Find the component of →r in the directioln of →a :- Solution in Gujrati
(a)(→r.→a)→aa2
(b)(→r.→a)→aa
(c)(→r.→a)→rr
(d)(→r.→a)→rr2
The correct Answer is:A
Step by step video solution for Find the component of vecr in the directioln of veca :- by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- UNIT & DIMENSIONS, BASIC MATHS AND VECTOR Book:ALLEN Chapter:UNIT & DIMENSIONS, BASIC MATHS AND VECTOR Exercise:Exercise (O-2) Multiple Correct Type Questions.
Explore 7 Videos
- UNIT & DIMENSIONS, BASIC MATHS AND VECTOR Book:ALLEN Chapter:UNIT & DIMENSIONS, BASIC MATHS AND VECTOR Exercise:Exercise (O-2) Comprehension Type Questions.
Explore 9 Videos
- UNIT & DIMENSIONS, BASIC MATHS AND VECTOR Book:ALLEN Chapter:UNIT & DIMENSIONS, BASIC MATHS AND VECTOR Exercise:Exercise (O-1) Matrix match type Questions.
Explore 3 Videos
- TEST PAPERSBook:ALLEN Chapter:TEST PAPERSExercise:MATHS
Explore 1 Video
- WAVE OPTICSBook:ALLEN Chapter:WAVE OPTICSExercise:Exercise 2 (Previous Year Questions)
Explore 7 Videos
Similar Questions
Four forces acting on a particle keep it in equilibrium, then :-
View SolutionA body lost in a jungle finds a note. In the note was written the following things.
Displacements
1. 300 m 53∘ South of East .
2. 400 m 37∘ North of East
3. 500 m North
4. 500√2m North- West
5. 500 m South
He starts walking at constant speed 2m/s following these displacements in the given order.
How far and in which direction is he from the starting ponit after 5 min. and 50 s ?
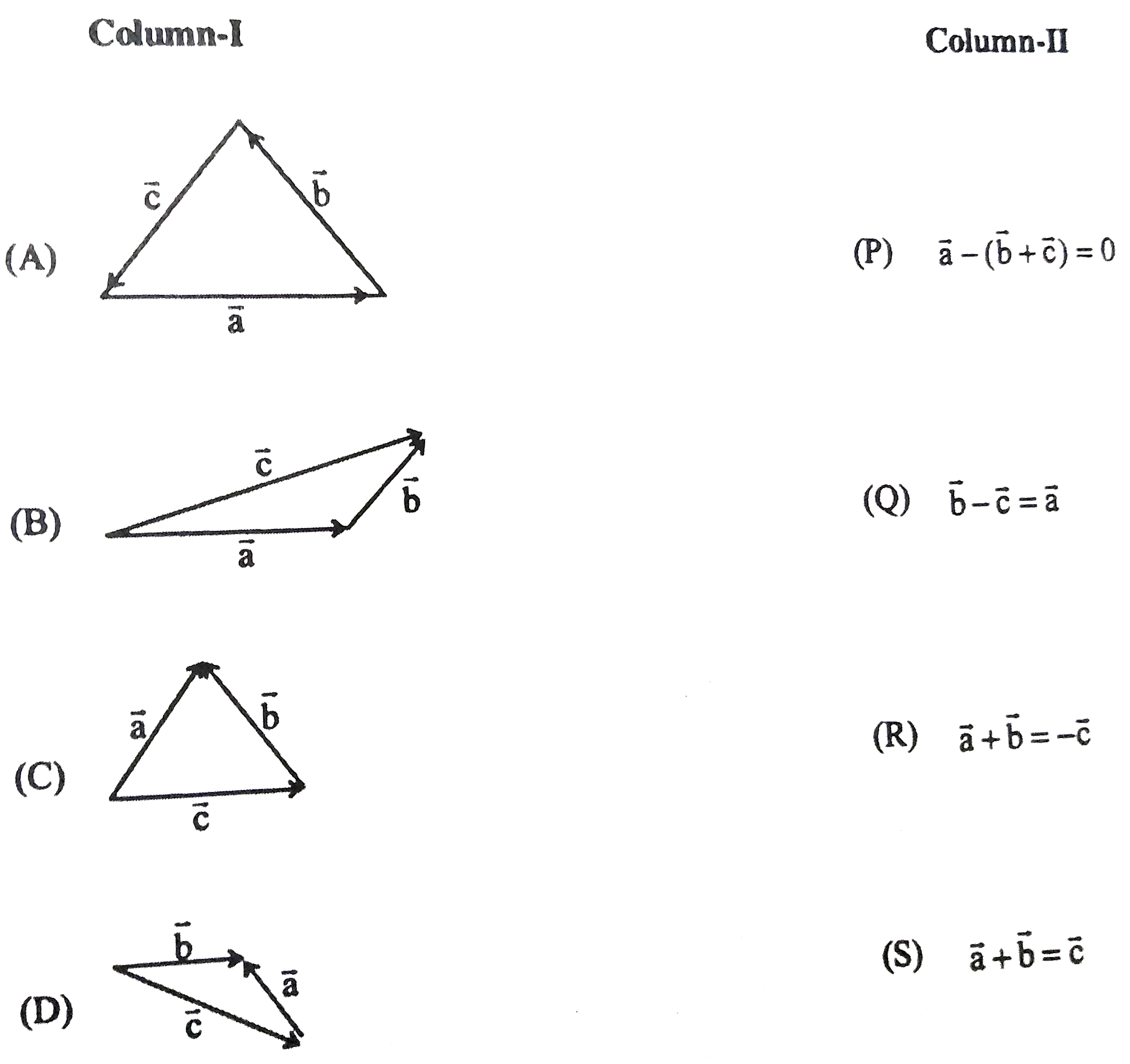
