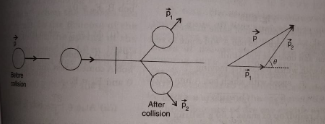
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0 collides inelastically (e>0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that For a general collision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90∘.
 Solution in Punjabi
Solution in Punjabi
Step by step video solution for A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v_0 collides inelastically (e>0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that For a general collision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90^@. by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Can mechanical waves travel through vacuum?
View SolutionA ball of mass m m , moving with a speed 2upsilon_(0) , collides inelasticaly (egt0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that (a) For head - on collision, both the balls move forward. (b) For a genergcollision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less that 90^(@) .
View SolutionA ball of mass M moving with a velocity v collides perfectly inelastically with another ball of same mass but moving with a velocity v in the opposite direction. After collision
View SolutionA ball of mass m moving with a velocity v undergoes an oblique elastic collision with another ball of the same mass m but at rest. After the collision if the two balls move with the same speeds , the angle between their directions of motion will be:
View SolutionA ball of mass m moving with a speed 2v0 collides head-on with an identical ball at rest. If e is the coefficient of restitution, then what will be the ratio of velocity of two balls after collision?
View SolutionA ball of mass M moving with speed v collides perfectly inelastically with another ball of mass m at rest. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the first ball is
View SolutionA ball moving with speed u collides with an identical ball at rest. The velocities of two balls after collision are (If the collision is elastic):
View Solutionनियत वेग u से गतिमान m द्रव्यमान की एक गेंद एक अन्य ऐसी गेंद से टकराती है जो विरामावस्था में है। यदि e प्रत्यवस्थान गुणांक है तो संघट्ट (Collision) के पश्चात् दोनों गेंदों के वेगों का अनुपात होगा-
View SolutionA ball of mass mm, moving with a speed 2υ0, collides inelasticaly (e>0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that (a) For head - on collision, both the balls move forward.
(b) For a genergcollision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less that 90∘.
View SolutionA billiard ball of mass M , moving with velocity v1 collides with another ball of the same mass but at rest . If the collision is elastic , the angle of divergence after the collision is
View SolutionA ball of mass m , moving with a speed 2v_(0) collides inelastically ( e gt 0) with an identical ball at rest . Show that (a) For head - on collision , both the balls move forward . (b) For a general collision , the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90^(@)
View SolutionA ball of mass m moving with a speed 2v0 collides head-on with an identical ball at rest. If e is the coefficient of restitution, then what will be the ratio of velocity of two balls after collision?
View SolutionA ball of mass m moving with a speed 2v_0 collides head-on with an identical ball at rest. If e is the coefficient of restitution, then what will be the ratio of velocity of two balls after collision?
View Solutionm द्रव्यमान की 2v0 वेग से चलती हुई एक गेंद विरामावस्था में रखी हुई एक अन्य सर्वसम गेंद से अप्रत्यास्थ (e > 0) रूप से टकराती है। दर्शाइए कि,
(a) सम्मुख संघट्ट होने पर दोनों गेंदें आगे चलेंगी।
(b) सामान्य संघट्ट में, संघट्ट के पश्चात् प्रकीर्णित गेंदों के वेगों के बीच कोण 90∘ से कम होगा।
View SolutionA ball of mass M moving with speed v collides perfectly inelastically with another ball of mass m at rest. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the first ball is
View SolutionA ball of mass M moving with speed v collides perfectly inelastically with another ball of mass m at rest. The magnitude of impulse imparted to the first ball is
View Solution

