AH3O+−−−→B+EtOH
BΔ−−→ Acetone
A is :
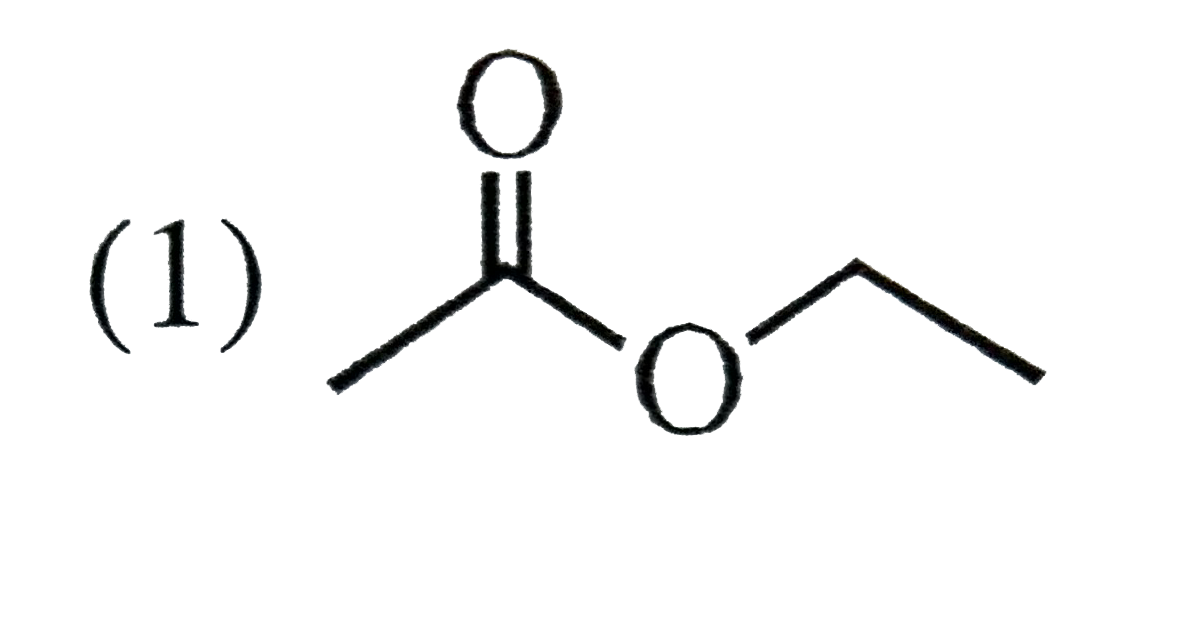
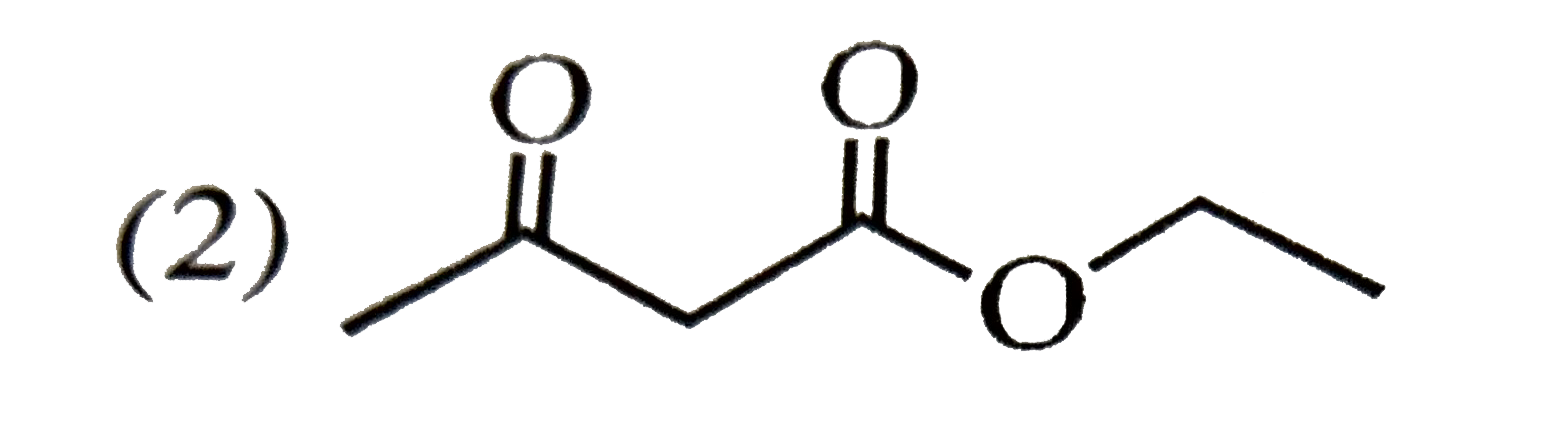
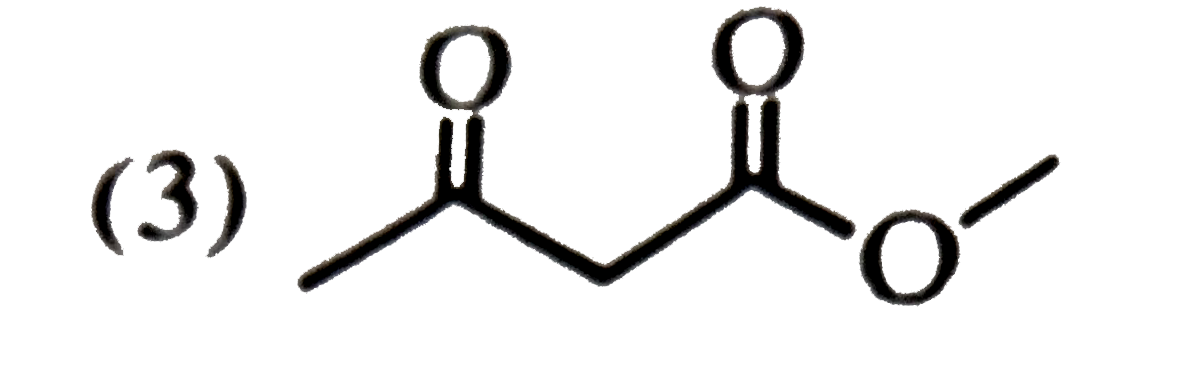
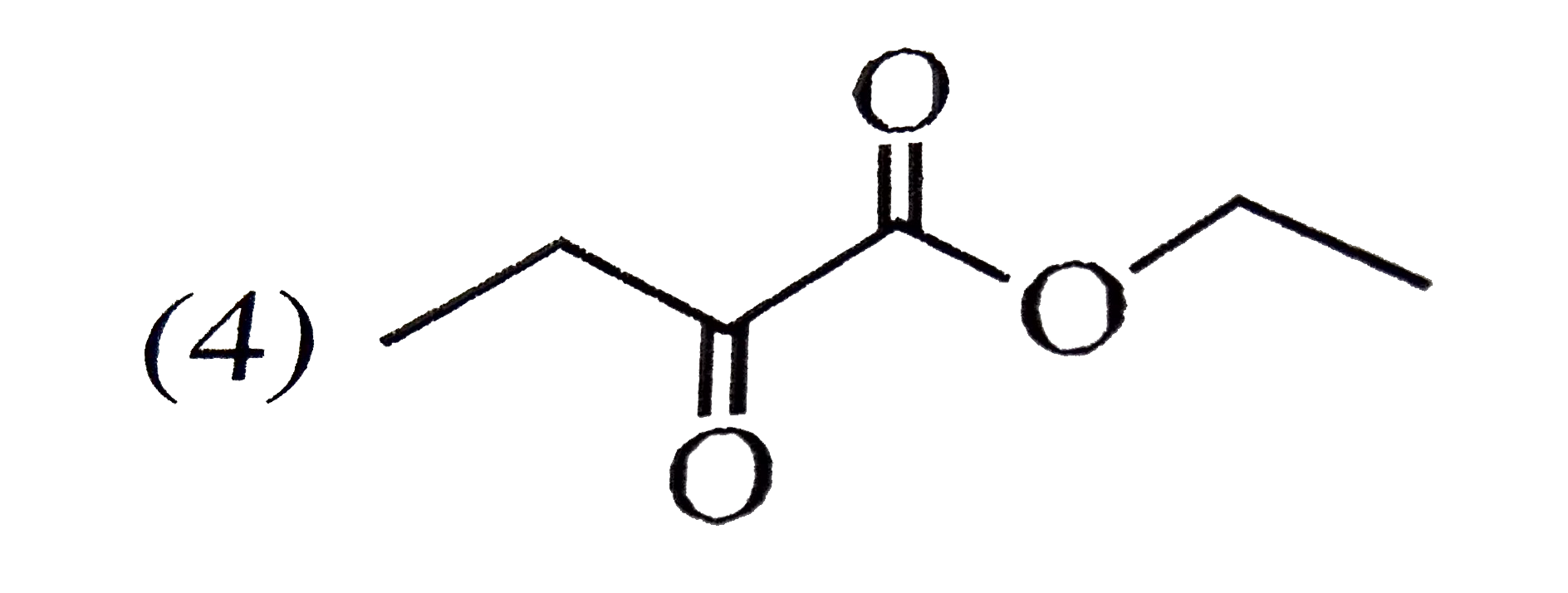
The correct Answer is:B
To solve the problem, we need to identify the compound A that can undergo hydrolysis to form compound B in the presence of hydronium ion (H₃O⁺) and then convert B to acetone upon heating.
1. Identify the Reaction Sequence:
- A reacts with H₃O⁺ to form B + EtOH (ethyl alcohol).
- B is then heated to form acetone.
2. Analyze the Hydrolysis Reaction:
- Hydrolysis typically involves the addition of water or a hydronium ion, leading to the formation of alcohols and other products.
