Which of the following reactions will result in the formation of a chiral centre in the product?
CH3CH=CHCH3+Hbr→
CH3CH=CH2+HOBr→
CH3CH2CH=CH2+HbrH2O2−−→
CH3CH2CH=CH2+Hbr→
The correct Answer is:A, B, D
To determine which of the given reactions will result in the formation of a chiral center in the product, we need to analyze each reaction step by step.
Step 1: Understanding Chiral Centers
A chiral center (or chiral carbon) is a carbon atom that is attached to four different groups. This asymmetry is what gives rise to chirality, meaning the molecule can exist in two non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers).
Step 2: Analyzing Each Reaction
1. Reaction A:
- The alkene reacts with HBr.
- According to Markovnikov's rule, the bromine (Br) will attach to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
- If both carbons have the same number of hydrogens, Br can attach to either carbon.
- In this case, we can see that one of the carbons will end up with four different groups attached (the other carbon will have two hydrogens, one bromine, and one carbon chain).
- Conclusion: This reaction will form a chiral center.
2. Reaction B:
- The alkene reacts with OH⁻ and Br⁺.
- Again, applying Markovnikov's rule, OH⁻ will go to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
- The product will have a carbon bonded to OH, Br, one hydrogen, and a carbon chain, resulting in four different groups.
- Conclusion: This reaction will also form a chiral center.
3. Reaction C:
- The alkene reacts with HBr in the presence of H₂O₂.
- Here, the anti-Markovnikov rule applies, meaning Br⁻ will attach to the carbon with more hydrogens.
- The resulting product will have one carbon bonded to two hydrogens and Br, and the other carbon will have two hydrogens, resulting in no chiral center.
- Conclusion: This reaction will not form a chiral center.
4. Reaction D:
- The alkene reacts with HBr.
- Following Markovnikov's rule, Br will attach to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
- The product will have a carbon bonded to Br, one hydrogen, and two different carbon chains, resulting in four different groups.
- Conclusion: This reaction will form a chiral center.
Final Answer
The reactions that will result in the formation of a chiral center are:
- Option A
- Option B
- Option D
A chiral center (or chiral carbon) is a carbon atom that is attached to four different groups. This asymmetry is what gives rise to chirality, meaning the molecule can exist in two non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers).
1. Reaction A:
- The alkene reacts with HBr.
- According to Markovnikov's rule, the bromine (Br) will attach to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
- If both carbons have the same number of hydrogens, Br can attach to either carbon.
- In this case, we can see that one of the carbons will end up with four different groups attached (the other carbon will have two hydrogens, one bromine, and one carbon chain).
- Conclusion: This reaction will form a chiral center.
- The alkene reacts with OH⁻ and Br⁺.
- Again, applying Markovnikov's rule, OH⁻ will go to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
- The product will have a carbon bonded to OH, Br, one hydrogen, and a carbon chain, resulting in four different groups.
- Conclusion: This reaction will also form a chiral center.
- The alkene reacts with HBr in the presence of H₂O₂.
- Here, the anti-Markovnikov rule applies, meaning Br⁻ will attach to the carbon with more hydrogens.
- The resulting product will have one carbon bonded to two hydrogens and Br, and the other carbon will have two hydrogens, resulting in no chiral center.
- Conclusion: This reaction will not form a chiral center.
- The alkene reacts with HBr.
- Following Markovnikov's rule, Br will attach to the carbon with fewer hydrogens.
- The product will have a carbon bonded to Br, one hydrogen, and two different carbon chains, resulting in four different groups.
- Conclusion: This reaction will form a chiral center.
The reactions that will result in the formation of a chiral center are:
- Option A
- Option B
- Option D
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE EXERCISE - EXERCISE-3
99 Videos
- ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE EXERCISE - EXERCISE-4(A)
10 Videos
- ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKENE, ALKANE & ALKYNE EXERCISE - EXERCISE-1
119 Videos
- AIIMS 2019BOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - AIIMS 2019EXERCISE - CHEMISTRY
40 Videos
- ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDEBOOK - ALLENCHAPTER - ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDEEXERCISE - EXERCISE-05 (B)
35 Videos
Similar Questions
Statement-I : Of two isomeric alkennes shown,
_E01_041_Q01.png) II is more stable than I.
II is more stable than I.
Because
Statement-II : The alkene (II) has sp^(2)-hybridlzed carbons.
View Solution_E01_062_Q01.png)
What are X and Y in above reaction.
View SolutionThe smallest alkane which can shown optical isomerism possesses:
View SolutionSelect the correct statements
View SolutionMonochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields
View SolutionIn which of the following reactions, the product obtained is chiral ?
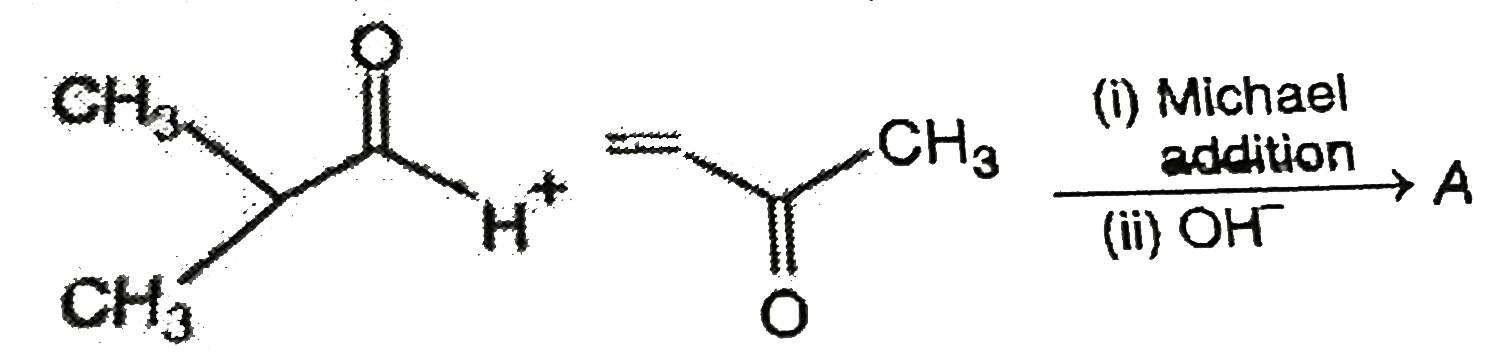
View SolutionHow many chiral centres are possible for the product of following reaction?
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions wil give 2^(@) chiral alcohol as major product ?
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions results in the formation of a pair of diastereomers?
View SolutionWhich of the following reaction will lead to creation of two chiral centres in the product?
View SolutionReaction which will produce chiral product :
View SolutionIn which reaction a chiral reactant is giving a chiral product.
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions will not result in the formation of anisole?
View SolutionOf the Chiral Center S_N1 The reaction results in the following:
View SolutionAt the Chiral Center S_N1 As a result of the reaction -
View SolutionIn an SN1 reaction on chiral centres, there is
View Solution

