Relation between kinetic energy and momentum
Let us consider a body of mass 'm' having a velocity 'v', then
momentum of the body P = mass × velocity
P=m×v⇒v=Pm ...(1)
From definition, kinetic energy (K.E) of the body
K.E=12mv2 ...(2)
Now putting the value of (1) in (2) we have
K.E=12m(Pm)2
K.E.=12mP2m2=12P2m=P22m ...(3)
Thus we can write
P2=2m×K.E
⇒P=√2m×K.E
Thus momentum = √2×mass×kinetic energy
Two bodies masses 1 kg and 4 kg having equal kinetic energies. The ratio of their momentum is
4:1
1:4
2:1
1:2
To solve the problem regarding the relation between kinetic energy and momentum, we will follow these steps:
Step 1: Define Momentum and Kinetic Energy
We start with the definitions:
- Momentum (P) of a body is given by the formula:
P=m×v
where m is the mass and v is the velocity.
- Kinetic Energy (K.E) of a body is given by the formula:
K.E=12mv2
Step 2: Express Velocity in Terms of Momentum
From the momentum equation, we can express velocity v as:
v=Pm(1)
Step 3: Substitute Velocity in Kinetic Energy Formula
Now, we substitute the expression for v from equation (1) into the kinetic energy formula:
K.E=12m(Pm)2
Step 4: Simplify the Kinetic Energy Equation
Now we simplify the equation:
K.E=12m⋅P2m2
K.E=P22m(2)
Step 5: Rearranging to Find Momentum in Terms of Kinetic Energy
From equation (2), we can rearrange it to express P2:
P2=2m⋅K.E
Taking the square root gives us:
P=√2m⋅K.E(3)
Step 6: Finding the Ratio of Momentum for Two Bodies
Now, we have two bodies with masses m1=1kg and m2=4kg having equal kinetic energies K.E1=K.E2.
Using the formula for momentum derived earlier:
- For the first body:
P1=√2⋅1⋅K.E
- For the second body:
P2=√2⋅4⋅K.E
Step 7: Calculate the Ratio of Momentum
Now, we find the ratio of their momenta:
P1P2=√2⋅1⋅K.E√2⋅4⋅K.E
The K.E cancels out, and we simplify:
P1P2=√2⋅1√2⋅4=√2√8=√22√2=12
Conclusion
Thus, the ratio of their momenta P1:P2 is:
1:2
We start with the definitions:
- Momentum (P) of a body is given by the formula:
P=m×v
where m is the mass and v is the velocity.
- Kinetic Energy (K.E) of a body is given by the formula:
K.E=12mv2
From the momentum equation, we can express velocity v as:
v=Pm(1)
Now, we substitute the expression for v from equation (1) into the kinetic energy formula:
K.E=12m(Pm)2
Now we simplify the equation:
K.E=12m⋅P2m2
K.E=P22m(2)
From equation (2), we can rearrange it to express P2:
P2=2m⋅K.E
Taking the square root gives us:
P=√2m⋅K.E(3)
Now, we have two bodies with masses m1=1kg and m2=4kg having equal kinetic energies K.E1=K.E2.
- For the first body:
P1=√2⋅1⋅K.E
- For the second body:
P2=√2⋅4⋅K.E
Now, we find the ratio of their momenta:
P1P2=√2⋅1⋅K.E√2⋅4⋅K.E
The K.E cancels out, and we simplify:
P1P2=√2⋅1√2⋅4=√2√8=√22√2=12
Thus, the ratio of their momenta P1:P2 is:
1:2
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
Which of the following quantities is a vector quantity ?
View SolutionMATCH THE FOLLOWING
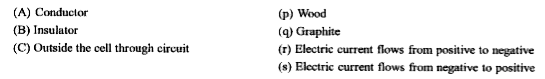
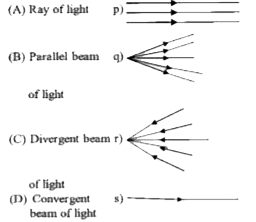
View SolutionMatrix matching
View SolutionThe kinetic energy passessed by a body of mass m moving with a velocity v is equal to 12mv2, provided
View SolutionWhat do you mean by kinetic energy ? Derive an expression for the kinetic energy of an object of mass m moving with velocity, υ.
View Solutionm द्रव्यमान की कोई वस्तु v वेग से चल रही है । यदि वस्तु का संवेग p तथा गतिज ऊर्जा K हो तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि -
p=√2mK.
View SolutionThe angular momentum of a rigid body of mass m about an axis is n times the linear momentum (P) of the body. Total kinetic energy of the rigid body is:
View SolutionWrite the kinetic energy of a body of momentum p and velocity v.
View SolutionThe kinetic energy passessed by a body of mass m moving with a velocity v is equal to 12mv2, provided
View SolutionWhat is the relation for momentum if mass of a body is m and velocity is v
View SolutionWhen a body of mass 'm' moves with a velocity 'v' its kinetic energy-
View SolutionWhat is the expression for kinetic energy of a body of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'v'.
View SolutionIf a body of mass m is moving with velocity v then prove that kinetic energy of the body =12mv2
View SolutionRelation between Kinetic energy (Ex) and Momentum (p) of a body of mass (m)
View SolutionRelation between kinetic energy and momentum Let us consider a body of mass 'm' having a velocity 'v', then momentum of the body P = mass xx velocity P = m xx v rArr v = (P)/(m) " "...(1) From definition, kinetic energy (K.E) of the body K.E = (1)/(2) mv^(2)" "...(2) Now putting the value of (1) in (2) we have K.E = (1)/(2)m ((P)/(m))^(2) K.E. = (1)/(2)m (P^(2))/(m^(2)) = (1)/(2) (P^(2))/(m) = (P^(2))/(2m)" "...(3) Thus we can write P^(2) = 2m xx K.E rArr P = sqrt(2m xx K.E) Thus momentum = sqrt(2 xx "mass" xx "kinetic energy") What will be the momentum of a body of mass 100 g having kinetic energy of 20 J ?
View Solution