Give a brief account of the following reactions:
Hunsdiecker's reaction
Step-by-Step Solution for Hunsdiecker's Reaction
Step 1: Definition of Hunsdiecker's Reaction
Hunsdiecker's reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the use of silver salts of carboxylic acids. When these silver salts react with halogens, they form an unstable intermediate that eventually leads to the formation of alkyl halides.
Step 2: Reaction Overview
The general reaction can be summarized as follows:
- Silver salt of a carboxylic acid (RCOOAg) reacts with a halogen (commonly bromine, Br2) in the presence of a solvent like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
- The product of this reaction is an alkyl halide (RBr).
Step 3: Mechanism of the Reaction
1. Heating the Silver Carboxylate: The reaction begins by heating the silver carboxylate (RCOOAg) along with bromine (Br2) in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
2. Formation of Acyl Hypobromide: During the reaction, the silver carboxylate is converted into acyl hypobromide (RCOBr), and silver bromide (AgBr) precipitates out of the solution.
3. Radical Chain Reaction: A radical chain reaction is initiated by the homolysis of the weaker oxygen-bromine bond in acyl hypobromide. This results in the formation of a bromine atom and a carboxyl radical (RCO•).
4. Decarboxylation: The carboxyl radical undergoes decarboxylation, leading to the formation of a diradical pair, which consists of an alkyl radical (R•).
5. Formation of Alkyl Halide: The alkyl radical then recombines with the bromine atom to form the desired alkyl halide (RBr).
Step 4: Summary of Products
The final product of Hunsdiecker's reaction is an alkyl halide, specifically an alkyl bromide if bromine is used in the reaction.
Hunsdiecker's reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the use of silver salts of carboxylic acids. When these silver salts react with halogens, they form an unstable intermediate that eventually leads to the formation of alkyl halides.
The general reaction can be summarized as follows:
- Silver salt of a carboxylic acid (RCOOAg) reacts with a halogen (commonly bromine, Br2) in the presence of a solvent like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
- The product of this reaction is an alkyl halide (RBr).
