50mL of 0.1MCuSO4 solution is electrolysed with a current of 0.965A for a period of 200sec. The reactions at electrodes are:
Cathode: Cu2++2e−→Cu(s)
Anode: 2H2O→O2+4H++4e.
Assuming no change in volume during electrolysis, calculate the molar concentration of Cu2+,H+ and SO2−4 at the end of electrolysis.
The correct Answer is:Cu2+=0.08M,H+=0.04M,SO2−4=0.1M
To solve the problem step by step, we will follow these calculations:
Step 1: Calculate the total charge (Q) passed through the solution
Using the formula:
Q=I×t
Where:
- I=0.965A (current)
- t=200s (time)
Calculating:
Q=0.965A×200s=193C
Step 2: Calculate the number of moles of electrons (n)
Using Faraday's law:
Q=n×F
Where:
- F=96500C/mol (Faraday's constant)
Rearranging the formula to find n:
n=QF=193C96500C/mol≈0.002mol
Step 3: Determine the moles of Cu2+ consumed
From the cathode reaction:
Cu2++2e−→Cu(s)
This indicates that 1 mole of Cu2+ consumes 2 moles of electrons. Therefore, the moles of Cu2+ consumed is:
Moles of Cu2+=n2=0.002mol2=0.001mol
Step 4: Calculate the initial moles of Cu2+
The initial concentration of Cu2+ is given as 0.1M and the volume is 50mL (or 0.050L):
Initial moles of Cu2+=Concentration×Volume=0.1mol/L×0.050L=0.005mol
Step 5: Calculate the remaining moles of Cu2+
Remaining moles of Cu2+=Initial moles−Consumed moles=0.005mol−0.001mol=0.004mol
Step 6: Calculate the final concentration of Cu2+
Using the remaining moles and the original volume:
Final concentration of Cu2+=Remaining molesVolume=0.004mol0.050L=0.08M
Step 7: Calculate the concentration of H+
From the anode reaction:
2H2O→O2+4H++4e−
This indicates that 4 moles of H+ are produced per 4 moles of electrons. Therefore, the moles of H+ produced is equal to the moles of electrons:
Moles of H+=n=0.002mol
Step 8: Calculate the final concentration of H+
Using the moles of H+ produced and the volume:
Final concentration of H+=0.002mol0.050L=0.04M
Step 9: Determine the concentration of SO2−4
Since there is no change in the amount of SO2−4 during the electrolysis, its concentration remains the same as the initial concentration:
Final concentration of SO2−4=0.1M
Summary of Final Concentrations:
- Final concentration of Cu2+=0.08M
- Final concentration of H+=0.04M
- Final concentration of SO2−4=0.1M
Using the formula:
Q=I×t
Where:
- I=0.965A (current)
- t=200s (time)
Q=0.965A×200s=193C
Using Faraday's law:
Q=n×F
Where:
- F=96500C/mol (Faraday's constant)
n=QF=193C96500C/mol≈0.002mol
From the cathode reaction:
Cu2++2e−→Cu(s)
This indicates that 1 mole of Cu2+ consumes 2 moles of electrons. Therefore, the moles of Cu2+ consumed is:
Moles of Cu2+=n2=0.002mol2=0.001mol
The initial concentration of Cu2+ is given as 0.1M and the volume is 50mL (or 0.050L):
Initial moles of Cu2+=Concentration×Volume=0.1mol/L×0.050L=0.005mol
Remaining moles of Cu2+=Initial moles−Consumed moles=0.005mol−0.001mol=0.004mol
Using the remaining moles and the original volume:
Final concentration of Cu2+=Remaining molesVolume=0.004mol0.050L=0.08M
From the anode reaction:
2H2O→O2+4H++4e−
This indicates that 4 moles of H+ are produced per 4 moles of electrons. Therefore, the moles of H+ produced is equal to the moles of electrons:
Moles of H+=n=0.002mol
Using the moles of H+ produced and the volume:
Final concentration of H+=0.002mol0.050L=0.04M
Since there is no change in the amount of SO2−4 during the electrolysis, its concentration remains the same as the initial concentration:
Final concentration of SO2−4=0.1M
- Final concentration of Cu2+=0.08M
- Final concentration of H+=0.04M
- Final concentration of SO2−4=0.1M
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBook:ALLENChapter:ELECTROCHEMISTRYExercise:EXERCISE-04 [B]
Explore 23 Videos
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBook:ALLENChapter:ELECTROCHEMISTRYExercise:EXERCISE-05 [A]
Explore 28 Videos
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBook:ALLENChapter:ELECTROCHEMISTRYExercise:EXERCISE-03
Explore 24 Videos
- CHEMISTRY AT A GLANCEBook:ALLENChapter:CHEMISTRY AT A GLANCEExercise:ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Explore 472 Videos
- HYDROCARBONBook:ALLENChapter:HYDROCARBONExercise:MCQ
Explore 15 Videos
Similar Questions
The e.m.f. of cell: H2(g) |Buffer| Normal calomal electrode is 0.6885V at 40∘C when the barometric pressure is 725mm of Hg. What is the pH of the solution E∘calomal=0.28.
