The optical rotation of the α-form of a pyranose is +150.7∘, that of the β-form is +52.8∘. In solution an equilibrium mixture of these anomers has an optical rotation of +80.2∘. The precentage of the α-form in equilibrium mixture is :
0.28
0.32
0.68
0.72
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the problem, we need to find the percentage of the alpha-form of pyranose in an equilibrium mixture given its optical rotations. Let's break down the solution step by step.
1. Identify Known Values:
- Optical rotation of the alpha-form (α): +150.7°
- Optical rotation of the beta-form (β): +52.8°
- Optical rotation of the equilibrium mixture: +80.2°
2. Let x be the percentage of the alpha-form:
- Therefore, the percentage of the beta-form will be (100 - x).
3. Set up the equation for optical rotation:
The optical rotation of the mixture can be expressed as:
x⋅(optical rotation of α)+(100−x)⋅(optical rotation of β)100=optical rotation of mixture
Substituting the known values:
x⋅150.7+(100−x)⋅52.8100=80.2
4. Multiply through by 100 to eliminate the denominator:
x⋅150.7+(100−x)⋅52.8=8020
5. Distribute the terms:
150.7x+5280−52.8x=8020
6. Combine like terms:
(150.7−52.8)x+5280=8020
97.9x+5280=8020
7. Isolate x:
97.9x=8020−5280
97.9x=2740
8. Solve for x:
x=274097.9≈27.94
9. Convert to percentage:
Since x is the percentage of the alpha-form:
Percentage of alpha-form≈27.94%
Final Answer:
The percentage of the alpha-form in the equilibrium mixture is approximately 28%.
- Optical rotation of the alpha-form (α): +150.7°
- Optical rotation of the beta-form (β): +52.8°
- Optical rotation of the equilibrium mixture: +80.2°
- Therefore, the percentage of the beta-form will be (100 - x).
The optical rotation of the mixture can be expressed as:
x⋅(optical rotation of α)+(100−x)⋅(optical rotation of β)100=optical rotation of mixture
Substituting the known values:
x⋅150.7+(100−x)⋅52.8100=80.2
x⋅150.7+(100−x)⋅52.8=8020
150.7x+5280−52.8x=8020
(150.7−52.8)x+5280=8020
97.9x+5280=8020
97.9x=8020−5280
97.9x=2740
x=274097.9≈27.94
Since x is the percentage of the alpha-form:
Percentage of alpha-form≈27.94%
The percentage of the alpha-form in the equilibrium mixture is approximately 28%.
समान प्रश्न
How much of the α-anomer and β-anomers are present in an equilibrium mixture with a specific rotation of +52.6∘?
View SolutionThe specific rotation of two glucose anomers are α=+110∘ and β=19∘ and for the constant equilibrium mixtures is +52.7∘. Calculate the percentage compositions of the anomers in the equilibrium mixture.
View Solution
ज्ञान जांच
The optical rotation of the ∝- form of a pyranose is +150.70, that of the β-form is +52.80. In solution and equilibrium mixture of the anomers has an optical rotation of +80.20. The percentage of the ∝- form at equilibrium is
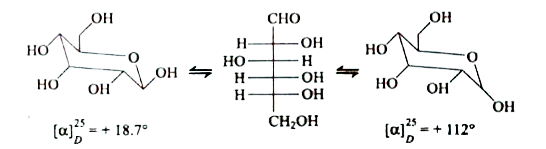
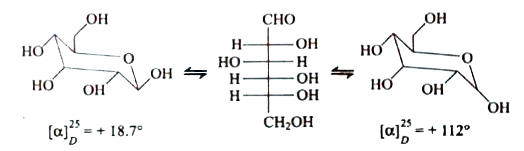
A0.28B0.32C0.68D0.72D (+) Glucose has melting point 146∘C and specific rotation [α]25D is + 112∘C. Another D(+) Glucose has melting point 150∘C and specific rotational [α]25Dis +18.7∘C. The two form have significantly different optical rotation but when an aqueous solution of either form is allowed to stand, it rotation changes. The specific rotation of one form decreases and rotation of other increases until both solution show the same value +52.7∘. The change in rotation towards an equilibrium value is called mutarotation.
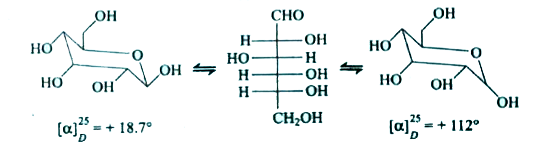
What percentage of β-D-(+) glucopyranose found at equilibrium in the aqueous solution?A50%B≈100%C38%D64%D (+) Glucose has melting point 146∘C and specific rotation [α]25D is + 112∘C. Another D(+) Glucose has melting point 150∘C and specific rotational [α]25Dis +18.7∘C. The two form have significantly different optical rotation but when an aqueous solution of either form is allowed to stand, it rotation changes. The specific rotation of one form decreases and rotation of other increases until both solution show the same value +52.7∘. The change in rotation towards an equilibrium value is called mutarotation.