1. Heating the Silver Carboxylate: The reaction begins by heating the silver carboxylate (RCOOAg) along with bromine (Br2) in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
2. Formation of Acyl Hypobromide: During the reaction, the silver carboxylate is converted into acyl hypobromide (RCOBr), and silver bromide (AgBr) precipitates out of the solution.
3. Radical Chain Reaction: A radical chain reaction is initiated by the homolysis of the weaker oxygen-bromine bond in acyl hypobromide. This results in the formation of a bromine atom and a carboxyl radical (RCO•).
4. Decarboxylation: The carboxyl radical undergoes decarboxylation, leading to the formation of a diradical pair, which consists of an alkyl radical (R•).
5. Formation of Alkyl Halide: The alkyl radical then recombines with the bromine atom to form the desired alkyl halide (RBr).
The final product of Hunsdiecker's reaction is an alkyl halide, specifically an alkyl bromide if bromine is used in the reaction.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSBOOK - ICSECHAPTER - ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDSEXERCISE - ISC EXAMINATION QUESTIONS (PART-II DESCRIPTIVE QUESTIONS) (CARBOXYLIC ACIDS)
99 Videos
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS EXERCISE - ISC EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
25 Videos
- APPENDIX II ( TYPICAL CONVERSIONS)BOOK - ICSECHAPTER - APPENDIX II ( TYPICAL CONVERSIONS)EXERCISE - AROMATIC CONVERSIONS
98 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Give the product of the following reaction sequence :
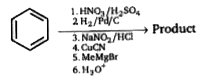 A
A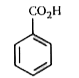 B
B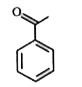 C
C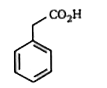 D
D
Give a brief account of the following reaction:
Cross-Aldol condensation
View SolutionGive product of the following reactions :-
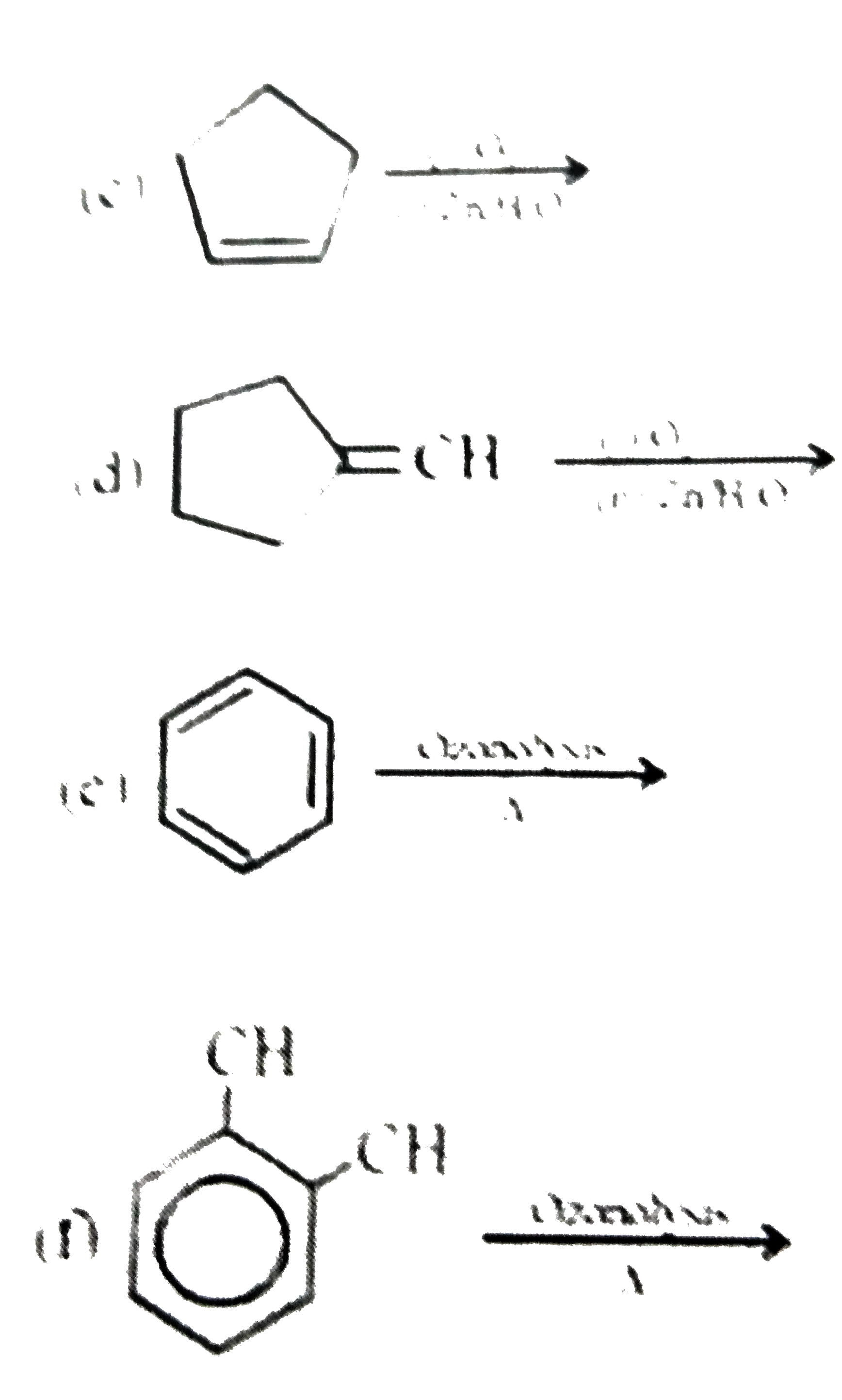
View SolutionGive the product of the following reactions:
a.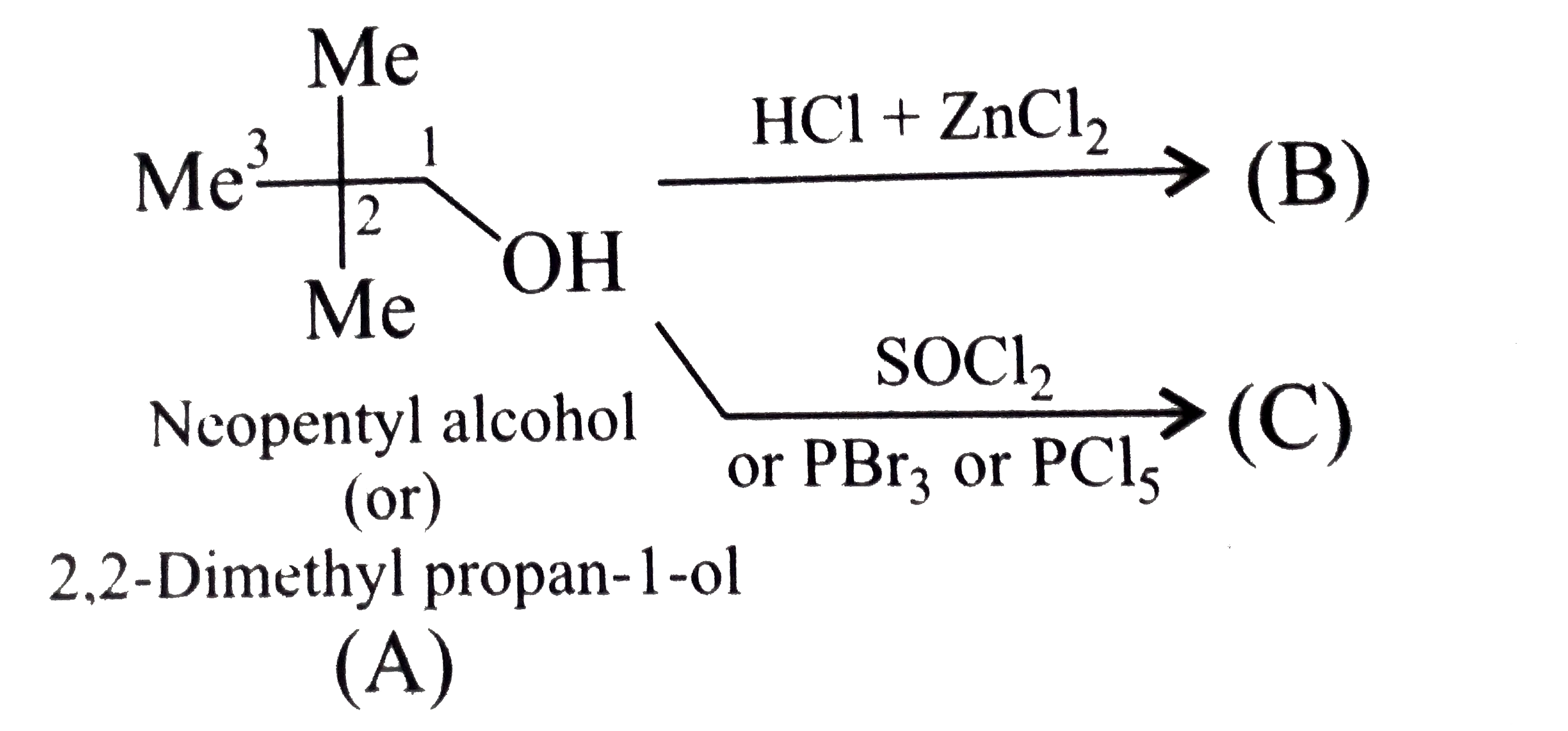
View SolutionGive the products of the following reactions.
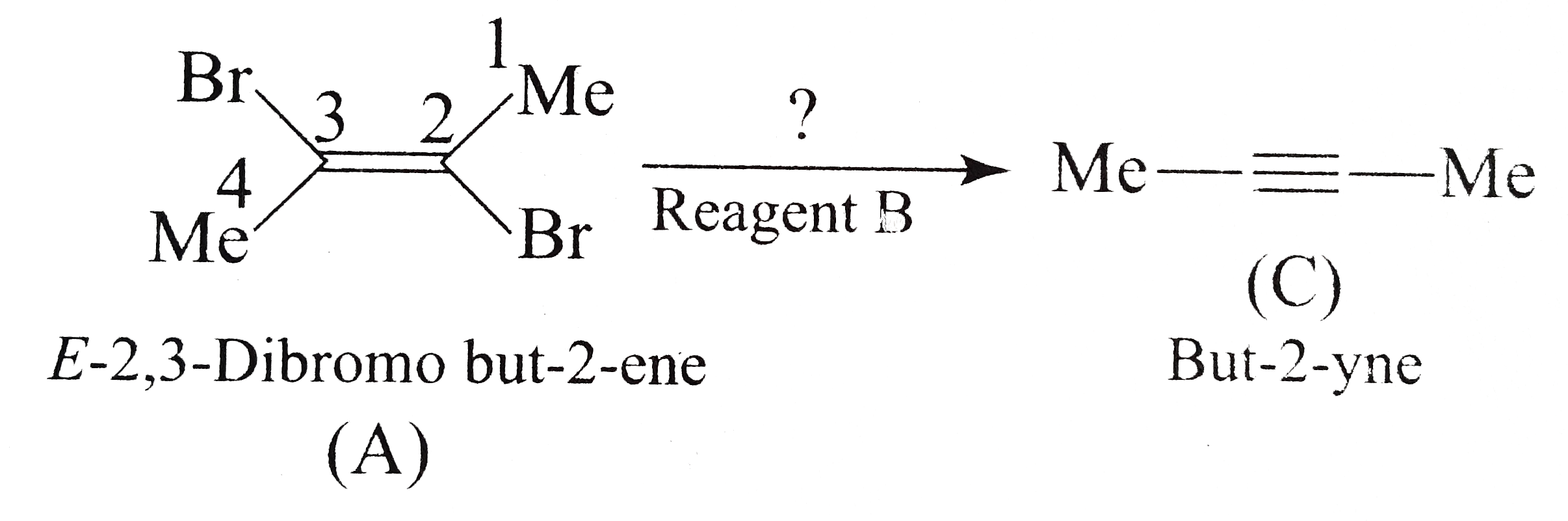
View SolutionGive the product of the following reactions:
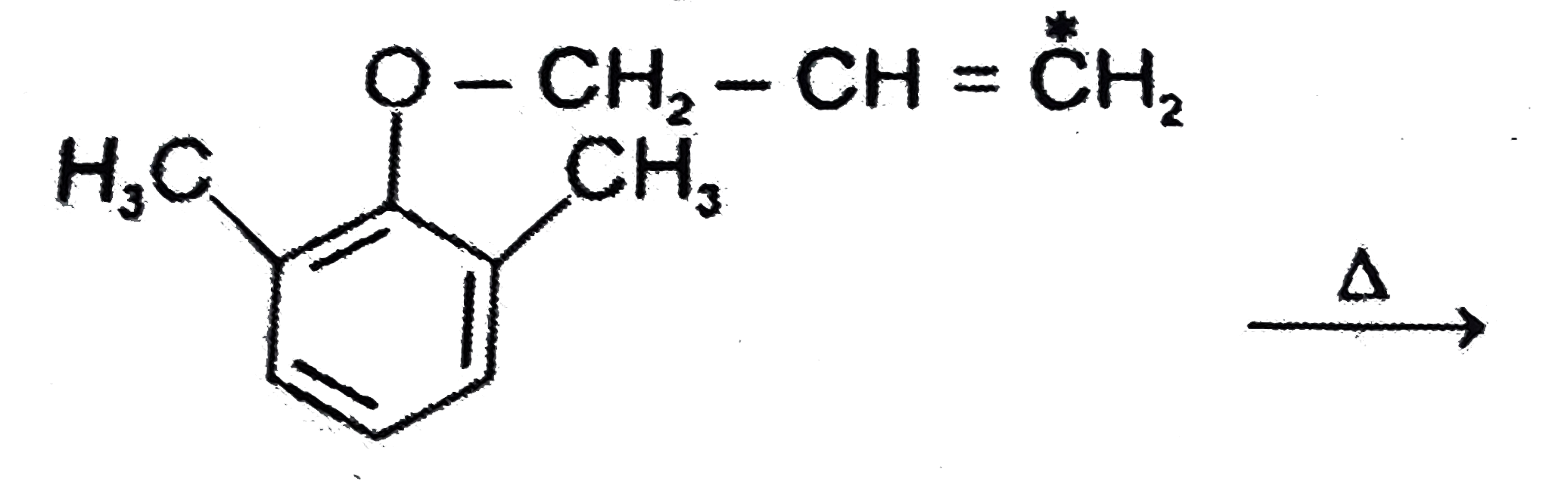
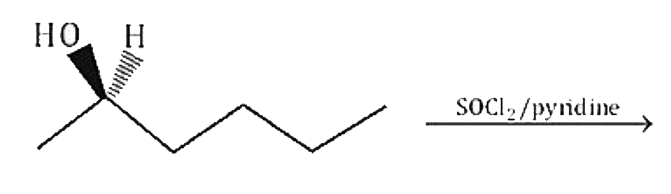
View SolutionGive the major product of the following reaction
View SolutionGive a brief account of the following with one example of Wurtz reaction.
View Solution