View SolutionDuring electrolysis of a solution of AgNO3 , 9650 coulombs of charge is passed through the solution. What be the mass of silver deposited on the cathode?
View SolutionMatch the items of column I to those of column I:
Column−IColumn−II(A)Cell constant(p)E0cathode+E0anode(B)Anode(q)l/A(C)Conductance(r)Mass of product by 1 coulomb of electricity(D)Electrochemical equivalent(s)(Resistance)−1(E)E0cell(u)Involve oxidation
View SolutionThe correct IUPAC name of the following compound is :
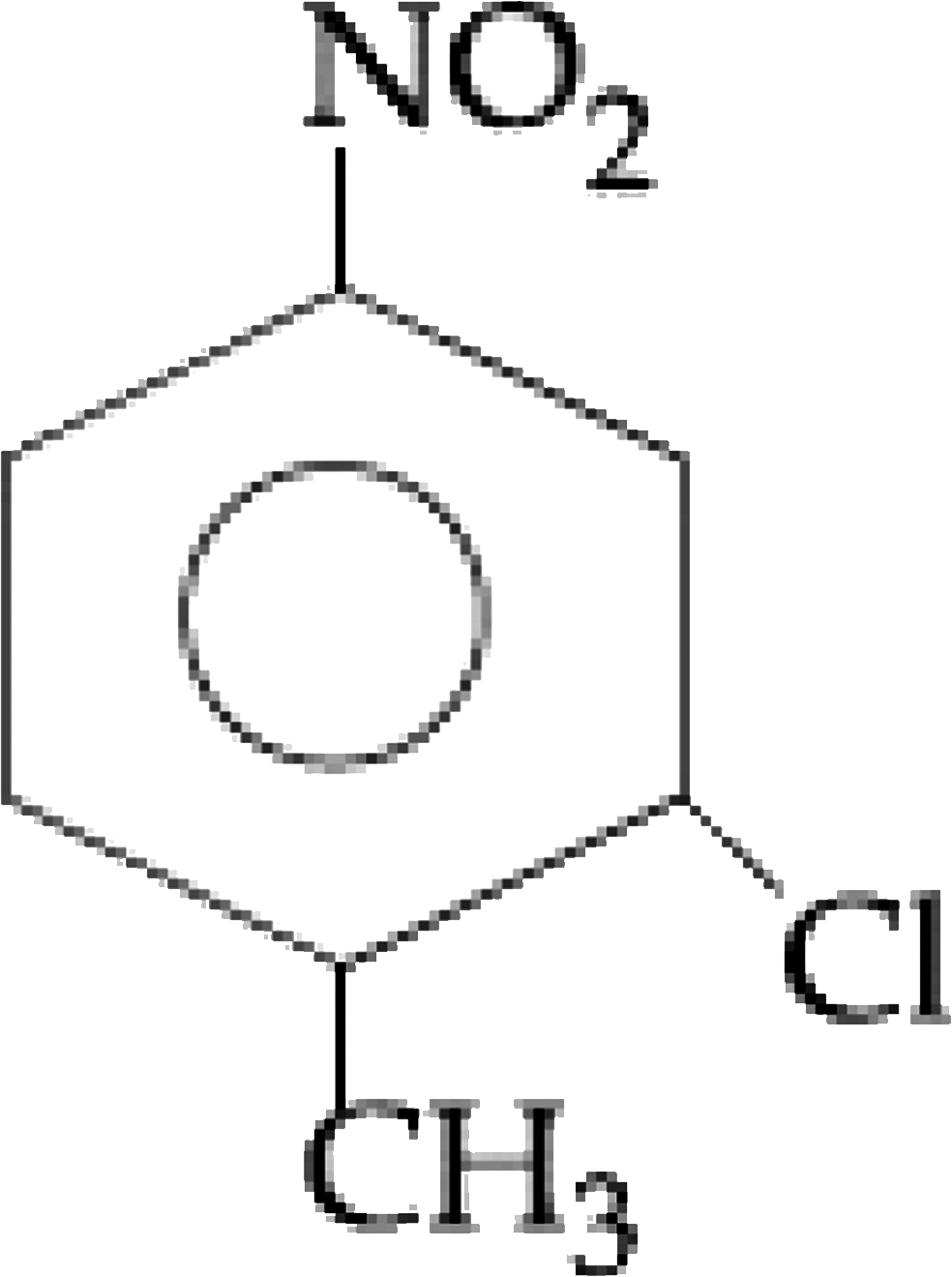
View Solution
View SolutionIn the electrolysis of 7.2L aqueous solution of CuSO_(4) , a current of 9.65A passed for 2 hours. a. Calculate the weight of Cu deposited at cathode. b. Calculate the volume of O_(2) produced at anode at 27^(@)C and 1 atm pressure. c. Calculate the pH of the solution after electrolysis. [ Atomic mass of Cu=63g]
View SolutionCu2++2e−→Cu. On increasing [Cu2+], electrode potential
View SolutionIn the electrolysis of a 40L CuSO_(4) solution, there are two possible reactions at anode : i. Cu rarr Cu^(2+)+2e^(-) ii. 2H_(2)O rarr 4H^(o+)+4e^(-)+O_(2) A current of 1.07 A is passed for 2 hours. The loss in the mass of Cu at anode was 1.27 g . ( Atomic weight of Cu =63.5g mol ^(1)) . Which of the following statement (s) is // are correct ?
