In ΔABC, prove that:
cotBcotC+cotCcotA+cotAcotB=1
To prove that in triangle ΔABC, the equation cotBcotC+cotCcotA+cotAcotB=1 holds true, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Use the Angle Sum Property
In any triangle, the sum of the angles is A+B+C=π.
Step 2: Express A+B
From the angle sum property, we can express A+B as:
A+B=π−C
Step 3: Apply the Cotangent Function
Now, we take the cotangent of both sides:
cot(A+B)=cot(π−C)
Step 4: Use the Cotangent Addition Formula
Using the cotangent addition formula:
cot(A+B)=cotAcotB−1cotA+cotB
And since cot(π−C)=−cotC, we can write:
cotAcotB−1cotA+cotB=−cotC
Step 5: Cross Multiply
Cross multiplying gives us:
cotAcotB−1=−cotC(cotA+cotB)
Step 6: Rearranging the Equation
Rearranging the equation, we have:
cotAcotB+cotC(cotA+cotB)=1
Step 7: Expand the Left Side
Expanding the left side:
cotAcotB+cotCcotA+cotCcotB=1
Step 8: Final Result
Thus, we can conclude:
cotBcotC+cotCcotA+cotAcotB=1
This completes the proof.
---
In any triangle, the sum of the angles is A+B+C=π.
From the angle sum property, we can express A+B as:
A+B=π−C
Now, we take the cotangent of both sides:
cot(A+B)=cot(π−C)
Using the cotangent addition formula:
cot(A+B)=cotAcotB−1cotA+cotB
And since cot(π−C)=−cotC, we can write:
cotAcotB−1cotA+cotB=−cotC
Cross multiplying gives us:
cotAcotB−1=−cotC(cotA+cotB)
Rearranging the equation, we have:
cotAcotB+cotC(cotA+cotB)=1
Expanding the left side:
cotAcotB+cotCcotA+cotCcotB=1
Thus, we can conclude:
cotBcotC+cotCcotA+cotAcotB=1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONSExercise:EXERCISES 3I
Explore 15 Videos
- TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONSExercise:EXERCISES 3J
Explore 13 Videos
- TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONSExercise:EXERCISES 3G
Explore 12 Videos
- STRAIGHT LINESBook:NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISHChapter:STRAIGHT LINESExercise:Exercise
Explore 207 Videos
Similar Questions
Find the geneal values of θ from the following equations:
i) sinθ=√32, ii) cosθ=1√2, iii) tanθ=√3, iv) secθ=2√3, v) cotθ=1√3, vi) cosecθ=√2
View SolutionSolve: tan4θ=tan2θ
View SolutionProve that:
i) tan(45∘−A2)=1−sinAcosA
ii) tan(45∘+A2)=cosA1−sinA
View SolutionFind the new co-ordinates of the following points when origin is shifted to the point (−1,4) :
(i)(2,5)
(ii)(−3,−2)
(iii)(1,−4)
View SolutionIn ΔABC, prove that:
cos2A+cos2B−cos2C=1−4sinAsinBcosC
View SolutionIn ΔABC, prove that:
cotBcotC+cotCcotA+cotAcotB=1
View SolutionIn ΔABC, prove that:
tanBtanC+tanCtanA+tanAtanB=1+secAsecBsecC
View SolutionΔABC की माध्यिकाएँ G बिन्दु पर प्रतिच्छेद करती है। सिद्ध कीजिए कि क्षेत्रफल (ΔAGB)=13 क्षेत्रफल (ΔABC).
