In a historical experiment to determine Planck's constant, a metal surface was irradiated with light of different wavelengths. The emitted photoelectron energies were measured by applying a stopping potential. The relevant data for the wavelength (λ). ) of incident light and the corresponding stopping potential (V0) are given below :
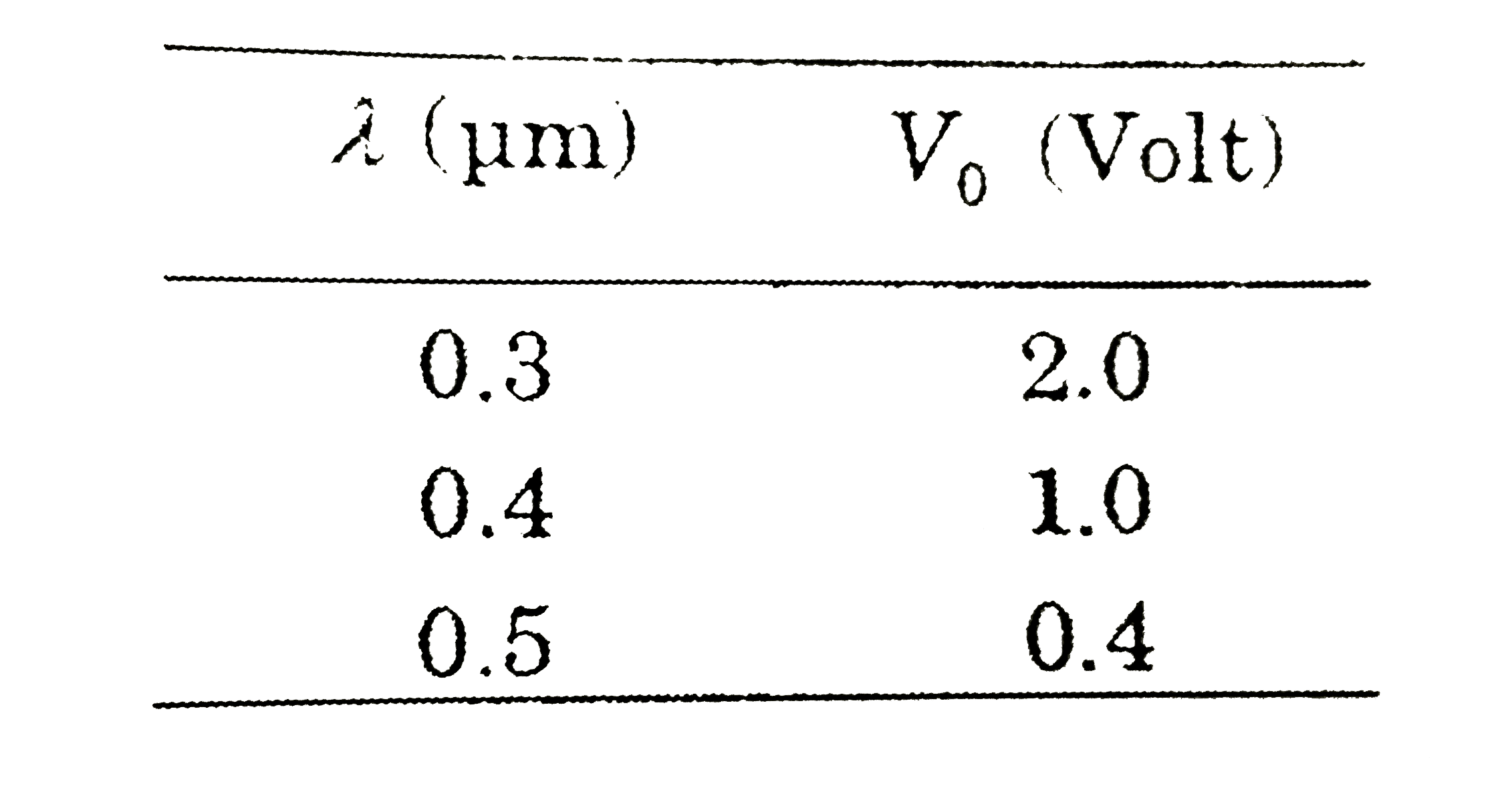
Given that c=3×108ms−1ande=1.6×10−19C Planck's constant (in units of J s) found from such an experiment is Solution in Gujrati
6.0×10−34
6.4×10−34
6.6×10−34
6.8×10−34
The correct Answer is:B
KEmax=hCλ−ϕ
eVs=hCλ−ϕ
1.6×10−19×2=h×3×1083000×10−10−ϕ.....(i)
1.6×10−19×1=h×3×1084000×10−10−ϕ......(ii)
From (ii) ϕ=h×3×1084000×10−10−1.6×10−19
1.6×10−19×2=h×3×1083000×10−10−h×3×1084000×10−10+1.6×10−19
1.6×10−19=h×3×10810−7(13−14)=h×3×10810−7[4−312]
1.6×10−19=h×3×10810−7×112
1.6×4×10−19×10−7108=h
6.4×10−34Js=h
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONBOOK - ALLEN CHAPTER - SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONEXERCISE - MCQ s
8 Videos
- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONBOOK - ALLEN CHAPTER - SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONEXERCISE - Comprehension #1
3 Videos
- SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONBOOK - ALLEN CHAPTER - SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTIONEXERCISE - Exercise - 04[A]
25 Videos
- RACEBOOK - ALLEN CHAPTER - RACEEXERCISE - Basic Maths (Wave Motion & Dopplers Effect) (Stationary waves & doppler effect, beats)
25 Videos
- TEST PAPERBOOK - ALLEN CHAPTER - TEST PAPEREXERCISE - PHYSICS
4 Videos
Similar Questions
Let mp be the mass of a poton , M1 the mass of a _(10)20Ne nucleus and M2 the mass of a _(20)40Ca nucleus . Then
View SolutionIn a mixture of H−He+ gas (He+is singly ionized He atom), H atom and He+ ions are excited to their respective first excited state. Subsequently H atoms transfer their total excitation energy to He+ ions (by collisions) Assume that the bohr model of atom is exactly valid.
