Cyclohexanol is dehydrated to cyclohexene on heating with conc. H2SO4. If the yeild of this reaction is 75% ,how much cyclohexene will be obtained from 100 g of cyclohexanol ?
C6H12Oconc.H2SO4−−−−−−→C6H10
The correct Answer is:61.5 gm
To solve the problem of how much cyclohexene will be obtained from 100 g of cyclohexanol with a yield of 75%, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Write the balanced chemical equation
The dehydration of cyclohexanol (C6H11OH) to cyclohexene (C6H10) can be represented as:
C6H11OHconc. H2SO4−−−−−−−→C6H10+H2O
Step 2: Calculate the molar mass of cyclohexanol
The molar mass of cyclohexanol (C6H11OH) can be calculated as follows:
- Carbon (C): 12 g/mol × 6 = 72 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1 g/mol × 12 = 12 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16 g/mol × 1 = 16 g/mol
Adding these together:
72+12+16=100 g/mol
Step 3: Calculate the number of moles of cyclohexanol
Given that we have 100 g of cyclohexanol, we can calculate the number of moles:
Number of moles=massmolar mass=100 g100 g/mol=1 mole
Step 4: Determine the theoretical yield of cyclohexene
From the balanced equation, we see that 1 mole of cyclohexanol produces 1 mole of cyclohexene. Therefore, the theoretical yield of cyclohexene in grams can be calculated by finding its molar mass:
- Molar mass of cyclohexene (C6H10):
- Carbon (C): 12 g/mol × 6 = 72 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1 g/mol × 10 = 10 g/mol
Adding these together:
72+10=82 g/mol
Since we have 1 mole of cyclohexanol, the theoretical yield of cyclohexene is:
1 mole×82 g/mol=82 g
Step 5: Calculate the experimental yield using the percentage yield
The experimental yield can be calculated using the percentage yield formula:
Experimental yield=(Percentage yield100)×Theoretical yield
Substituting the values:
Experimental yield=(75100)×82 g=0.75×82=61.5 g
Conclusion
The amount of cyclohexene that will be obtained from 100 g of cyclohexanol is 61.5 grams.
---
The dehydration of cyclohexanol (C6H11OH) to cyclohexene (C6H10) can be represented as:
C6H11OHconc. H2SO4−−−−−−−→C6H10+H2O
The molar mass of cyclohexanol (C6H11OH) can be calculated as follows:
- Carbon (C): 12 g/mol × 6 = 72 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1 g/mol × 12 = 12 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16 g/mol × 1 = 16 g/mol
72+12+16=100 g/mol
Given that we have 100 g of cyclohexanol, we can calculate the number of moles:
Number of moles=massmolar mass=100 g100 g/mol=1 mole
From the balanced equation, we see that 1 mole of cyclohexanol produces 1 mole of cyclohexene. Therefore, the theoretical yield of cyclohexene in grams can be calculated by finding its molar mass:
- Molar mass of cyclohexene (C6H10):
- Carbon (C): 12 g/mol × 6 = 72 g/mol
- Hydrogen (H): 1 g/mol × 10 = 10 g/mol
72+10=82 g/mol
1 mole×82 g/mol=82 g
The experimental yield can be calculated using the percentage yield formula:
Experimental yield=(Percentage yield100)×Theoretical yield
Experimental yield=(75100)×82 g=0.75×82=61.5 g
The amount of cyclohexene that will be obtained from 100 g of cyclohexanol is 61.5 grams.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- MOLE CONCEPTBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - MOLE CONCEPTEXERCISE - S-II
18 Videos
- MOLE CONCEPTBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - MOLE CONCEPTEXERCISE - O-I
45 Videos
- MOLE CONCEPTBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - MOLE CONCEPTEXERCISE - Basic Exercise
29 Videos
- METALLURGYBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - METALLURGYEXERCISE - EXERCISE-05 [B]
26 Videos
- p-Block Element BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - p-Block Element EXERCISE - All Questions
20 Videos
समान प्रश्न
ज्ञान जांच
Acetone on heating with conc. H2SO4 mainly gives
AmesityleneBmesityl oxideCtolueneDxylene.Acetone on heating with conc. H2SO4 mainly gives
AmesityleneBmesityl oxideCtolueneDxylene.Acetone on heating with conc. H2SO4 mainly gives
AmesityleneBmesityl oxideCtolueneDxylene.
When aluminium is heated with conc. H2SO4
View SolutionDuring the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with conc. H2SO4, the initiating step is :
View SolutionThe dehydrated product obtained when cane sugar reacts with conc. H2SO4.
View SolutionMethanoic acid is heated with conc. H2SO4, to form
View SolutionEthylene glycol
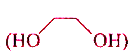 on heating with conc. H2SO4 gives mainly :
on heating with conc. H2SO4 gives mainly :
View Solution


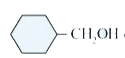 on dehydration with conc.
on dehydration with conc.