Assertion : Electric field outside the conducting wire which carreis a constant is zero.
Reason : Net charge on conducting wire is zero.
If both Assertion & Reason are True & the Reason is a correct explanantion of the Assertion
If both Assertion & Reason True but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion
If Assertion is True but the Reason is False
If both Assertion & Reason are False.
The correct Answer is:1
To analyze the assertion and reason provided in the question, we can break down the concepts step by step.
Step 1: Understanding the Assertion
The assertion states that the electric field outside a conducting wire carrying a constant current is zero.
- Explanation: When a conducting wire carries a constant current, the charges (usually electrons) within the wire are in motion. However, the wire itself remains electrically neutral overall, meaning that the number of positive charges (protons) is equal to the number of negative charges (electrons). Since there is no net charge outside the wire, the electric field outside the wire is zero.
Step 2: Understanding the Reason
The reason given is that the net charge on the conducting wire is zero.
- Explanation: In a conductor, when a current flows, the free electrons move, but they do not leave the conductor. The number of electrons (negative charges) moving in one direction is balanced by the positive charges (protons) that remain stationary. Therefore, the net charge remains zero, which is crucial for maintaining the electric field outside the wire at zero.
Step 3: Connecting Assertion and Reason
Now we need to connect the assertion and the reason to determine if the reason supports the assertion.
- Explanation: The assertion is true because the electric field outside the conducting wire is indeed zero when it carries a constant current. The reason is also true as the net charge on the conducting wire is zero. Since the reason correctly explains why the assertion is true, we can conclude that both the assertion and reason are correct, and the reason provides a valid explanation for the assertion.
