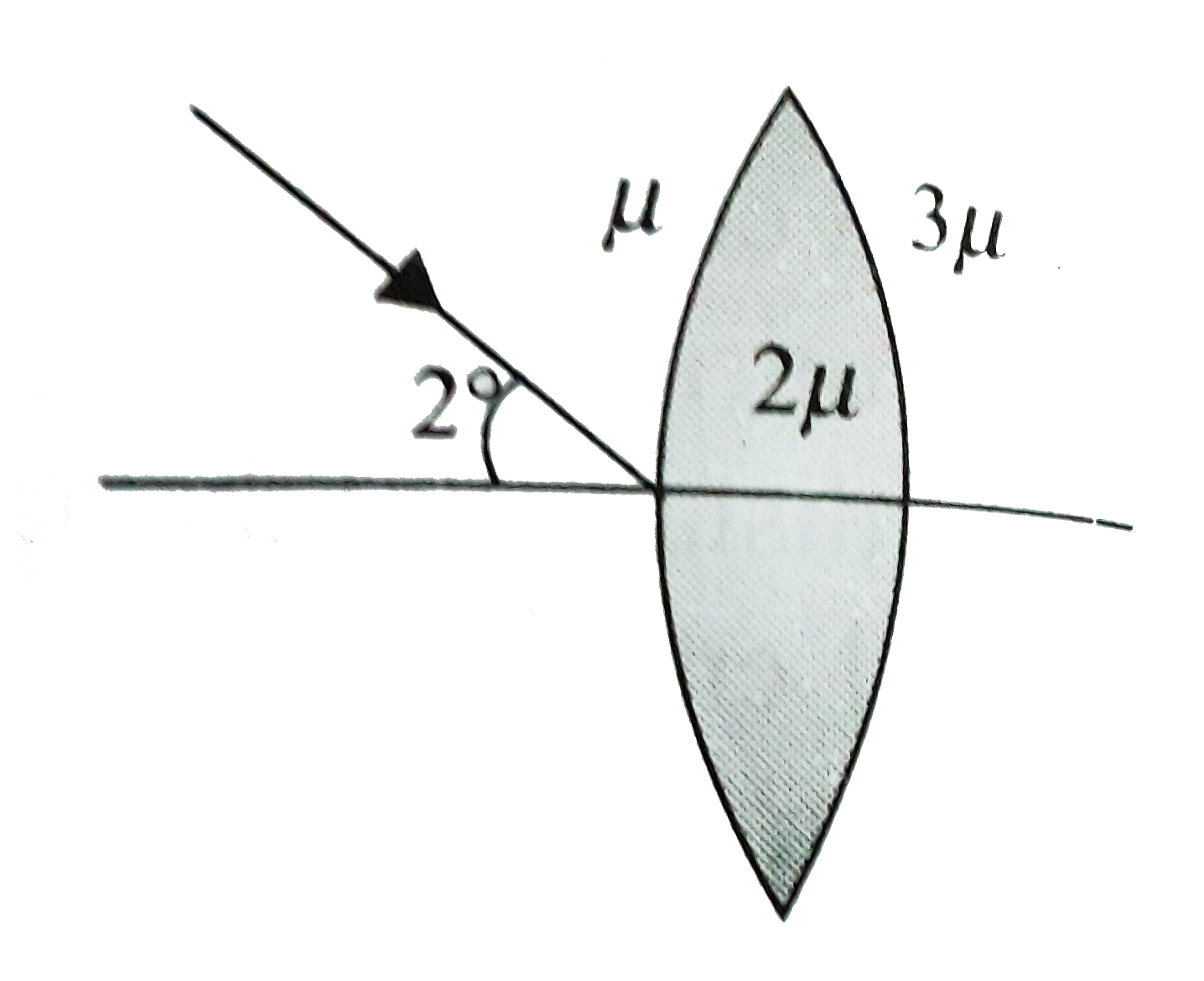
A light ray hits the pole of a thin biconvex lens as shown in fig. The angle made by the emergent ray with the optic axis will be approximately
0∘
(1/3)∘
(2/3)∘
2∘
The correct Answer is:C
From Snell's law ∴μsin2∘=2μsinr
∵θ=2∘ (small angle)
_E01_066_S01.png)
sin2∘=2∘,μ×2∘=2μr∘
r=1∘ & 2μ×1∘=3μr',r'=(23)∘
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE-3
12 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE-04[A]
23 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE- 01
45 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - CURRENT ELECTRICITYEXERCISE - EX.II
66 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - GRAVITATIONEXERCISE - EXERCISE 4
9 Videos
Similar Questions
Plane mirrors are arranged parallel to each other as shown in column-I and the number of images formed by the combination is in column- II
_E01_090_S01.png)
View SolutionA plane mirror of circular shape with radius r = 20 cm is fixed to the celling. A bulb is to be placed on the axis of the mirror. A circular area of the radius R = 1m on the floor is to be illuminated after reflection of light from the mirror. The height of the room is 3m . What is the maximum distance from the centre of the mirror and the bulb so that the required area is illuminated ?
