Which of the following is correct regarding formation of reactive inter mediate formed on heterolytic bond cleavage :
CH3−S−CH3→Θ⋅⋅CH3+CH3−ΘS
CH3−Cu→Θ⋅⋅CH3+ΘCu
CH3−Cl→Θ⋅⋅CH3+ΘCl
1 & 2 both
The correct Answer is:B
To solve the question regarding the correct statement about the formation of reactive intermediates formed on heterolytic bond cleavage, we will analyze each option provided.
1. Understanding Heterolytic Bond Cleavage:
- Heterolytic bond cleavage occurs when a bond breaks unevenly, resulting in the formation of charged species. One atom takes both electrons from the bond, leading to the formation of a cation and an anion.
2. Analyzing Option A: CH3SCH3:
- For the molecule CH3SCH3, when heterolytic cleavage occurs, the bond electrons shift towards the more electronegative atom, which is sulfur (S).
- This results in the formation of CH3^+ (methyl cation) and CH3S^- (methylthio anion).
- The option states a different product (TSA negative), which does not match our findings.
- Conclusion: Option A is incorrect.
3. Analyzing Option B: CH3Cu:
- In the case of CH3Cu, the electrons will shift towards the CH3 group.
- This results in the formation of CH3^- (methyl anion) and Cu^+ (copper cation).
- The products mentioned in this option match our analysis.
- Conclusion: Option B is correct.
4. Analyzing Option C: CH3Cl:
- For CH3Cl, the electrons will shift towards chlorine (Cl), which is more electronegative.
- This results in the formation of CH3^+ (methyl cation) and Cl^- (chloride anion).
- The products mentioned do not match the expected products.
- Conclusion: Option C is incorrect.
5. Analyzing Option D: A and B both:
- Since we have established that Option A is incorrect and Option B is correct, this option cannot be true.
- Conclusion: Option D is incorrect.
Final Answer:
- The correct answer regarding the formation of reactive intermediates formed on heterolytic bond cleavage is Option B.
- Heterolytic bond cleavage occurs when a bond breaks unevenly, resulting in the formation of charged species. One atom takes both electrons from the bond, leading to the formation of a cation and an anion.
- For the molecule CH3SCH3, when heterolytic cleavage occurs, the bond electrons shift towards the more electronegative atom, which is sulfur (S).
- This results in the formation of CH3^+ (methyl cation) and CH3S^- (methylthio anion).
- The option states a different product (TSA negative), which does not match our findings.
- Conclusion: Option A is incorrect.
- In the case of CH3Cu, the electrons will shift towards the CH3 group.
- This results in the formation of CH3^- (methyl anion) and Cu^+ (copper cation).
- The products mentioned in this option match our analysis.
- Conclusion: Option B is correct.
- For CH3Cl, the electrons will shift towards chlorine (Cl), which is more electronegative.
