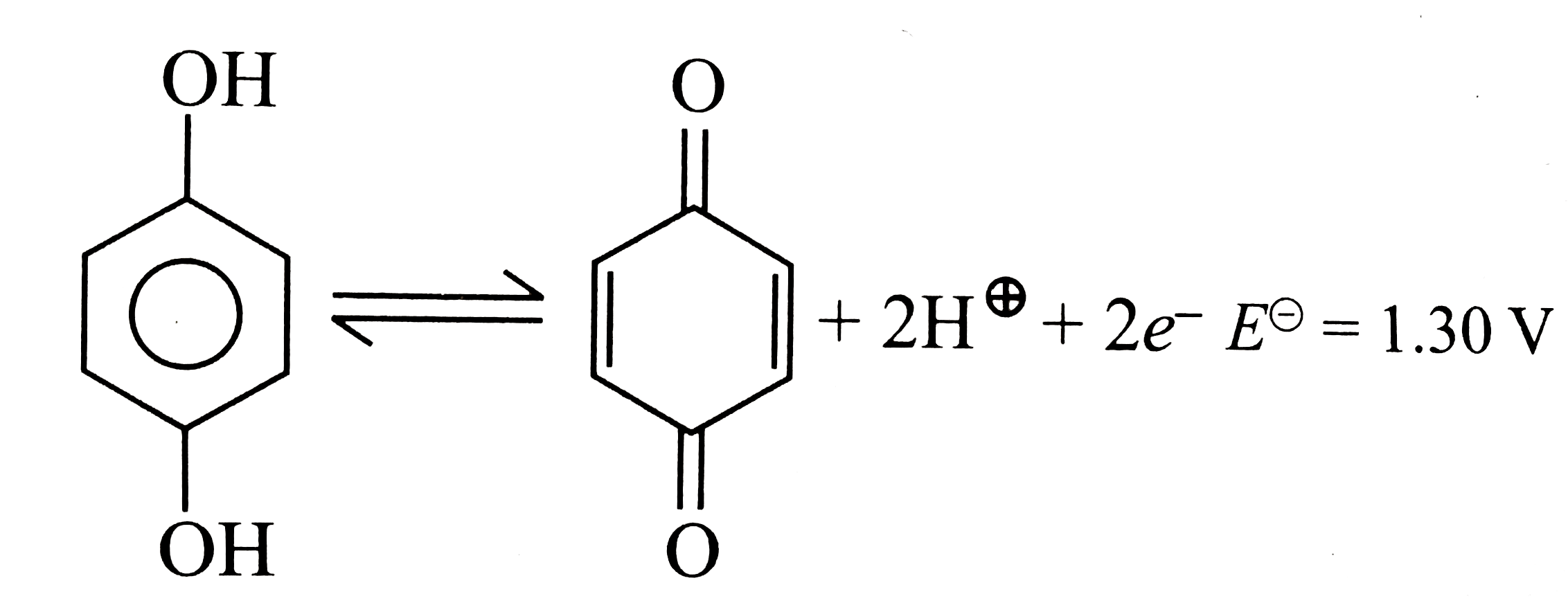
At pH=2, the electrode potential is
View SolutionThe half-cell reduction potential of a hudrogen electrode at pH= 10 will be.
View SolutionThe reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH 10 at 298K is : (p =1 atm)
View SolutionFor the half cell
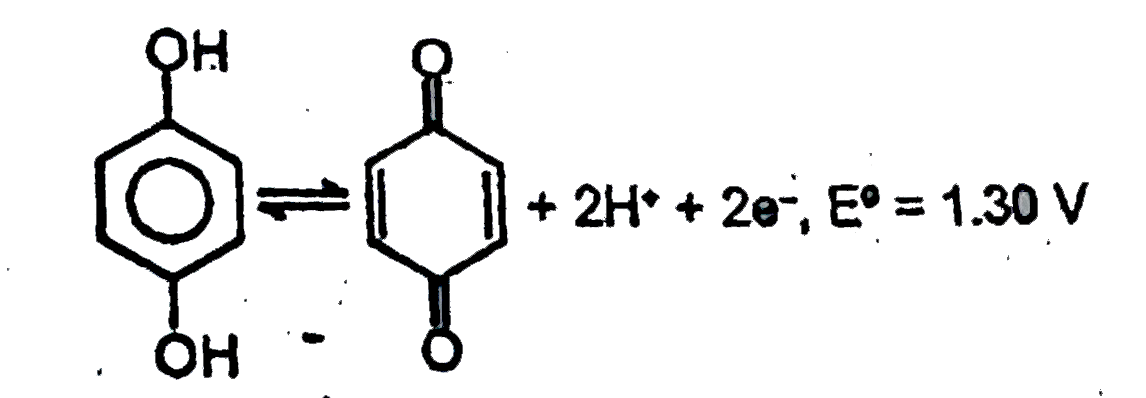
At pH=2. Electrod potential is :
View SolutionFor the half cell At pH = 3 electrode potential is
View SolutionThe reduction potential of hydrogen electrode containing a solution of pH=4 is
View SolutionThe half cell reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH= 10 and H2 gas at 1 atmi will be
View SolutionThe half cell reduction potential of a hydrogen electrode at pH=5 will be :
View SolutionThe hydrogen electrode is dipped in a solution of pH 3 at 25∘ C. The reduction potential of half cell would be :
View SolutionFor the half cell At pH=2 , the electrode potential is
View Solution
