Select the Z - isomer from the following alkenes

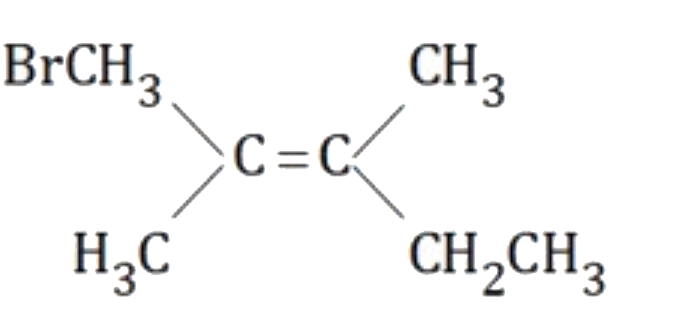
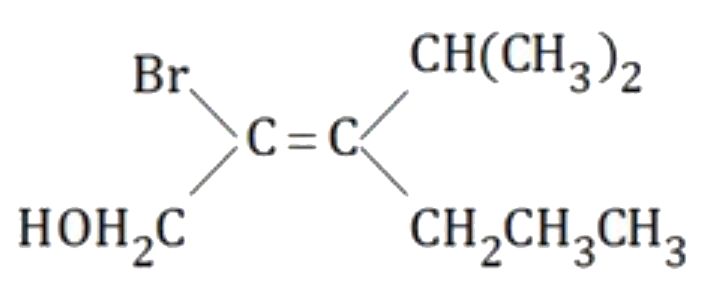
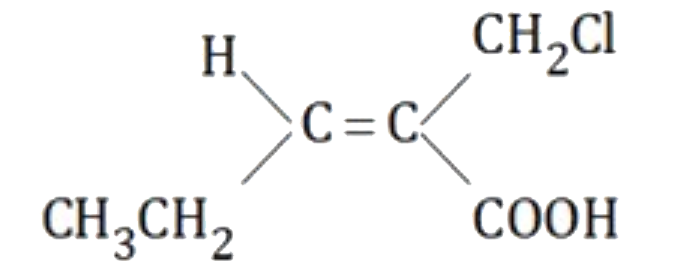
The correct Answer is:C
To solve the question of selecting the Z-isomer from the given alkenes, we need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Understand E-Z Isomerism
E-Z isomerism occurs in alkenes where there are two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond. For E-Z nomenclature:
- Z (from the German "zusammen") means that the higher priority groups are on the same side of the double bond.
- E (from the German "entgegen") means that the higher priority groups are on opposite sides of the double bond.
Step 2: Identify Groups Attached to the Double Bond
For each alkene, identify the groups attached to each carbon of the double bond. Ensure that the groups are different to apply E-Z nomenclature.
Step 3: Assign Priorities Using Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules
Using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules, assign priorities to the groups attached to each carbon of the double bond:
- Compare the atomic numbers of the atoms directly attached to the double-bonded carbons. The group with the higher atomic number gets the higher priority.
- If the first atoms are the same, move to the next atoms in the groups until a difference is found.
Step 4: Determine the Configuration (Z or E)
Once the priorities are assigned, check the positions of the groups:
- If the higher priority groups are on the same side, it is a Z-isomer.
- If the higher priority groups are on opposite sides, it is an E-isomer.
Step 5: Analyze Each Given Alkene
Now, we will analyze each option provided in the question to determine which one is the Z-isomer.
1. Option A: Groups are the same on one side → Not applicable for E-Z isomerism.
2. Option B: Higher priority groups are on opposite sides → This is an E-isomer.
3. Option C: Higher priority groups are on the same side → This is a Z-isomer.
4. Option D: Higher priority groups are on opposite sides → This is an E-isomer.
Conclusion
After analyzing all the options, the correct answer is Option C, which is the Z-isomer.
---
E-Z isomerism occurs in alkenes where there are two different groups attached to each carbon of the double bond. For E-Z nomenclature:
- Z (from the German "zusammen") means that the higher priority groups are on the same side of the double bond.
- E (from the German "entgegen") means that the higher priority groups are on opposite sides of the double bond.
For each alkene, identify the groups attached to each carbon of the double bond. Ensure that the groups are different to apply E-Z nomenclature.
Using the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules, assign priorities to the groups attached to each carbon of the double bond:
- Compare the atomic numbers of the atoms directly attached to the double-bonded carbons. The group with the higher atomic number gets the higher priority.
- If the first atoms are the same, move to the next atoms in the groups until a difference is found.
Once the priorities are assigned, check the positions of the groups:
- If the higher priority groups are on the same side, it is a Z-isomer.
- If the higher priority groups are on opposite sides, it is an E-isomer.
Now, we will analyze each option provided in the question to determine which one is the Z-isomer.
2. Option B: Higher priority groups are on opposite sides → This is an E-isomer.
3. Option C: Higher priority groups are on the same side → This is a Z-isomer.
4. Option D: Higher priority groups are on opposite sides → This is an E-isomer.
After analyzing all the options, the correct answer is Option C, which is the Z-isomer.
समान प्रश्न
ज्ञान जांच
Select the aryl halide from the following.
A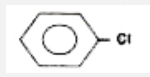 B
B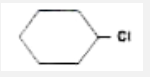 C
C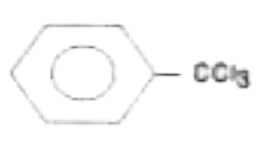 DNone of these
DNone of theseThe Z-isomers among the following are :
A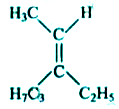 B
B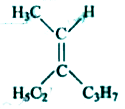 C
C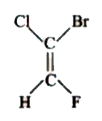 D
D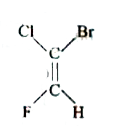
Select'cis' isomer among the following:
A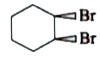 B
B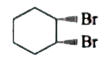 C
C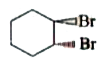 D
D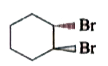
Select the CORRECT pair from the following.
View SolutionThe E-isomer among the following is:
View SolutionSelect pair of chain isomers from the following :
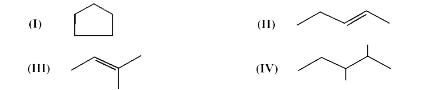
View SolutionSelect the odd from the following
View SolutionSelect the correct answer from the following for DNA can be
1. A-DNA 2. B-DNA
3. Z-DNA 4. Y-DNA.
View Solution