- This results in the formation of CH3^+ (methyl cation) and Cl^- (chloride anion).
- The products mentioned do not match the expected products.
- Conclusion: Option C is incorrect.
- Since we have established that Option A is incorrect and Option B is correct, this option cannot be true.
- Conclusion: Option D is incorrect.
- The correct answer regarding the formation of reactive intermediates formed on heterolytic bond cleavage is Option B.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
If atomic number 117,120 are discovered then their blocks will be
View Solution48 g of SO3 , 12.8 g of SO2 and 9.6 g of O2 are present in one litre . The respective active masses will be
View SolutionFind the solubility product of a saturated solution of Ag2CrO4 in water at 298K, if the EMF of the cell :
Ag∣∣Ag⊕(satAg2CrO4sol)∣∣|Ag(0.1M)|Agis0.164V at 298K.
View SolutionTHE BREAKING OF BONDS-HOMOLYTIC AND HETEROLYTIC CLEAVAGE
View SolutionFind out correct order of energy required for heterolytic cleavage of indicated C−Cl bonds forming carbocation :
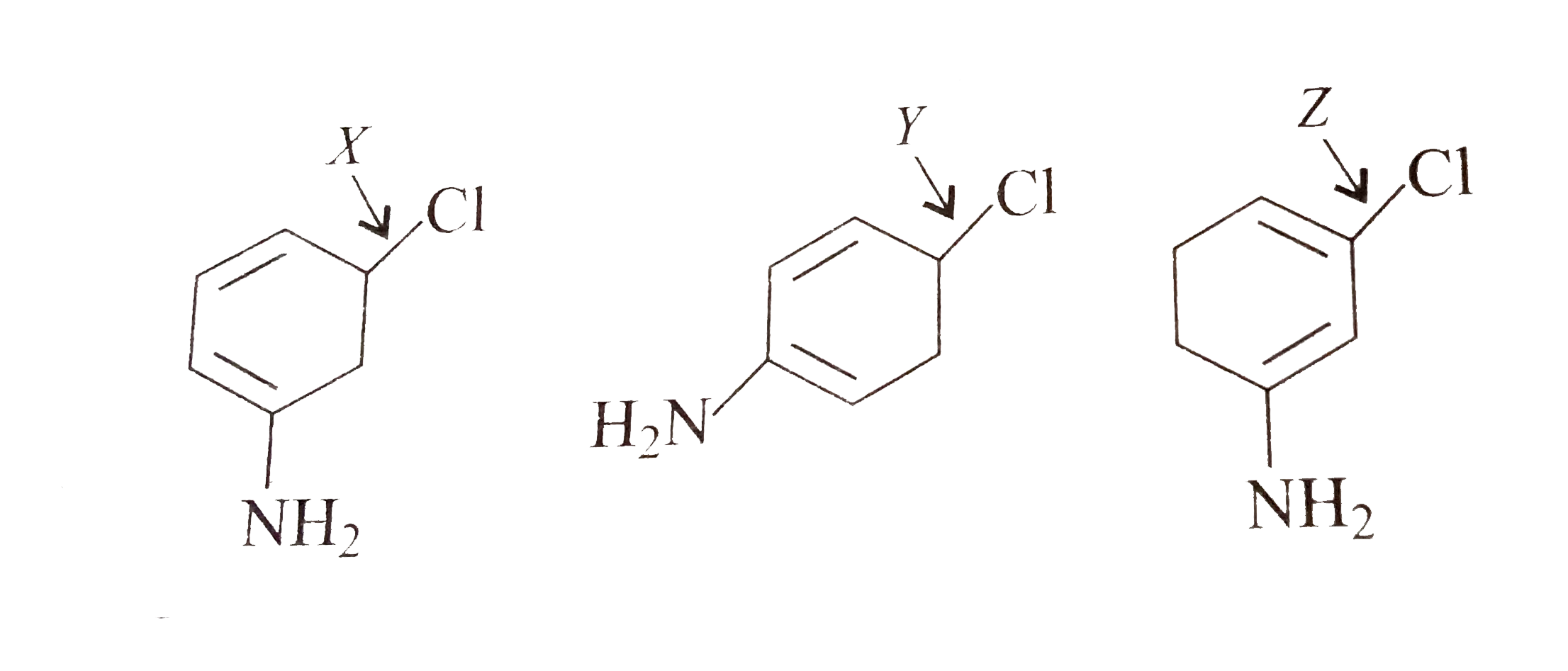
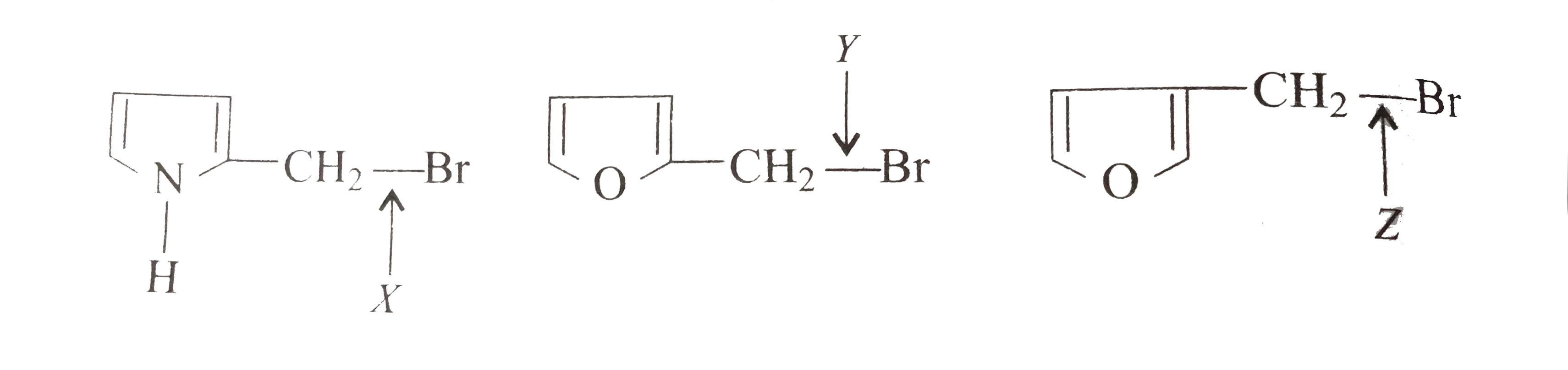
View SolutionFind out correct order for the energy requried for heterolytic cleavage of indicated C−Br bonds forming carbocation :
View SolutionOrganic reactions take place through the formations of reactive carbon intermediates formed by cleavage of covalent bonds. Formation of these intermediates depends upon the dissociation energies of covalent bonds. 1. Which is not the intermediate formed by cleavage of covalent bonds.
View Solutionविषम विदलन (heterolytic cleavage) में कौन-सा प्रमाण काबन-धनायन बनाता है?
View SolutionWrite structures of the ions expected to be formed by the heterolytic cleavage of a C - C bond of 2,2 - dimethylpropane and explain their formation.
View SolutionThe heterolytic cleavage of C-H bonds results in the formation of __________
View SolutionWhat is heterolytic cleavage of chemical bond?
View Solution(i) Positive and negative ion are formed by homolytic cleavage of covalent bond.
(ii) Positive and negative ion formed by heterolytic cleavage of covalent bond.
(iii) Only homolytic cleavage is possible in C−C−Cl bond of CH3−Cl
(iv) If the heterolytic cleavage of bond then there are ionic or polar types reaction occurs in it
View SolutionWhat is heterolytic cleavage of chemical bond?
View Solution(i) Positive and negative ion are formed by homolytic cleavage of covalent bond.
(ii) Positive and negative ion formed by heterolytic cleavage of covalent bond.
(iii) Only homolytic cleavage is possible in C−C−Cl bond of CH3−Cl
(iv) If the heterolytic cleavage of bond then there are ionic or polar types reaction occurs in it
View SolutionHeterolytic cleavage of a covalent bond gives only:
View SolutionCarbocations are formed by the heterolytic cleavage of a covalent bond.
a) What is heterolytic bond fission?
View Solution