Conclusion
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation for the assertion.
Final Answer
- Assertion: True
- Reason: True
- Explanation: The net charge on the conducting wire is zero, which leads to the electric field outside the wire being zero when it carries a constant current.
---
The assertion states that the electric field outside a conducting wire carrying a constant current is zero.
The reason given is that the net charge on the conducting wire is zero.
Now we need to connect the assertion and the reason to determine if the reason supports the assertion.
Both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation for the assertion.
- Assertion: True
- Reason: True
- Explanation: The net charge on the conducting wire is zero, which leads to the electric field outside the wire being zero when it carries a constant current.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Which of the following is / are correct about electric current ?
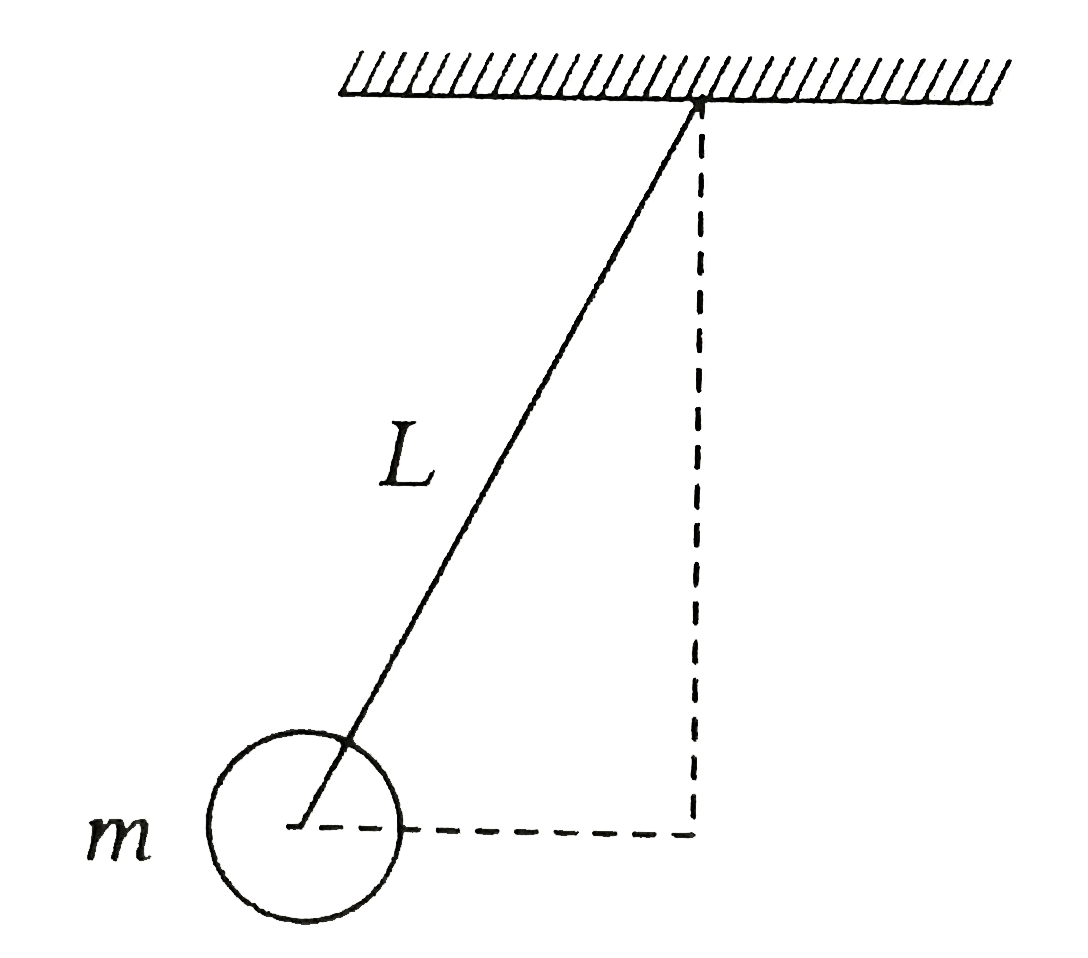
View SolutionA ball of mass (m) 0.5 kg is attached to the end of a string having length (L) 0.5m. The ball is rotated on a horizontal circular path about vertical axis. The maximum tension that the string can bear is 324 N. Find the maximum possible value of angular velocity of ball (in rads−1).
View SolutionA prism of refractive index n1 & another prism of reactive index n2 are stuck together without a gap as shown in the figure.The angle of the prisms are as shown. n1&n2depend onλ,the wavelength of light according to n1=1.20+10.8×104λ2&n2=1.45+1.80×104λ2 where λ is in nm.
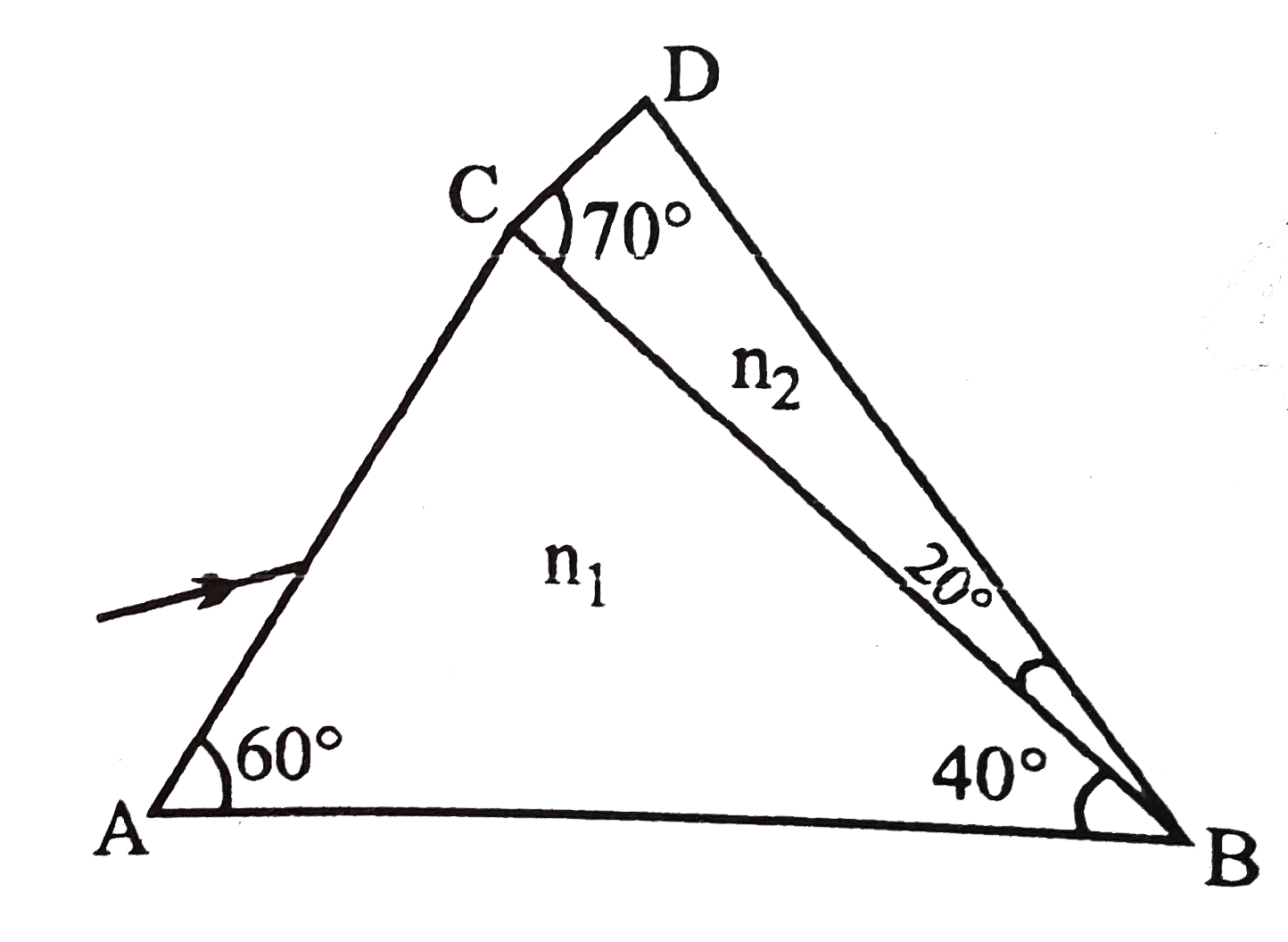
(i)Calculate the wavelength λ0for which rays incident at any angle on the interfaceBCpass through without bending at that interface.
View SolutionAssertion : Electric field outside the conducting wire accurate measurement. Reason : The potential gradient for a potentiometer of accurate measurement. Reason : Net charge on conducting wire is zero.
View SolutionAssertion : The connecting wires are made of copper.
