about to only mathematics
are such that the number of common tangents on them is 2
are orthogonal
are such that the length of their common tangent is 5(12/5)1/4
are such that the length of their common chord is 5√3/2
The correct Answer is:1,2,3,4
r1=5,r2=√15,C1C2=√40
∴r1+r2>C1C2>r1−r2
Hence, the circles intersect at two distinct points.
There are two common tangents. Also,
2g1g2+2f1f2=2(1)(3)+2(2)(−4)=−10
and c1+c2=−20+10=−10
Thus, the two circles are orthogonal.
Length of common chord =2r1r2√r21+r21=5√32
Length of common tangent =√C1C22−(r1−r2)2=5(125)1/4
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CIRCLE Book:CENGAGE PUBLICATIONChapter:CIRCLE Exercise:Linked Comprehension Type (For Problem 1-3)
Explore 3 Videos
- CIRCLE Book:CENGAGE PUBLICATIONChapter:CIRCLE Exercise:For Problems
Explore 43 Videos
- CIRCLE Book:CENGAGE PUBLICATIONChapter:CIRCLE Exercise:Excercises (Single Correct Answer Type)
Explore 109 Videos
- BINOMIAL THEOREMBook:CENGAGE PUBLICATIONChapter:BINOMIAL THEOREMExercise:Comprehension
Explore 11 Videos
- CIRCLESBook:CENGAGE PUBLICATIONChapter:CIRCLESExercise:Comprehension Type
Explore 8 Videos
Similar Questions
Each side of a square is of length 6 units and the centre of the square Is ( - 1, 2). One of its diagonals is parallel to x+y=0. Find the co-ordinates of the vertices of the square.
View SolutionTangents PA and PB are drawn to the circle (x−4)2+(y−5)2=4 from the point P on the curvey=sinx , where A and B lie on the circle. Consider the function y=f(x) represented by the locus of the center of the circumcircle of triangle PAB. Then answer the following questions.
Which of the following is true ?
View SolutionThe number of rational point(s) [a point (a, b) is called rational, if aandb both are rational numbers] on the circumference of a circle having center (π,e) is at most one (b) at least two exactly two (d) infinite
View SolutionConsider a G.P. with first term (1+x)n, |x|<1, common ratio 1+x2 and number of terms (n+1). Let 'S' be sum of all the terms of the G.P., then
The coefficient of xn is 'S' is
View Solution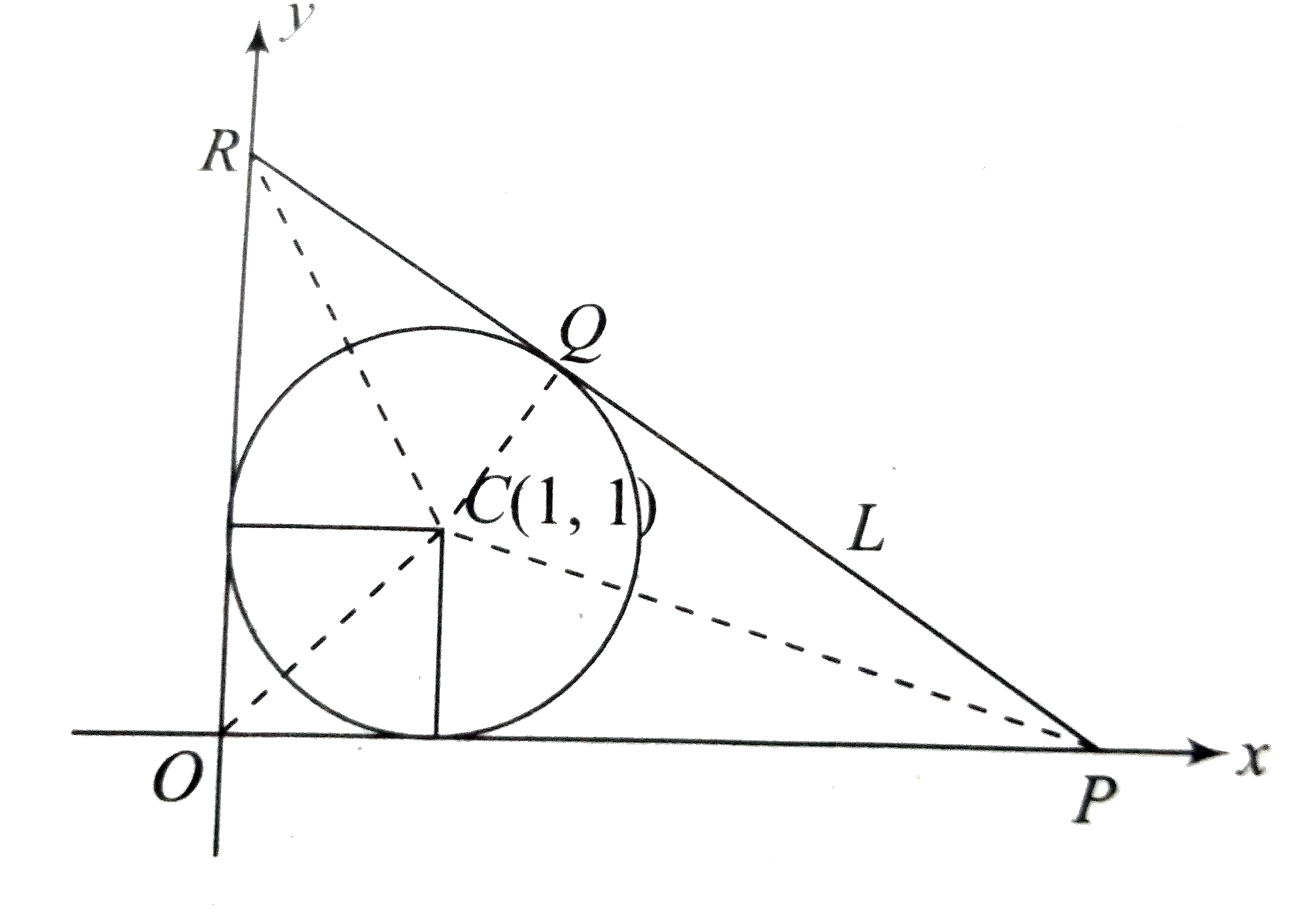
In the diagram as shown, a circle is drawn with centre C(1,1) and radius 1 and a line L. The line L is tangent to the circle at Q. Further L meets the y-axis at R and the x-axis at P in such a way that the angle OPQ equals θ where 0<θ<π2.
Coordinate of Q is
View SolutionWhat did Schimba say about mathematics?
View SolutionWhich of the following statements is not true about 'mapping in Mathematics?
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solutionabout to only mathematics
View Solution

