1200gm aqueous solution contains 200gm calcium bromide
(CaBr2). Calculate molality of solution
The correct Answer is:1
To calculate the molality of the solution, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify the mass of the solution and the solute
We are given that the total mass of the aqueous solution is 1200 grams, and the mass of the solute (calcium bromide, CaBr₂) is 200 grams.
Step 2: Calculate the mass of the solvent
To find the mass of the solvent, we subtract the mass of the solute from the total mass of the solution.
Mass of solvent=Mass of solution−Mass of solute
Mass of solvent=1200g−200g=1000g
Step 3: Convert the mass of the solvent to kilograms
Since molality is defined in terms of kilograms of solvent, we convert the mass of the solvent from grams to kilograms.
Mass of solvent in kg=1000g1000=1kg
Step 4: Calculate the number of moles of the solute
To find the number of moles of calcium bromide (CaBr₂), we need to use its molar mass. The molar mass of CaBr₂ can be calculated as follows:
- Molar mass of Ca = 40 g/mol
- Molar mass of Br = 80 g/mol (since there are 2 bromine atoms, we multiply by 2)
Molar mass of CaBr₂=40+(2×80)=40+160=200g/mol
Now, we can calculate the number of moles of CaBr₂:
Number of moles of CaBr₂=Mass of soluteMolar mass of solute=200g200g/mol=1mol
Step 5: Calculate the molality of the solution
Now that we have the number of moles of the solute and the mass of the solvent in kilograms, we can calculate the molality (m) of the solution using the formula:
Molality (m)=Number of moles of soluteMass of solvent in kg=1mol1kg=1molal
Final Answer
The molality of the solution is 1 molal.
---
We are given that the total mass of the aqueous solution is 1200 grams, and the mass of the solute (calcium bromide, CaBr₂) is 200 grams.
To find the mass of the solvent, we subtract the mass of the solute from the total mass of the solution.
Mass of solvent=1200g−200g=1000g
Since molality is defined in terms of kilograms of solvent, we convert the mass of the solvent from grams to kilograms.
To find the number of moles of calcium bromide (CaBr₂), we need to use its molar mass. The molar mass of CaBr₂ can be calculated as follows:
- Molar mass of Br = 80 g/mol (since there are 2 bromine atoms, we multiply by 2)
Now that we have the number of moles of the solute and the mass of the solvent in kilograms, we can calculate the molality (m) of the solution using the formula:
The molality of the solution is 1 molal.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CONCENTRATION TERMSBook:ALLENChapter: CONCENTRATION TERMSExercise:Exercise S - II
Explore 10 Videos
