Arrange acididy of given compounds in decreasing order
(I). CH3−N−CH2−OH
(II). CH3−NH−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH
(III). (CH3)3⊕N−CH2−CH2−OH
IIIgtIgtII
IIIgtIIgtI
IgtIIgtIII
IIgtIgtIII
The correct Answer is:A
To determine the acidity of the given compounds, we need to analyze the structural features that influence their ability to donate protons (H⁺ ions). Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the reasoning:
Step 1: Identify the Compounds
We have three compounds to analyze:
1. (I) CH₃-N-CH₂-OH
2. (II) CH₃-NH-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-OH
3. (III) (CH₃)₃N⁺-CH₂-CH₂-OH
Step 2: Understand the Role of Proximity
The acidity of alcohols and amines is influenced by the proximity of the nitrogen atom (N) to the hydroxyl group (OH). The closer the nitrogen is to the hydroxyl group, the more it can stabilize the negative charge that forms when the hydroxyl group donates a proton.
Step 3: Analyze Each Compound
1. Compound I (CH₃-N-CH₂-OH):
- The nitrogen (N) is directly adjacent to the hydroxyl group (OH). The lone pair on nitrogen can interact with the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group, making it less likely to release H⁺. Thus, this compound has the least acidity.
2. Compound II (CH₃-NH-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-OH):
- Here, the nitrogen is three CH₂ groups away from the hydroxyl group. The increased distance reduces the interaction between the lone pair on nitrogen and the hydroxyl group, allowing for a slightly greater tendency to donate H⁺ compared to Compound I. Therefore, this compound has moderate acidity.
3. Compound III ((CH₃)₃N⁺-CH₂-CH₂-OH):
- In this case, the nitrogen is positively charged (ammonium ion). The positive charge on nitrogen is electron-withdrawing, which increases the acidity of the hydroxyl group by stabilizing the negative charge that forms when H⁺ is released. Thus, this compound has the highest acidity.
Step 4: Arrange in Decreasing Order of Acidity
Based on the analysis:
- Most Acidic: (III) (CH₃)₃N⁺-CH₂-CH₂-OH
- Moderately Acidic: (II) CH₃-NH-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-OH
- Least Acidic: (I) CH₃-N-CH₂-OH
Final Order of Acidity
The final order of acidity in decreasing order is:
(III) > (II) > (I)
We have three compounds to analyze:
1. (I) CH₃-N-CH₂-OH
2. (II) CH₃-NH-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-OH
3. (III) (CH₃)₃N⁺-CH₂-CH₂-OH
The acidity of alcohols and amines is influenced by the proximity of the nitrogen atom (N) to the hydroxyl group (OH). The closer the nitrogen is to the hydroxyl group, the more it can stabilize the negative charge that forms when the hydroxyl group donates a proton.
1. Compound I (CH₃-N-CH₂-OH):
- The nitrogen (N) is directly adjacent to the hydroxyl group (OH). The lone pair on nitrogen can interact with the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group, making it less likely to release H⁺. Thus, this compound has the least acidity.
- Here, the nitrogen is three CH₂ groups away from the hydroxyl group. The increased distance reduces the interaction between the lone pair on nitrogen and the hydroxyl group, allowing for a slightly greater tendency to donate H⁺ compared to Compound I. Therefore, this compound has moderate acidity.
- In this case, the nitrogen is positively charged (ammonium ion). The positive charge on nitrogen is electron-withdrawing, which increases the acidity of the hydroxyl group by stabilizing the negative charge that forms when H⁺ is released. Thus, this compound has the highest acidity.
