Consider the two samples of DNA shown below. Single strands are shown for simplicity:
Sample #1
CAGTGATCTCGA ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT
Sample #2
TCATGA ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA
If both samples are treated with a restriction enzyme (recognition sequence GAATTC) then indicate the number of fragments and the size of each fragment from each sample of DNA.
Sample # 1
# of fragments:_____
Sample # 2
# of fragments:_______
List fragment size in order: largest → smallest
Sample # 1
Sample # 2
To solve the problem, we need to analyze both DNA samples and identify where the restriction enzyme (recognition sequence GAATTC) cuts each strand. Let's break down the steps:
Step 1: Identify the recognition sequence in Sample #1
- Sample #1: CAGTGATCTCGA ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT
- We need to find the sequence GAATTC in this sample.
- The sequence GAATTC is present in the DNA strand at the position "ATTCGCTA".
Step 2: Cut the DNA at the recognition site in Sample #1
- The enzyme will cut between G and A in GAATTC.
- After cutting, we will have two fragments:
1. Fragment 1: CAGTGATCTCGA (from the start to G)
2. Fragment 2: ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT (from A to the end)
Step 3: Determine the size of each fragment in Sample #1
- Fragment 1: CAGTGATCTCGA has 12 nucleotides.
- Fragment 2: ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT has 17 nucleotides.
- Thus, the sizes in order from largest to smallest are:
- Fragment 2: 17 nucleotides
- Fragment 1: 12 nucleotides
Step 4: Identify the recognition sequence in Sample #2
- Sample #2: TCATGA ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA
- We need to find the sequence GAATTC in this sample.
- The sequence GAATTC is present at the position "ATTCCTGGA".
Step 5: Cut the DNA at the recognition site in Sample #2
- The enzyme will cut between G and A in GAATTC.
- After cutting, we will have two fragments:
1. Fragment 1: TCATGA (from the start to G)
2. Fragment 2: ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA (from A to the end)
Step 6: Determine the size of each fragment in Sample #2
- Fragment 1: TCATGA has 6 nucleotides.
- Fragment 2: ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA has 24 nucleotides.
- Thus, the sizes in order from largest to smallest are:
- Fragment 2: 24 nucleotides
- Fragment 1: 6 nucleotides
Final Results
- Sample #1:
- # of fragments: 2
- Fragment sizes: 17, 12
- Sample #2:
- # of fragments: 2
- Fragment sizes: 24, 6
Summary
- Sample #1:
- # of fragments: 2
- Sizes: 17, 12
- Sample #2:
- # of fragments: 2
- Sizes: 24, 6
- Sample #1: CAGTGATCTCGA ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT
- We need to find the sequence GAATTC in this sample.
- The sequence GAATTC is present in the DNA strand at the position "ATTCGCTA".
- The enzyme will cut between G and A in GAATTC.
- After cutting, we will have two fragments:
1. Fragment 1: CAGTGATCTCGA (from the start to G)
2. Fragment 2: ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT (from A to the end)
- Fragment 1: CAGTGATCTCGA has 12 nucleotides.
- Fragment 2: ATTCGCTA GTA ACGTT has 17 nucleotides.
- Thus, the sizes in order from largest to smallest are:
- Fragment 2: 17 nucleotides
- Fragment 1: 12 nucleotides
- Sample #2: TCATGA ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA
- We need to find the sequence GAATTC in this sample.
- The sequence GAATTC is present at the position "ATTCCTGGA".
- The enzyme will cut between G and A in GAATTC.
- After cutting, we will have two fragments:
1. Fragment 1: TCATGA (from the start to G)
2. Fragment 2: ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA (from A to the end)
- Fragment 1: TCATGA has 6 nucleotides.
- Fragment 2: ATTCCTGGA ATCAGCAAATGCA has 24 nucleotides.
- Thus, the sizes in order from largest to smallest are:
- Fragment 2: 24 nucleotides
- Fragment 1: 6 nucleotides
- Sample #1:
- # of fragments: 2
- Fragment sizes: 17, 12
- Sample #2:
- # of fragments: 2
- Fragment sizes: 24, 6
- Sample #1:
- # of fragments: 2
- Sizes: 17, 12
- Sample #2:
- # of fragments: 2
- Sizes: 24, 6
Topper's Solved these Questions
- BIOTECHNOLOGYBOOK - CENGAGE BIOLOGYCHAPTER - BIOTECHNOLOGYEXERCISE - CONSOLIDATED EXERCISE (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS WITH ONE OR MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER)
49 Videos
- BIOTECHNOLOGYBOOK - CENGAGE BIOLOGYCHAPTER - BIOTECHNOLOGYEXERCISE - OLYMPIAD AND NTSE LEVEL EXERCISES
11 Videos
- BIOTECHNOLOGYBOOK - CENGAGE BIOLOGYCHAPTER - BIOTECHNOLOGYEXERCISE - CHALLENGING EXERCISE
2 Videos
- CHROMOSOMAL THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND GENETIC DISORDERSBOOK - CENGAGE BIOLOGYCHAPTER - CHROMOSOMAL THEORY OF INHERITANCE AND GENETIC DISORDERSEXERCISE - MANDATORY CHALLENGING EXERCISE
3 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
The sample with largest number of atoms is
A1 g of O2(g)B1 g of Ni (g)C1 g of B (s)D1 g of N2 (g)A sample of oleum is labelled 109% . The % of free SO3 in the sample is
A40%B80%C60%D9%Which sample A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life ?
