A cell that passes the restriction point in G1 will most likely
undergo chromosome duplication
have just have completed cytokinesis
continue to divide only if it is a cancer cell
show a drop in MPF concentration
The correct Answer is:A
To answer the question "A cell that passes the restriction point in G1 will most likely," we need to analyze the cell cycle and the implications of passing the restriction point (also known as the G1 checkpoint).
1. Understanding the Cell Cycle: The cell cycle consists of several phases: G1 (Gap 1), S (Synthesis), G2 (Gap 2), and M (Mitosis). The restriction point in G1 is a critical checkpoint that determines whether a cell will proceed to the S phase.
2. Role of the Restriction Point: If a cell passes the restriction point in G1, it is committed to entering the S phase. This means that the cell is preparing to replicate its DNA.
3. Consequences of Passing the Restriction Point:
- Chromosome Duplication: Once the cell enters the S phase, it will undergo DNA replication, leading to chromosome duplication. This is a key event in the cell cycle.
- Cytokinesis: Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis (M phase), not during G1 or S phase. Therefore, passing the restriction point does not mean the cell has just completed cytokinesis.
- Cancer Cells: While cancer cells may continue to divide uncontrollably, normal cells that pass the restriction point will also divide. Thus, this statement is not exclusive to cancer cells.
- MPF Concentration: Maturation Promoting Factor (MPF) is involved in the regulation of the cell cycle. After passing the restriction point, MPF levels typically increase, not decrease.
4. Conclusion: The most likely outcome for a cell that passes the restriction point in G1 is that it will undergo chromosome duplication during the S phase.
Final Answer:
A cell that passes the restriction point in G1 will most likely undergo chromosome duplication.
---
- Chromosome Duplication: Once the cell enters the S phase, it will undergo DNA replication, leading to chromosome duplication. This is a key event in the cell cycle.
- Cytokinesis: Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis (M phase), not during G1 or S phase. Therefore, passing the restriction point does not mean the cell has just completed cytokinesis.
- Cancer Cells: While cancer cells may continue to divide uncontrollably, normal cells that pass the restriction point will also divide. Thus, this statement is not exclusive to cancer cells.
- MPF Concentration: Maturation Promoting Factor (MPF) is involved in the regulation of the cell cycle. After passing the restriction point, MPF levels typically increase, not decrease.
A cell that passes the restriction point in G1 will most likely undergo chromosome duplication.
Similar Questions
Glutomic acid (A) has isoelectric point 3.22
(a) What is the most likely structure of the compound at its isoelectric point ?
(b) What is the most likely structure of monosodium glutamate.
H2N−CH−COOH∣CH2(A)−CH2−COOH.
View SolutionDifferences between the members of a population will most likely be passed to future generations if they are:
View Solution
Knowledge Check
A cell that passes the restriction point in G1 will most likely.
AUndergo chromosome duplicationBHave just completed cytokinesis.CContinue to divide only if it is a cancerDMove into the G0 phaseThe 'restriction point' occurs here:
AG0BG1CSDG2In a certain species of mouse, grey fur (G) is dominant over cream -coloured fur (g). If a homozygous grey mouse is crossed with a cream -coloured mouse, the genot pe of the F1 -generation will most likely be
A100% GgB25%GG,50%Gg and 25%ggC50% GG and 50% ggD75% Gg and 25%gg
The first genetic material was most likely
View SolutionThe first genetic material was most likely to be
View SolutionThe diagram below represents a change that occured in a pair of chromosomes during the formation of an egg cell. The letters represent genes on the pair of chromosomes.
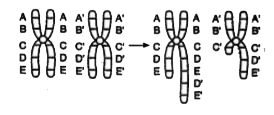
The alteration that occured will most likely
View SolutionThe egg cell measuring about 17 cm ×13cm is most likely that of:
View SolutionWhen a bomb calorimeter is used to determine the heat of recation is most likely of the system under investigation is most likely to remain constant ?
View Solution
