Explain the principle of a photographic camera.
Step-by-Step Solution:
1. Understanding the Components of a Camera:
- A photographic camera consists of several key components: a lens, a shutter, an aperture (diaphragm), and a photographic film or sensor.
- The lens is typically a convex lens, which is crucial for focusing light.
2. The Role of the Lens:
- The convex lens converges light rays coming from an object. The lens has two important points: the focal point (F) and the point twice the focal length (2F).
- When an object is placed at a distance greater than 2F from the lens, the lens forms a real and inverted image on the opposite side.
3. Light Path through the Camera:
- Light rays from the object enter the camera and pass through the lens.
- A ray that travels parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and pass through the focal point (F).
- A ray that passes through the focal point will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
4. Image Formation:
- When the object is positioned beyond 2F, the image is formed between F and 2F on the opposite side of the lens.
- The image formed is real (can be projected on a screen) and inverted.
5. Shutter and Exposure:
- The shutter controls the amount of light that reaches the photographic film or sensor. It opens for a specific duration to allow light to expose the film.
- The aperture (diaphragm) controls the amount of light entering the camera, affecting the depth of field and exposure.
6. Final Image Capture:
- The photographic film or sensor captures the real image formed by the lens. This image can then be developed into a photograph.
Summary:
The principle of a photographic camera is based on the use of a convex lens to form a real and inverted image of an object on a photographic film or sensor. The camera's shutter and aperture work together to control the exposure of light to the film.
---
- A photographic camera consists of several key components: a lens, a shutter, an aperture (diaphragm), and a photographic film or sensor.
- The lens is typically a convex lens, which is crucial for focusing light.
- The convex lens converges light rays coming from an object. The lens has two important points: the focal point (F) and the point twice the focal length (2F).
- When an object is placed at a distance greater than 2F from the lens, the lens forms a real and inverted image on the opposite side.
- Light rays from the object enter the camera and pass through the lens.
- A ray that travels parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and pass through the focal point (F).
- A ray that passes through the focal point will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
- When the object is positioned beyond 2F, the image is formed between F and 2F on the opposite side of the lens.
- The image formed is real (can be projected on a screen) and inverted.
- The shutter controls the amount of light that reaches the photographic film or sensor. It opens for a specific duration to allow light to expose the film.
- The aperture (diaphragm) controls the amount of light entering the camera, affecting the depth of field and exposure.
- The photographic film or sensor captures the real image formed by the lens. This image can then be developed into a photograph.
The principle of a photographic camera is based on the use of a convex lens to form a real and inverted image of an object on a photographic film or sensor. The camera's shutter and aperture work together to control the exposure of light to the film.
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
- LIGHTBOOK - PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATIONCHAPTER - LIGHTEXERCISE - Test Your Concepts (Essay Type Question)
5 Videos
- LIGHTBOOK - PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATIONCHAPTER - LIGHTEXERCISE - Concept Application (Level 1) True or False
7 Videos
- LIGHTBOOK - PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATIONCHAPTER - LIGHTEXERCISE - Test Your Concepts (Very Short Answer Type Question)
29 Videos
- KINEMATICS BOOK - PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATIONCHAPTER - KINEMATICS EXERCISE - CONCEPT APPLICATION (Level 3) (Application Based Questions )
5 Videos
- MAGNETISM BOOK - PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATIONCHAPTER - MAGNETISM EXERCISE - CONCEPT APPLICATION (Level 3)
4 Videos
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
জ্ঞান পরীক্ষা করুন
The diaphragm in a photographic camera
Acontrols the exposure time of the film.Bcontrols the amount of light entering the camera.Cvaries the focal length of the lens.Dprevents internal reflection of light.
Explain the principle of a potentiomater.
View SolutionExplain the working principle of a photodiode.
Or
Explain briefly how a photodiode operates.
View SolutionThe huaman eye is very similar to a photographic camera. The figure given shows the main parts of a photographic camera.
Now answer the following question
: A → Aperture, B → Lens, C → photographic film.
a. Name the parts of the human eye similar to the following parts of the photographic camera : (i) Photographic film (ii) Aperture.
View SolutionThe human eye is very similar to a photographic camera. The figure given shows the main parts of a photographic camera , Now answer the question.