View SolutionTwo plane mirror M1andM2 are inclined to each other at 70∘. A ray incident on the mirror M1 at an angle θ fallls on M2 and is then reflected parallel to M1 for
View SolutionIn the Bohr's model of hy drogen atom, the electron moves around the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius 5×10−11m. Its time period is 1.5×10−16s. The current associated with the electron motion is:-
View SolutionAssertion : The difference in the value of acceleration due to gravity at pole and equator is proportional to square of angular velocity of earth.
Reason : the value of acceleration due to gravity is minimum at the equator and maximum at the pole.
View SolutionA light ray hits the pole of a thin biconvex lens as shown in fig. The angle made by the emergent ray with the optic axis will be approximately
View SolutionWhich of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a lens shown in Fig. ? Choices are given in Fig.
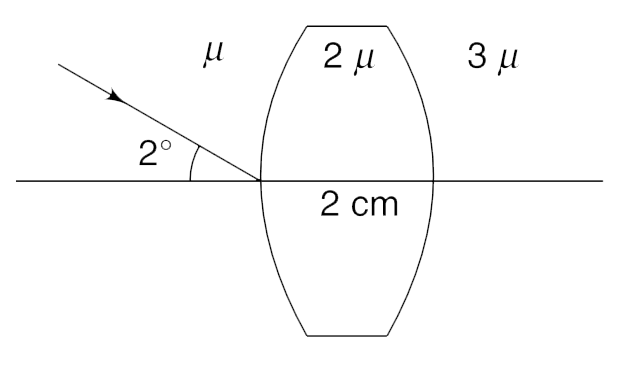
View SolutionAn equiconvex lens has its two surfaces of radius of curvature R=10cm. Thickness of the lens at its centre is 2 cm. A light ray is incident making an angle of 2° with the optic axis of the lens. Find the angle that the emergent ray will make with the optic axis. The refractive index of all media is as marked in the Figure.
View SolutionA ray of light is directed towards a corner reflector as shown. The incident ray makes an angle of 22^(@) with one of the mirrors. At what angle theta does the ray emerge?
View SolutionThe rays passing through the optic centre of a thin lens suffers no lateral displacement.
View SolutionThe point on the principal axis of a lens such that a ray of light passing through it, emerges undeviated
View Solutionपतले लेंस में प्रकाशिक केंद्र से जाती किरण अपवर्तन के पश्चात ....... में जाती है |
View Solutionकाँच (μ=1⋅5) के बने हुए एक उभयोत्तल पतले लेंस की दोनों वक्रता त्रिज्याओं का मान 20 सेमी है | लेंस की अक्ष के समान्तर प्रकाश की आपतित किरणे इससे दुरी d पर अभिसरित होंगी, जहाँ :
View SolutionWhich of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a lens shown in Fig. ? Choices are given in Fig.

View SolutionThe angle of deviation of emergent light ray (BC) with respect to incident ray (OA) on glass sphere Is, as shown in figure.
View SolutionThe point on the principal axis of a lens such that a ray of light passing through it, emerges undeviated
View Solution