For mannose the mutarotation can be shown in brief as follow:
 Aα-formBβ-formCopen chainDNone of these
Aα-formBβ-formCopen chainDNone of these
When either form of D-Glucose is dissolved In water, the solution gradually changes its optical rotation and finally attains a constant optical rotation of +52∘.

What is the percentage of open chain D-Glucose in solution?
View Solution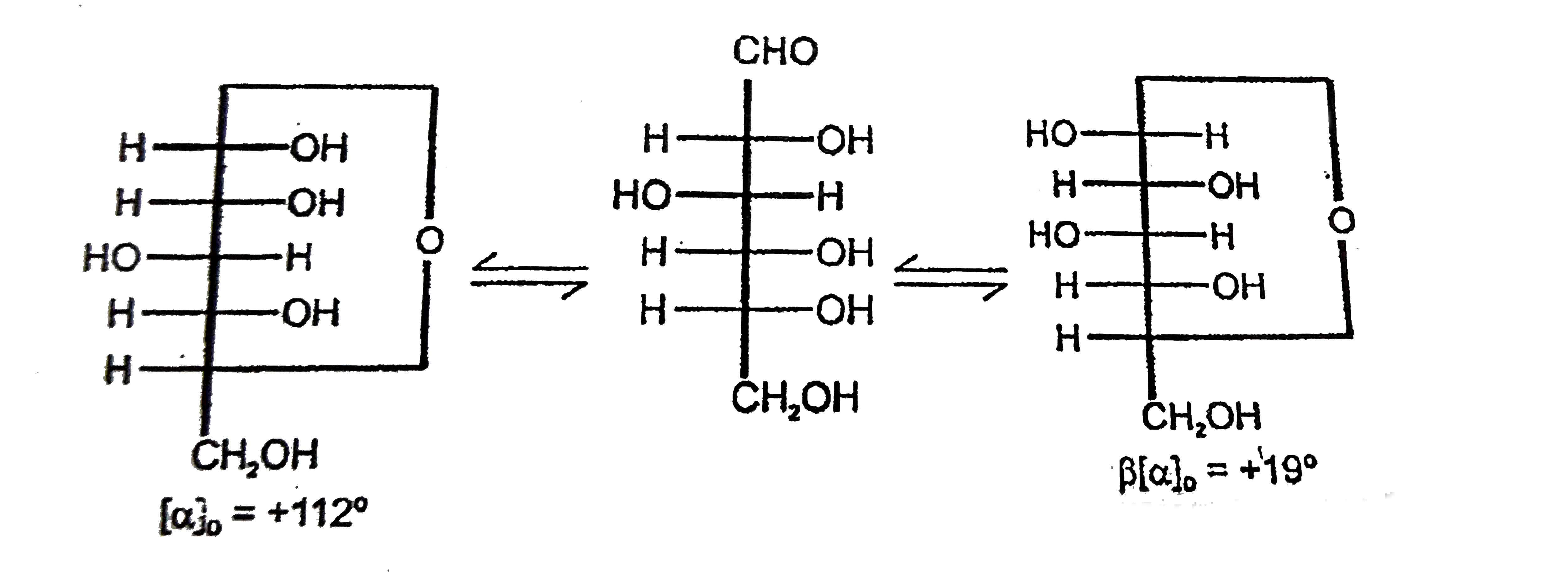
The above process in which α and β form remain in equilibrium with acyclic form and a change in optical rotation is observed which is known as−
View SolutionThe degree of dissociation of HI at a particualr temperature is 0.8. Calculate the volume of 2MNa2S2O3 solution required to neutralise the iodine present in an equilibrium mixture of a reaction when 2 mol each of H2 and I2 are heated in a closed vessel of 2L capacity and the equilibrium mixture is freezed.
View SolutionIf (±) 2-methyl butanoic acid were esterified by reaction with (±) 2-butanol, how many optically active compounds would be present in the final equilibrium reaction mixture?
View SolutionD (+) Glucose has melting point 146∘C and specific rotation [α]25D is + 112∘C. Another D(+) Glucose has melting point 150∘C and specific rotational [α]25Dis +18.7∘C. The two form have significantly different optical rotation but when an aqueous solution of either form is allowed to stand, it rotation changes. The specific rotation of one form decreases and rotation of other increases until both solution show the same value +52.7∘. The change in rotation towards an equilibrium value is called mutarotation.
Mutarotation is characteristic feature of:
View Solution
