How will you convert anisole to phenol ?
To convert anisole to phenol, we can follow a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
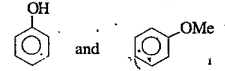
Step 1: Understand the Structures
- Anisole is methyl phenyl ether, which has a benzene ring with a methoxy group (–OCH₃).
- Phenol is a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group (–OH).
Step 2: Protonation of Anisole
- We will react anisole with a strong hydrogen halide, such as HI (hydroiodic acid) or HBr (hydrobromic acid).
- The oxygen in the methoxy group has lone pairs and can act as a Lewis base, accepting a proton (H⁺) from the acid.
- This results in the formation of an oxonium ion (methyl phenyl oxonium ion), where the oxygen carries a positive charge.
Step 3: Formation of the Oxonium Ion
- The reaction can be represented as:
Anisole+HI→Methyl phenyl oxonium ion
- In this ion, the bond between the oxygen and the methyl group (O–CH₃) is weaker than the bond between the oxygen and the benzene ring (O–C₆H₅).
Step 4: Nucleophilic Attack
- The iodide ion (I⁻), which is generated from the dissociation of HI, will attack the weaker O–CH₃ bond.
- This results in the cleavage of the O–CH₃ bond and the formation of phenol and methyl iodide (CH₃I).
Step 5: Final Products
- The overall reaction can be summarized as:
Anisole+HI→Phenol+CH3I
Conclusion
- Therefore, anisole can be converted to phenol through the reaction with hydroiodic acid (HI), resulting in phenol and methyl iodide as products.
---
- Anisole is methyl phenyl ether, which has a benzene ring with a methoxy group (–OCH₃).
- Phenol is a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group (–OH).
- We will react anisole with a strong hydrogen halide, such as HI (hydroiodic acid) or HBr (hydrobromic acid).
- The oxygen in the methoxy group has lone pairs and can act as a Lewis base, accepting a proton (H⁺) from the acid.
- This results in the formation of an oxonium ion (methyl phenyl oxonium ion), where the oxygen carries a positive charge.
- The reaction can be represented as:
Anisole+HI→Methyl phenyl oxonium ion
- In this ion, the bond between the oxygen and the methyl group (O–CH₃) is weaker than the bond between the oxygen and the benzene ring (O–C₆H₅).
- The iodide ion (I⁻), which is generated from the dissociation of HI, will attack the weaker O–CH₃ bond.
- This results in the cleavage of the O–CH₃ bond and the formation of phenol and methyl iodide (CH₃I).
- The overall reaction can be summarized as:
Anisole+HI→Phenol+CH3I
- Therefore, anisole can be converted to phenol through the reaction with hydroiodic acid (HI), resulting in phenol and methyl iodide as products.
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
How will you convert the following :
(i) Phenol to anisole
(ii) Propan -2- ol to 2-methylpropan-2- ol
(iii) Aniline to phenol.
View SolutionHow will you convert: Phenol→ Anisole (one step)
View SolutionHow can you distinguish? Phenol and Anisole.
View SolutionHow will you Convert: Anisole to 4-methoxy acetophenone.
View SolutionHow will you obtain the following ? (Give balanced equation.) Anisole from phenol
View SolutionHow will you convert phenol to 2,4,6-tribromo phenol?
View SolutionDo the conversion : Phenol to anisole
View SolutionHow benzene diazonium chloride is converted to (a) benzene (b) anisole (c) phenol ?
View Solution
