Heat given to a body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is
water equivalent
thermal capacity
specific heat
temperature gradient
The correct Answer is:B
To solve the question regarding the heat given to a body that raises its temperature by 1∘C, we can follow these steps:
1. Understanding Specific Heat:
- The specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of the substance by 1∘C (or 1 K).
- Mathematically, it is expressed as:
c=QmΔT
where:
- c = specific heat,
- Q = heat added,
- m = mass of the substance,
- ΔT = change in temperature.
2. Identifying the Heat for 1∘C:
- If we want to find the heat Q that raises the temperature of a body by 1∘C, we can rearrange the formula:
Q=m⋅c⋅ΔT
- For our case, since ΔT=1∘C, we have:
Q=m⋅c⋅1
- Therefore, the heat given to the body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is simply:
Q=m⋅c
3. Conclusion:
- The heat given to a body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is equal to the specific heat of the body multiplied by its mass.
- If we consider the specific heat alone (without mass), the heat given to raise the temperature by 1∘C can be referred to as the specific heat c.
Final Answer:
The heat given to a body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is the specific heat of the body.
- The specific heat of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of the substance by 1∘C (or 1 K).
- Mathematically, it is expressed as:
c=QmΔT
where:
- c = specific heat,
- Q = heat added,
- m = mass of the substance,
- ΔT = change in temperature.
- If we want to find the heat Q that raises the temperature of a body by 1∘C, we can rearrange the formula:
Q=m⋅c⋅ΔT
- For our case, since ΔT=1∘C, we have:
Q=m⋅c⋅1
- Therefore, the heat given to the body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is simply:
Q=m⋅c
- The heat given to a body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is equal to the specific heat of the body multiplied by its mass.
- If we consider the specific heat alone (without mass), the heat given to raise the temperature by 1∘C can be referred to as the specific heat c.
The heat given to a body which raises its temperature by 1∘C is the specific heat of the body.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE - 05 (B)
58 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE - 05 (B) (MCQ)
9 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE - 04 (B)
15 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - EX.II
66 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GRAVITATIONEXERCISE - EXERCISE 4
9 Videos
समान प्रश्न
A vessel contains a mixture of one mole of Oxygen and two moles of Nitrogen at 300 K. The ratio of the average kinetic energy per O2 molecule to that per N2 molecule is :
View SolutionLet →V,Vm s and Vp respectively, denote the mean speed, root mean square speed and most probable speed of the molecules in an ideal monatomic gas at absolute temperature T. The mass of a molecule is m. then :
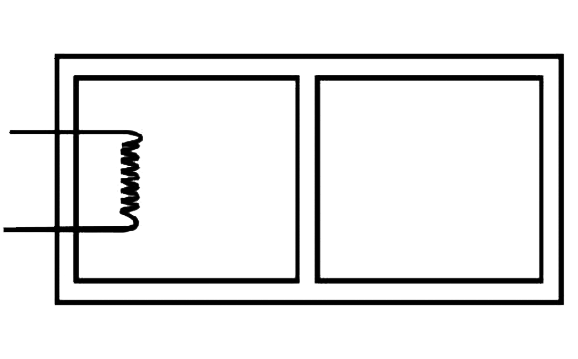
View SolutionThe rectangular box shown in Fig has partition which can slide without friction along the length of the box. Initially each of the two chambers of the box has one mole of a mono-atomic ideal gas (λ=5/3) at a pressure P0, volume V0 and temperature T0. The chamber on the left is slowly heated by an electric heater. The walls of the box and the lead wires of the heater is negligible. The gas in the left chamber expands pushing the partition until the final pressure in both chambers becomes 243P0/32. Determine (i) the final temperature of the gas in each chamber.
View SolutionIn the Bohr's model of hy drogen atom, the electron moves around the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 5×10−11m. Its time period is 1.5×10−16s. The current associated with the electron motion is:-
View SolutionAssertion : The difference in the value of acceleration due to gravity at pole and equator is proportional to square of angular velocity of earth.
Reason : the value of acceleration due to gravity is minimum at the equator and maximum at the pole.
View SolutionAmount of heat required to raise the temperature of a body through 1K is called its.
View SolutionThe heat requried to raise the temperature of body by 1∘C is called :
View SolutionThe heat required to raise the temperature of body by 1^(@)C is called:
View SolutionHeat is absorbed by a body. But its temperature does not raised. Which of the following statement explains the phenomena?
View SolutionThe heat required to raise the temperature of a body by 1^(@)C is called
View SolutionThe heat required to raise the temperature of a body by 1 K is called
View SolutionThe heat required to raise the temperature of a body by 1 K is called
View SolutionA black body, at a temperature of 227∘C, radiates heat at a rate of 20 cal m−2s−1. When its temperature is raised to 727∘C, the heat radiated by it in cal M−2s−1 will be closest to
View SolutionThe heat required to raise the temperature of a body by 1 K is called ____
View SolutionThe heat required to raise the temperature of body by 1 K is called .......
View SolutionThe amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a body by 1^@C is called
View Solution