- The presence of EtOH suggests that B must have a structure that can yield ethyl alcohol upon hydrolysis.
3. Examine Possible Structures for A:
- We need to consider structures that can produce an alcohol and a carbonyl compound upon hydrolysis.
- A common structure that fits this description is an ester or a ketone.
4. Check Each Option:
- Option 1: If A is an ester, hydrolysis would yield an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. However, we need to ensure that the product B can be converted to acetone.
- Option 2: If A is a compound like an acid anhydride or a specific ester that can yield a ketone upon heating, we should analyze if it can yield B and then acetone.
5. Determine the Structure of B:
- From the hydrolysis reaction, B must be a compound that can be heated to yield acetone.
- If B is a β-keto ester or a similar compound, it can undergo decarboxylation or elimination to form acetone.
6. Final Verification:
- After testing the structures, if we find that the second option leads to the formation of acetone upon heating, we can conclude that A is the correct structure.
Conclusion:
The correct structure of A is the one that, upon hydrolysis, yields B (which can then be heated to form acetone). Based on the analysis, the second option is the correct answer.
- A reacts with H₃O⁺ to form B + EtOH (ethyl alcohol).
- B is then heated to form acetone.
- Hydrolysis typically involves the addition of water or a hydronium ion, leading to the formation of alcohols and other products.
- The presence of EtOH suggests that B must have a structure that can yield ethyl alcohol upon hydrolysis.
- We need to consider structures that can produce an alcohol and a carbonyl compound upon hydrolysis.
- A common structure that fits this description is an ester or a ketone.
- Option 1: If A is an ester, hydrolysis would yield an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. However, we need to ensure that the product B can be converted to acetone.
- Option 2: If A is a compound like an acid anhydride or a specific ester that can yield a ketone upon heating, we should analyze if it can yield B and then acetone.
- From the hydrolysis reaction, B must be a compound that can be heated to yield acetone.
- If B is a β-keto ester or a similar compound, it can undergo decarboxylation or elimination to form acetone.
- After testing the structures, if we find that the second option leads to the formation of acetone upon heating, we can conclude that A is the correct structure.
The correct structure of A is the one that, upon hydrolysis, yields B (which can then be heated to form acetone). Based on the analysis, the second option is the correct answer.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
If atomic number 117,120 are discovered then their blocks will be
View Solution48 g of SO3 , 12.8 g of SO2 and 9.6 g of O2 are present in one litre . The respective active masses will be
View SolutionFind the solubility product of a saturated solution of Ag2CrO4 in water at 298K, if the EMF of the cell :
Ag∣∣Ag⊕(satAg2CrO4sol)∣∣|Ag(0.1M)|Agis0.164V at 298K.
View SolutionA, b तथा C की सरंचना किजीय --- CH3COOHNH3−−−−−→ΔANaOBr−−−→BNaNO2/HCI−−−−−−−−→C
View SolutionMetal M+"air" overset(delta)(to)Aoverset(H_(2)O)(to)Boverset(HCl)(to) White fumes, Metal M can be:
View SolutionNaoverset(H_(2)O)(to)Aoverset(CO_(2))(to)Boverset(SO_(2))(to)Coverset(Na_(2)S"/"I_(2))underset(delta)(to)Doverset(Ag^(+)"/"Salt)(to)E (complex) Q. The compounds B and C is
View SolutionNaH2O−−→ACO2−−→BSO2−−→CNa2S/I2−−−−−→δDAg+/Sa<−−−−−−→E(complex)
Q. The compound D is
View SolutionA[O]−−→BNa2OH−−−−→(CH3)2C=NOH. Identify A.
View Solutionunderset(HCl)overset(NaNO_(2))(to)Aoverset(CuCN)(to)Boverset(H_(3)O^(+))(to)C .C is identified as
View SolutionNaH2O−−→ACO2−−→BSO2−−→CNa2S/I2−−−−−→δDAg+/Sa<−−−−−−→E(complex)
Q. The compound D is
View Solutionअभिक्रिया,
CH3ClKCN−−→AH2O−−→BNH3−−→CΔ−−→D
में यौगिक D है
View SolutionComplete the reaction, i. H_(3)BO_(3)overset(373K)toA+H_(2)O ii. Aoverset(413K)toB+H_(2)O iii. Boverset("Red hot")toC+H_(2)O
View SolutionCH3CH2CH2−OHPCl3−−→AAlc.KOH−−−−−→BH2OorH+−−−−−−−→C उत्पाद C है
View Solutionअभिक्रिया क्रम AHBr−−→BC2H5ONa−−−−−→ एथॉक्सीएथेन में A तथा B क्या है:
View Solutionअभिक्रिया क्रम में A,B,C क्रमशः क्या है:
ROCl+H2Pd+BaSO4−−−−−−→AHCN−−→BH2O⊕−−−→C
View SolutionMetal M+airδ−−→AH2O−−→BHCl−−→ White fumes, Metal M can be:
View Solution
