Explain, what is total internal reflection?
Text Solution
Total Internal Reflection (TIR) When a ray of light travelling from a denser medium falls on a rarer transparent medium, it bends away from normal. When angle of incidence is increased beyond a certain limit (critical angle), ic it is reflected back to first medium. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection (TIR).
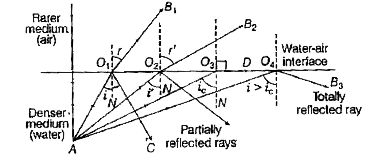
This phenomenon can be understood from the figure given above. Suppose a ray of light AO1 in the denser medium (water) is incident at the water air interface at an angle, such that i<ic . Thus, obeying law of refraction, it gets deviated away from the normal and refracted along O1B1
Now, consider another ray AO2 , such that i. > i but i.<ic . Then, the ray again gets deviated and refracted along O2B2 , but this time closer to the interface. Next, consider another ray AO3 , such that i=ic . Then, no refraction takes place, rather the ray passes along the interface as O3D .
Lastly, consider a ray AO4 , such that i>ic. Then, according to TIR, no refraction takes place, but the entire ray gets reflected back as O4B2 in its original denser medium. Thus, for a pair of given media in contact critical angle can be defined as, "the angle of incidence in denser medium for which angle of refraction in rarer medium is 90∘ ". Its value depends on the nature of two media in contact.

From snell.s law , μ2×sinic=μ1×sin90∘
∴μ1μ2=sinicsin90∘
⇒μ1μ2=sinic
or μ2μ1=−1sinic⇒1μ2=1sinic
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Which is true for total internal reflection?
ALight travels from rarer to denser mediumBLight travels from denser to rarer mediumCIndependent of the optical densities of two mediumDTakes place in the same medium
What is total internal reflection ? Under what conditions it takes place ?
View SolutionWhat is critical angle? Give one application of total internal reflection.
View SolutionWhat will be the minimum angle of incidence such that the total internal reflection occurs on both the surfaces?

View SolutionWhat is total internal reflection of light ? What are conditions for total internal reflection ?
View Solution(a) What is total internal reflection ?
(b) State two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur.
(c) draw diagrams to illustrate total internal reflection.
View SolutionExplain partial reflection, critical angle and total internal reflection with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
View SolutionDefine total internal reflection of light.
View Solution