Reason : The electrical conductivity of copper is high
View SolutionAssertion : Half of the ring is uniformly positively charged and other half uniformly negatively charged. Then, electric field is zero at centre. Then , electric field is zero at centre. Reason : At the centre of uniformly charged ring, electric field is zero.
View SolutionAssertion : For a non-uniformly charged thin circular ring with net charge zero, the electric field at any point on axis of the ring is zero. Reason : For a non-uniformly charged thin circular ring with net charge zero, the electric potential at each point on axis of the ring is zero.
View SolutionAssertion: Electric field inside a current carrying wire is zero. Reason: Net charge on the current carrying wire is non zero.
View Solutionआवेशित चालक गोलीय कोष के अंदर विद्युत् क्षेत्र की तीव्रता शून्य होती है | क्या इसके अंदर विद्युत् विभव भी शून्य होता है?
View SolutionAssertion (A): Bending of a conducting wire effects electrical resistance.
Reason( R): Resistance of a wire depends on resistivity of that material.
View Solutionकथन : धारावाही तार के अन्दर विद्युत क्षेत्र शून्य होता है।
कारण : तार में कुल आवेश अशून्य होता है।
View Solutionकथन : धारावाही तार जिसमें नियत धारा बह रही है, तार के बाहर विद्युत क्षेत्र शून्य होता है।
कारण : धारावाही तार पर कुल आवेश शून्य होता है।
View SolutionIs the electric field due to a system of charges with net charge zero necessarily zero?
View Solution(A): Electric field outside the wire due to a steady current through it is zero.
(R): Net charge present on current carrying wire is zero.
View SolutionAssertion: Sharper is the curvature of spot on a charged body lesser will be the surface density of charge at that point. Reason: Electric field is zero inside a charged non conducting sphere .
View SolutionAssertion : For a non-uniformly charged thin circular ring with net charge zero, the electric field at any point on axis of the ring is zero. Reason : For a non-uniformly charged thin circular ring with net charge zero, the electric potential at each point on axis of the ring is zero.
View Solution