View SolutionIf cosA=cosBcosC and A+B+C=π, then the value of cotBcotC is
View Solutionयदि ΔABC की माध्यिकायें बिंदु G पर प्रतिच्छेद करती है, तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि
ar(ΔAGB)=ar(ΔAGC)=ar(ΔBGC)=13ar(ΔABC)
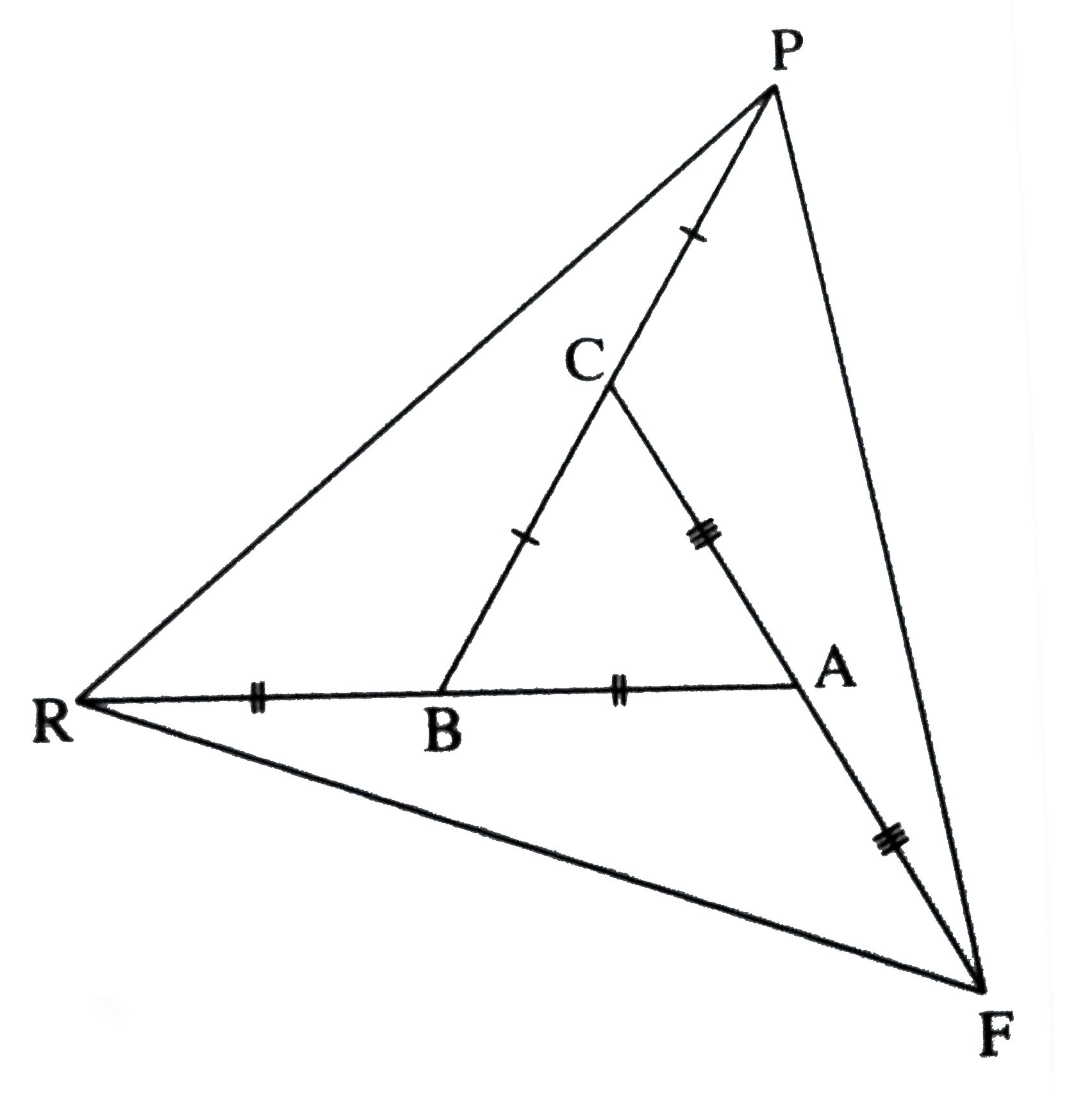
View SolutionIn the figure sides AB,BC,CA of ΔABC are produced upto points R,P,F respectively such that AB=BR,BC=CP and CA=AF. Prove that:
(ΔPFR)=7A(ΔABC)
View Solutionयदि A+B+C=π हो तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि -
cotBcotC+cotCcotA+cotAcotB=1
View SolutionIf G is the centroid of a ΔABC, Prove that ( area of ΔGAB) =( area of ΔGBC)=(area fo ΔGCA)=13( area of ΔABC)
View SolutioncosecA+secA=cosecB+secB হলে প্রমাণ করো যে,tanA+B2=cotAcotB
View Solutionநிறுவுக:cot(A+B)=cotAcotB−1cotA+cotB
View SolutionIf cosA=cosBcosC And A+B+C=pi , so cotBcotC The value of
View Solution