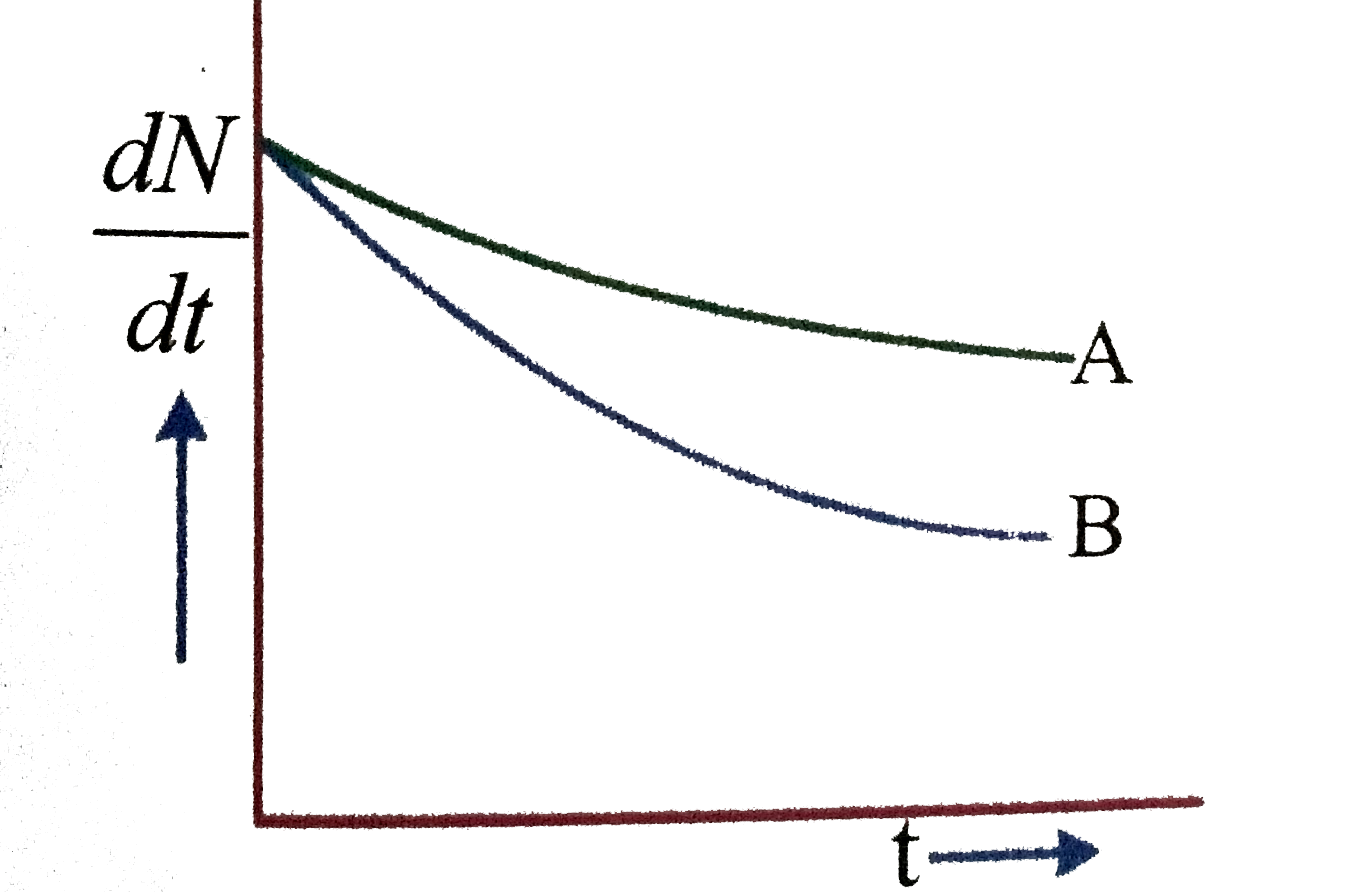 AτB<τABτB>τACτB=τADNothing can be concluded
AτB<τABτB>τACτB=τADNothing can be concluded
Define random sampling. How is it different from haphazard sampling?
View SolutionSampling erros are related to the size of nature of the sample selected. (True/False)
View SolutionTwo dice are thrown. The number of sample points in the sample space when six does not appear on either dice is
View SolutionThe outcomes of 5 tosses of a coin are recorded in a single sequence as H(head) and T(tail) for each toss. What is the number of elementary events in the sample space ?
View SolutionAfter the fragmentation by restriction endonuclease enzyme, the fragments are separated according to their size, this is called
View Solution