The quantum number n of the state finally populated in He+ inos is -
View SolutionWhen a monochromatic point source of light is at a distance
of 0.2 m from a photoelectric cell, the cut off voltage and the saturation current
are respectively 0.6 V and 18.0 mA. If the same source is placed 0.6 m away
from the photoelectric cell, then
(a) the stopping potential will be 0.2 V
(b) the stopping potential will be 0.6 V
(c ) the saturation current will be 6.0 mA
(d) the saturation current will be 2.0 mA
View SolutionThe frequency of a radar is 780 MHz. After getting reflected from an approaching aeroplane, the apparent frequency is more than the actual frequency by 2.6 kHz. The aeroplane has a speed of
View SolutionChoose the correct statement:
View Solutiona. A stopping potential of 0.82V is required to stop the emission of photoelectrons from the surface of a metal by light of eavelength 4000A. For light of wavelength 3000A, the stopping potential is 1.85V. Find the value of Planck's constant. [1 electrons volt (eV)=1.6×10−19J]
b. At stopping potential, if the wavelength of the incident light is kept fixed at 4000A, but the intensity of light increases two times, will photoelectric current be botained ? Give reasons for your answer.
View SolutionWhen light of wavelength 400nm is incident on the cathode of photocell, the stopping potential recorded is 6V. If the wavelength of the incident light is to 600nm, calculate the new stopping potential. [Given h=6.6xx10^(-34) Js, c=3xx10^(8)m//s , e=1.6xx10^(-19)C ]
View SolutionPhotons of frequencies 2.2×1015Hz and 4.6×1015Hz are incident on a metal surface. The corresponding stopping potentials were found to be 6.6V and 16.5V respectively. Given e=1.6×10−19c, the value of universal planck's constant is
View SolutionIf the energy of a photon is given by E=hcλ, where h is the Plank's constant c is the velocity of light and λ is the wavelength of the radiation then the unit of Planck's constant is ______
View SolutionIn a historical experiment to determine Planck's constant, a metal surface was irradiated with light of different wavelengths. The emitted photoelectron energies were measured by applying a stopping potential. The relevant data for the wavelength (lambda) . ) of incident light and the corresponding stopping potential (V_0 ) are given below : ltimg src="https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/physics_images/JA_16_PHY_P1_E01_001_Q01.png" width="80%"gt Given that c=3xx10^8ms^(-1) and e=1.6xx10^(-19)C Planck's constant (in units of J s) found from such an experiment is
View Solutionप्लांक नियतांक ज्ञात करने के लिए एक ऐतिहासिक प्रयोग में एक धातु की सतह को अलग-अलग तरंगदैर्घ्य के प्रकाश से प्रदीप्त किया गया। उत्सर्जित प्रकाशिक इलेक्ट्रॉन की ऊर्जा को निरोधी विभव (stopping potential ) लगाकर मापा गया । उपयोग में लाये गए आपतित प्रकाश की तरंगदैर्घ्य (λ) एवं सम्बन्धित निरोधी विभव (V0) के आँकड़े नीचे दिये गए हैं

प्रकाश की गति c=3×108ms−1 तथा इलेक्ट्रॉन का आवेश e=1.6×10−19C, दिया गया है । इस प्रयोग से निकाले गए प्लांक नियतांक ( J s मात्रक में ) का मान है :
View SolutionIn an experiment on photoelectric emission from a metallic surface ,wavelength of incident light 2xx10^(-7) m and stopping potential is 2.5V .The threshold frequency of the metal (in Hz) approximately (Charge of electrons e=1.6xx10^(-19) C, Planck's constant , h=6.6xx10^(-34)J-s)
View SolutionA stopping potential of 0.82 volt is required to stop the photoelectrons emitted from a metallic surface by light of wavelength 4000 Å . The stopping potential for wavelength 3000 Å will be :
View SolutionThreshold wavelength for metal is 10,000Å . If light of wavelength 5461Å is incident on it, then stopping potential is 1.02 V, then value of Planck's constant is :
View SolutionThreshold wavelength for metal is 10,000 Å. If light of wavelength 5461 Å is incident on it, then stopping potential is 1.02 V, then value of Planck's constant is :
View SolutionFigure shows the stopping potential (V0) for the photo electron vers (1λ) graph, for two metals A and B, λ being the wavelength of incident light.
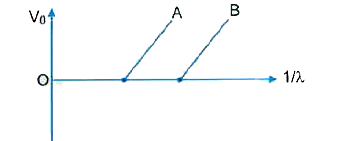
How is the value of Planck's constant determined from the graph ?
View Solution