- CONCENTRATION TERMSBook:ALLENChapter: CONCENTRATION TERMSExercise:Exercise O-I
Explore 33 Videos
- CONCENTRATION TERMSBook:ALLENChapter: CONCENTRATION TERMSExercise:Basic Exercise
Explore 14 Videos
- ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTHBook:ALLENChapter:ACIDIC STRENGTH & BASIC STRENGTHExercise:Exercise V
Explore 16 Videos
Similar Questions
What volume of 0.2 M NaOH (in ml) solution should be mixed to 500 ml of 0.5 M NaOH solution so that 300 ml of final solution is completely neutralised by 20 ml of 2MH3PO4 solution [Assuming 100% dissociation]
View Solution125 ml of 8% w/v NaOH solution (sp. gravity 1) is added to 125 ml of 10% w/v HCl solution. The nature of resultant solution would be ____
View SolutionComplete the following table (all are aqueous solution)
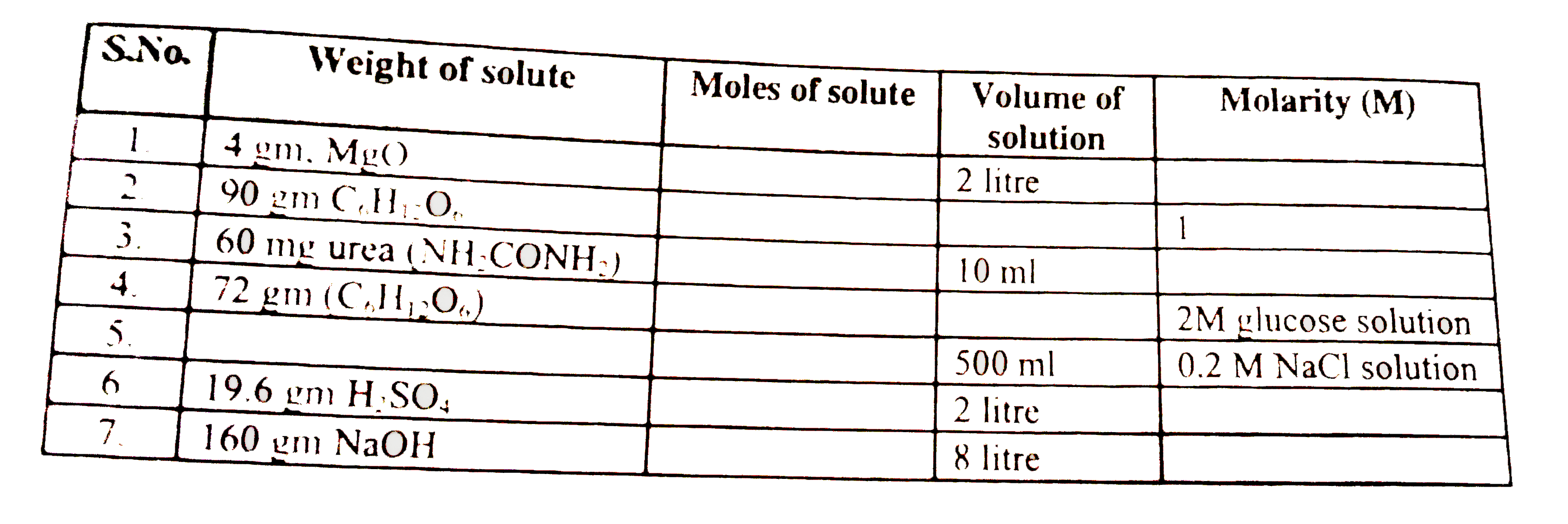
View SolutionIn the following compounds
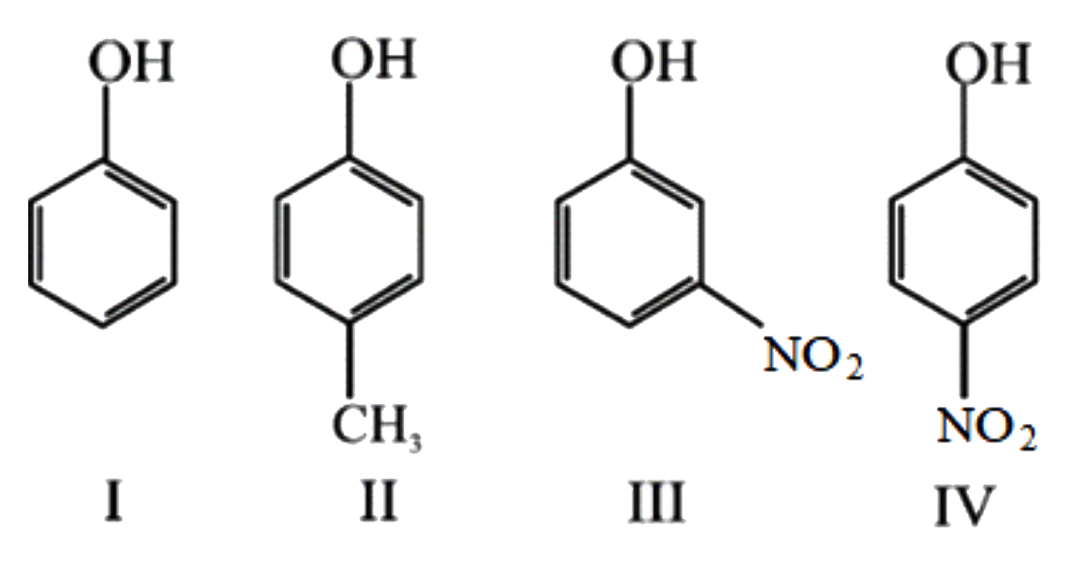
The order of acidity is
View SolutionAn electrolyte AB is 50% ionised in aqueous solution. Calculate the freezing point of 1 molal aqueous solution.
View SolutionA solution is made by dissolving CaBr2 in water (solvent) such that mass fraction of solute and solvent is same in the solution. The molality of solution is :
View SolutionCalculate molality of one litre of solution containing 200 gm CaBr_(2) . Given density of solution equal to 1.0 gm/ml. (Atomic mass of Ca = 40, Br = 80)
View SolutionA solution is made by dissolving CaBr2 in water (solvent) such that mass fraction of solute and solvent is same in the solution. The molality of solution is :[Atomic mass of Br=80,Ca=40]
View SolutionThe relative lowering of vapour pressure of an aqueous solution containing a non-volatile solute, is 0.0125. The molality of the solution is
View Solution1000 ml solution of CaBr2 contain 200 gm CaBr2 if density of solution is 1200kg/m3. Calculate molarity of solution
View SolutionCalculate mole fraction of solute in its 2 molal aqueous solution .
View SolutionDepression in freezing point of 0.01 molal aqueous HCOOH solution is 0.02046^(@)C . 1 molal aqueous urea solution freezes at -1.86^@ C . Assuming molality equal to molarity , calculate the pH of HCOOH solution.
View SolutionCalculate the mole fraction of the solute in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution.
View SolutionA: 1M solution and 1 molal solution contain same mass of solute. R: 1M and 1m aqueous solution are equally concentrated.
View SolutionCompare the lowering of vapour pressure of equimolar calcium bromide and glucose in aqueous solutions.
View Solutionब्रोमाइड आयन युक्त जलीय घोल में से निम्न में कौन Br2 विस्थापित करेगा
View Solution