View SolutionColumn-I show vector diagram relating three vectors →a,→b and →c. Match the vector equation in column -II, with vector diagram in column-I:
View SolutionIf complex number z(z≠2) satisfies the equation z2=4z+|z|2+16|z|3, then what is the value of |z|4 ?
View SolutionElectromagnetic waves are transverse is nature is evident by
View SolutionFind →r such that t→r+→r+→a=→b.
View SolutionThe plane contaning the two straight lines →r=→a+λ→band→r=→b+μ→a is (A) [→r→as→b]=0 (B) [→r→a→a×→b]=0 (C) [→r→b→a×→b]=0 (D) [→r→a+→b→a×→b]=0
View SolutionIf →aand→b are two given vectors and k is any scalar,then find the vector →r satisfying →r×→a+k→r=→b.
View SolutionIf →aand→b are two given vectors and k is any scalar,then find the vector →r satisfying →r×→a+k→r=→b.
View Solution→a,→band→c are three non-coplanar vectors and →r. Is any arbitrary vector. Prove that [→b→c→r]→a+[→c→a→r]→b+[→a→b→r]→c=[→a→b→c]→r.
View SolutionIf →a,→b,→c are three non-zero non-null vectors are →r is any vector in space then
[→b→c→r]→a+[→c→a→r]→b+[→a→b→r]→c is equal to
View Solutionरेखाओं →r=→a+s→b तथा →r=tˆk के बीच की न्यूनतम दूरी ज्ञात कीजिए।
View SolutionShow that the projection or component of a vector vecR on another vector vecA is vecR*hata , where hata is a unit vector along vecA .
View SolutionIf →aand→b are two given vectors and k is any scalar,then find the vector →r satisfying →r×→a+k→r=→b.
View SolutionIf →r.→a=0,→r.→b=1and[→r→a→b]=1,→a.→b≠0,(→a.→b)2−|→a|2∣∣→b∣∣2=1, then find →r in terms of →aand→b.
View Solution→a,→band→c are three non-coplanar vectors and →r. Is any arbitrary vector. Prove that [→b→c→r]→a+[→c→a→r]→b+[→a→b→r]→c=[→a→b→c]→r.
View Solution
