CH3CHONH2−NH2−−−−−−→[A]KOH−−→[B]Br2/hv−−−−→[C]KOH(alc)−−−−−→[D]
Identify D
To solve the given reaction sequence step by step, let's break down each part of the process:
Step 1: Reaction of CH₃CHO with NH₂NH₂
- Starting Compound: CH₃CHO (acetaldehyde)
- Reagent: NH₂NH₂ (hydrazine)
- Reaction Type: Wolff-Kishner reduction
- Product A: When acetaldehyde reacts with hydrazine, it forms a hydrazone intermediate, which upon heating leads to the removal of water and reduction to form ethane (C₂H₆).
Product A: CH₃CH=NH₂ (hydrazone)
Step 2: Reaction of A with KOH
- Starting Compound: A (hydrazone)
- Reagent: KOH
- Reaction Type: Wolff-Kishner reduction
- Product B: The hydrazone undergoes a reduction in the presence of KOH, leading to the formation of ethane (C₂H₆) and nitrogen gas (N₂).
Product B: C₂H₆ (ethane)
Step 3: Reaction of B with Br₂ under UV light
- Starting Compound: B (ethane)
- Reagent: Br₂ (bromine) and UV light
- Reaction Type: Free radical halogenation
- Product C: Ethane undergoes monobromination in the presence of bromine and UV light, resulting in bromoethane (C₂H₅Br).
Product C: C₂H₅Br (bromoethane)
Step 4: Reaction of C with KOH (alcoholic)
- Starting Compound: C (bromoethane)
- Reagent: KOH (alcoholic)
- Reaction Type: Elimination reaction (dehydrohalogenation)
- Product D: Bromoethane reacts with KOH in an alcoholic medium to eliminate HBr and form ethylene (C₂H₄).
Product D: C₂H₄ (ethylene)
Final Answer
The final product D is ethylene (C₂H₄).
---
- Starting Compound: CH₃CHO (acetaldehyde)
- Reagent: NH₂NH₂ (hydrazine)
- Reaction Type: Wolff-Kishner reduction
- Product A: When acetaldehyde reacts with hydrazine, it forms a hydrazone intermediate, which upon heating leads to the removal of water and reduction to form ethane (C₂H₆).
Product A: CH₃CH=NH₂ (hydrazone)
- Starting Compound: A (hydrazone)
- Reagent: KOH
- Reaction Type: Wolff-Kishner reduction
- Product B: The hydrazone undergoes a reduction in the presence of KOH, leading to the formation of ethane (C₂H₆) and nitrogen gas (N₂).
- Starting Compound: B (ethane)
- Reagent: Br₂ (bromine) and UV light
- Reaction Type: Free radical halogenation
- Product C: Ethane undergoes monobromination in the presence of bromine and UV light, resulting in bromoethane (C₂H₅Br).
- Starting Compound: C (bromoethane)
- Reagent: KOH (alcoholic)
- Reaction Type: Elimination reaction (dehydrohalogenation)
- Product D: Bromoethane reacts with KOH in an alcoholic medium to eliminate HBr and form ethylene (C₂H₄).
The final product D is ethylene (C₂H₄).
Similar Questions
CH3CH2CH2OHPBr5−−→(A)KOH(Alc)−−−−−−→(B)HBr−−→(C)NH3−−→(D)
Identify the product
View SolutionCHCl3+MeCOMeOH−−−→Aexcess KOH−−−−−−→BNaOH−CaO−−−−−−−→CKOBr−−→D
View SolutionHC≡CHHgSO4/H2SO4−−−−−−−−−→[A]Oxidation−−−−−→[B]PCl5−−→[C]H2−−−−−−→Pd/BaSO4[D]CH3MgBr−−−−−→H3O+[E]
View Solution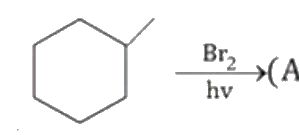 Br2−−→hv(A)alc. KOH−−−−→(B)OsO4−−→(C)HlO4−−→(D), Identify 'D'
Br2−−→hv(A)alc. KOH−−−−→(B)OsO4−−→(C)HlO4−−→(D), Identify 'D'
View SolutionC2H5OHPCl5−−→(A)KCN−−→(B)H3O+−−−→(C)NH3−−→(D)heat−−→(E)
Identify the products
View SolutionCH3CH2CHCl2Aq.KOH−−−−−→?
View SolutionCH3CH=CH2NBS−−→AKCN−−→BOH−/Δ−−−−−→CP/Br2−−−→DNH3−−→EΔ−−→F
View SolutionIdentify A to G in the following.
(a)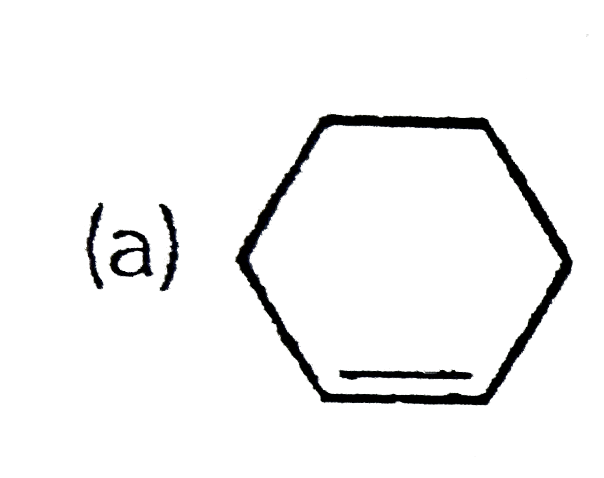 Br2,CCl4−−−−−→AKCN−−→BH3O+−−−→C
Br2,CCl4−−−−−→AKCN−−→BH3O+−−−→C
(b)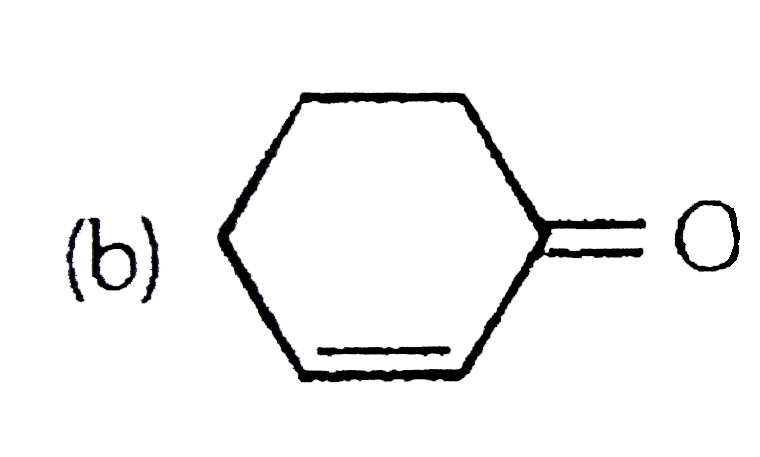 Br2,CCl4−−−−−→DKCN−−→EH3O+−−−→G
Br2,CCl4−−−−−→DKCN−−→EH3O+−−−→G
View SolutionIn the following sequence of reactions,
CH3CH2CH2BrKOH(Alc)−−−−−−→ (A) HBr−−→ (B) KOH(aq)−−−−−→ (C ) The product (C) is
View SolutionThe product D of the reaction CH3ClKCN−−→(A)H2O−−→(B)NH3−−→(C)Δ−−→(D) is
View Solution