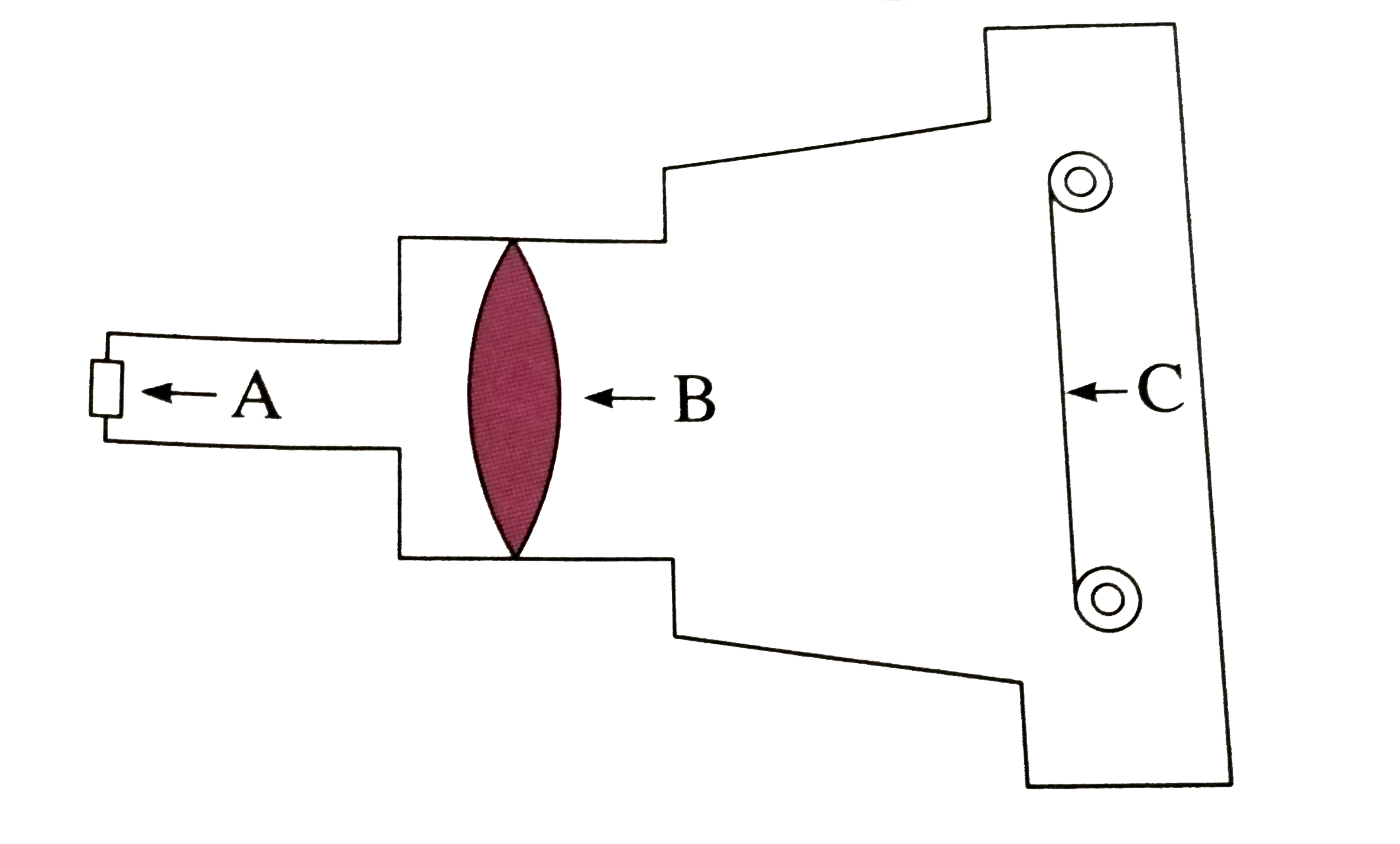
Name the parts of the human eye similar to the followign parts of the photographic camera:
(a) Photographic film (b) Aperture.
View SolutionThe huaman eye is very similar to a photographic camera. The figure given shows the main parts of a photographic camera.
Now answer the following question
: A → Aperture, B → Lens, C → photographic film.
b. Sate one difference between human eye lens and camera lens.
View SolutionThe huaman eye is very similar to a photographic camera. The figure given shows the main parts of a photographic camera.
Now answer the following question
: A → Aperture, B → Lens, C → photographic film.
d. Which phenomenon of light is responsible for the working of the eye?
View SolutionThe huaman eye is very similar to a photographic camera. The figure given shows the main parts of a photographic camera.
Now answer the following question
: A → Aperture, B → Lens, C → photographic film.
c. Name the muscle which adjusts the size of the eye lens.
View Solution