Based on the analysis:
- Most Acidic: (III) (CH₃)₃N⁺-CH₂-CH₂-OH
- Moderately Acidic: (II) CH₃-NH-CH₂-CH₂-CH₂-OH
- Least Acidic: (I) CH₃-N-CH₂-OH
The final order of acidity in decreasing order is:
(III) > (II) > (I)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTHBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTHEXERCISE - Exercise II
15 Videos
- ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTHBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTHEXERCISE - Exercise III
14 Videos
- CONCENTRATION TERMSBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - CONCENTRATION TERMSEXERCISE - Exercise Jee-Advance
3 Videos
- AIIMS 2019BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - AIIMS 2019EXERCISE - CHEMISTRY
40 Videos
Similar Questions
Write decreasing order of basic strength of following:

View SolutionIn given reaction gas liberated is/are
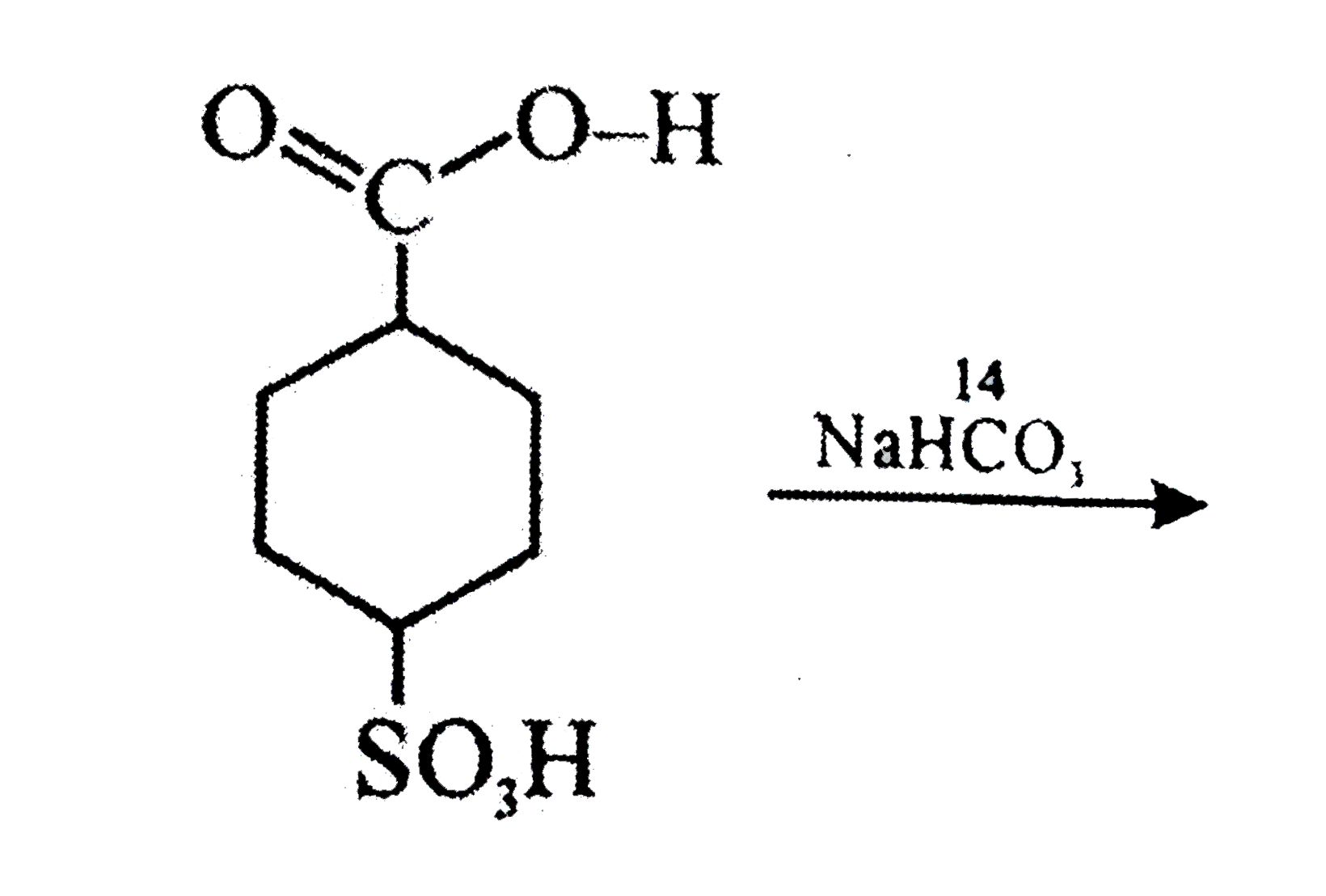
View SolutionCalculate the molarity of water if its density is 1000kgm−3
View SolutionSelect the correct statements
View SolutionCH_(3)CH_(2)C = N overset (X) to CH_(3)CH_(2)OH The compound X is
View SolutionGive the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i)C6H5−CH2−CH2−OH (ii)CH3−CH3∣C∣CH3−CH2−CH2−OH
(iii)[(CH3)2CH]3COH. (iv)CH3−CH∣OH−CH2−CH2−O−CH2CH3
(v)CH3−CH2−CH∣Cl−CH∣CH3−CH3∣C∣OH−CH3 (vi)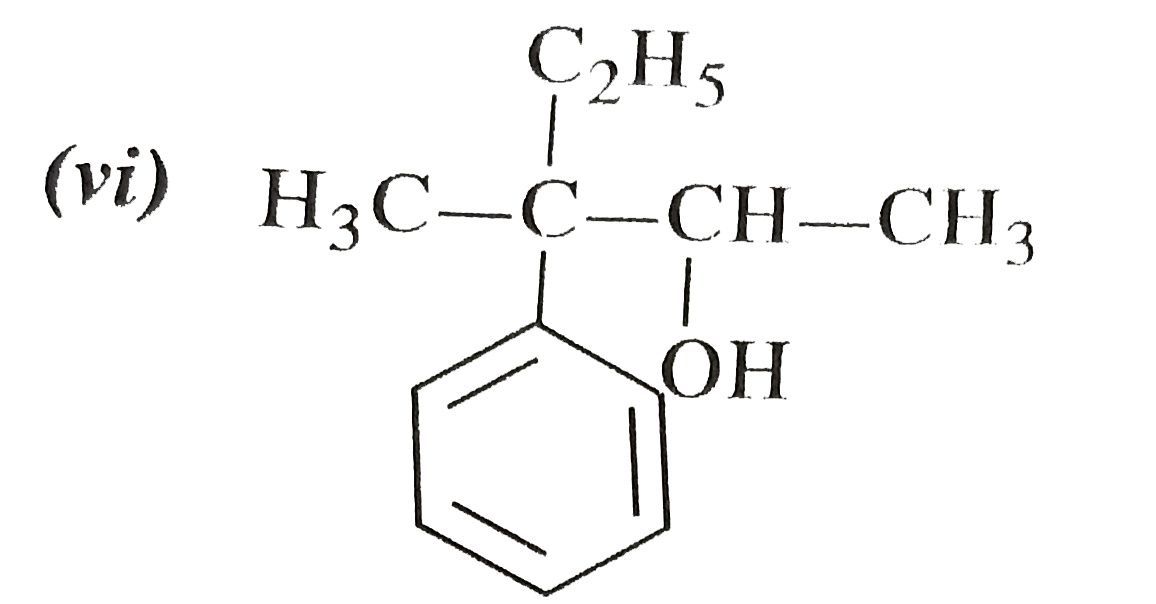
(vii)(CH3)3COH (viii)CH3−CH∣CH3−CH∣OH−CH2−CH∣CH3−CH3
(ix) CH2OH |CH2−CH2−CH−CH−CH−CH3 | | CH2Cl CH3, (x) CH3−C=C−CH2OH | | CH3Br
(xi) CH2=CH−CH∣OH−CH2−CH3, (xii) CH2OH |CH3−CH−CH2−CH−CH−CH3 | | CH3 OH
View SolutionAmong these chain isomers are : (I) CH_(3)-CH_(3)-CH_(2)-CH_(2)-OH (II) CH_(3)-CH_(2)-underset(OH)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(3) (III) CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(OH)overset(|)(C)-CH_(3)
View SolutionI. CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH
II. CH3−CH2−CH∣OH−CH3
III. CH3−CH3∣C∣OH−CH3
IV. CH3−CH∣CH3−CH2−OH
V. CH3−CH2−O−CH2−CH3
VI. CH3−O−CH2−CH2−CH3
VII. CH3−O−CH∣CH3−CH3
Which of the above compounds form pairs of metamers ?