View SolutionIn the electrolysis of CuSO_(4) , the reaction Cu^(2+) + 2 e^(-) to Cu , takes place at
View SolutionDuring the electrolysis of CuSO_(4) solution in presence of cooper electrodes, the Cu - anode is depleted. Why ?
View SolutionReaction at the anode during the electrolysis of aqueous CuSO_(4) solution in presence of Cu electrode is -
View Solution50 mL of 0.1 M CuSO4 solution is electrolysed using Pt electrodes with a current of 0.965 ampere for a period of 1 minute. Assuming that volume of solution does not change during electrolysis, calculate [Cu2+].[H+] and [SO2–4] after electrolysis. What will be the concentration of each species if current is passed using Cu electrodes ?
View SolutionIn the electrolysis of CuSO_4 , the reaction: Cu^(2+)+2e^(-) rarr Cu ,takes place at:
View SolutionElectrochemical equivalent of Cu in the reaction
Cu2++2e−→Cu(s) is :
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions are disproportionation reactions?
(a) Cu+→Cu2++Cu
(b) MnO2−4+4H+→2MnO−4+MnO2+2H2O
(c ) 2KMnO4→K2MnO4+MnO2+O2
(d) 2MnO−4+3Mn2++2H2O→5MnO2+4H+
View SolutionThe ion which is discharged at the anode during the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution using platinum electrode as anode and cathode [Cu^(2+) OH^(-),SO_(4)^(2-) H^(+)]
View Solution