View SolutionI. CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH
II. CH3−CH2−CH∣OH−CH3
III. CH3−CH3∣C∣OH−CH3
IV. CH3−CH∣CH3−CH2−OH
V. CH3−CH2−O−CH2−CH3
VI. CH3−O−CH2−CH2−CH3
VII. CH3−O−CH∣CH3−CH3
Identify the pairs of compounds which are functional group isomers
View SolutionI. CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH
II. CH3−CH2−CH∣OH−CH3
III. CH3−CH3∣C∣OH−CH3
IV. CH3−CH∣CH3−CH2−OH
V. CH3−CH2−O−CH2−CH3
VI. CH3−O−CH2−CH2−CH3
VII. CH3−O−CH∣CH3−CH3
Identify the pairs of compounds that represents position isomerism.
View SolutionI. CH_(3) - CH_(2) - CH_(2) - CH_(2) - OH II. CH_(3) - CH_(2) - underset(OH)underset(|)(CH) - CH_(3) III. CH_(3) - underset(OH) underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C) - CH_(3) IV. CH_(3) - underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH) - CH_(2) - OH V. CH_(3) - CH_(2) - O - CH_(2) - CH_(3) VI. CH_(3) - O - CH_(2) - CH_(2) - CH_(3) VII. CH_(3) - O - underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH) - CH_(3) Identify the pair of compounds that represents chain isomerism
View SolutionArrange the following compounds in decreasing order fo solubility and boiling point : (i) CH_(3)CH_(2)OH,CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)OH,CH_(3)CH_(2)CH_(2)CH_(2)OH
View SolutionArrange the following acid in decreasing order of their acidic strength : (I) CH_(3)-OH (II) CH_(3)CH_(2)-OH (III) CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(CH)-OH (IV) CH_(3)-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C)-OH
View SolutionArrange the compounds in order of decreasing acidic strength :
(I) ClCH2−CH2−OH
(II) Cl2CH−CH2−OH
(III) Cl−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH
(IV) CH3−CH2−CH2−OH
View SolutionWhich of the following compounds gives fastest reaction with HBr and why?
(i) (CH3)3_OH (ii) CH3CH2CH2OH
(iii) CH3OH∣CHCH3 (iv) CH3CH3∣CHCH2OH
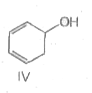
View SolutionWhich of the following is the correct ease of dehydration ?
I CH3−CH2−CH2−CH2∣OH , II CH3−CH2−OH∣CH−CH3 , III CH2=CH−OH∣CH−CH3, IV
View Solution

