In the reaction N2(g)+O2(g)⇒2NO(g)at equilibrium the concentrations of N2,O2andNO are 0.25 , 0.05 and 1 M respectively . Calculate intial concentrations of N2andO2.
0.25 M , 0.35 M
0.05 M , 0.35 M
0.75 M , 0.55 M
0.75 M , 0.45 M
The correct Answer is:3
To solve the problem, we need to find the initial concentrations of N2 and O2 in the reaction:
N2(g)+O2(g)⇌2NO(g)
Given the equilibrium concentrations:
- (N2)=0.25M
- (O2)=0.05M
- (NO)=1M
Step 1: Set up the equilibrium expression
Let the initial concentrations of N2 and O2 be A and B respectively.
At equilibrium, we can express the changes in concentration as follows:
- Change in N2: −x
- Change in O2: −x
- Change in NO: +2x
Thus, we can write the equilibrium concentrations as:
- (N2)=A−x
- (O2)=B−x
- (NO)=2x
Step 2: Relate x to the concentration of NO
From the equilibrium concentration of NO:
2x=1M⟹x=0.5M
Step 3: Substitute x to find A
Using the equilibrium concentration of N2:
A−x=0.25M
Substituting x=0.5:
A−0.5=0.25⟹A=0.25+0.5=0.75M
Step 4: Substitute x to find B
Using the equilibrium concentration of O2:
B−x=0.05M
Substituting x=0.5:
B−0.5=0.05⟹B=0.05+0.5=0.55M
Final Answer
The initial concentrations are:
- (N2)=0.75M
- (O2)=0.55M
- (N2)=0.25M
- (O2)=0.05M
- (NO)=1M
Let the initial concentrations of N2 and O2 be A and B respectively.
- Change in N2: −x
- Change in O2: −x
- Change in NO: +2x
- (N2)=A−x
- (O2)=B−x
- (NO)=2x
From the equilibrium concentration of NO:
2x=1M⟹x=0.5M
Using the equilibrium concentration of N2:
A−x=0.25M
Substituting x=0.5:
A−0.5=0.25⟹A=0.25+0.5=0.75M
Using the equilibrium concentration of O2:
B−x=0.05M
Substituting x=0.5:
B−0.5=0.05⟹B=0.05+0.5=0.55M
The initial concentrations are:
- (N2)=0.75M
- (O2)=0.55M
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Which of the following statement is not correct from the point of view of molecular orbital ?
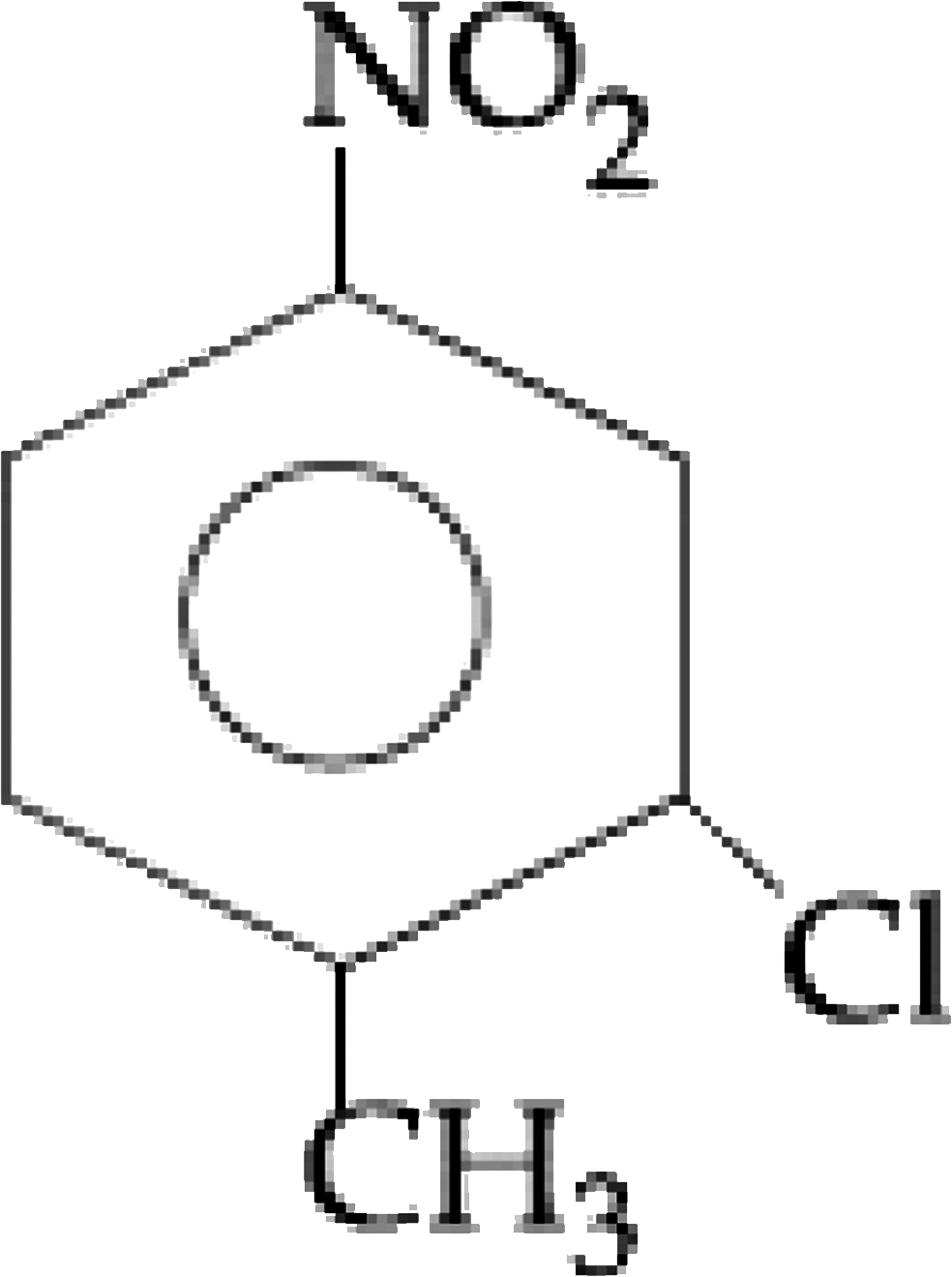
View SolutionThe correct IUPAC name of the following compound is :
View SolutionAt equilibrium, the concentrations of N2=3.0×10−3M,O2=4.2×10−3M, and NO=2.8×10−3M in a sealed vessel at 800K. What will be Kc for the reaction
N2(g)+O2(g)N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g)2NO(g)
View SolutionIn the equilibrium constant for N_(2)(g) + O_(2)(g)hArr2NO(g) is K, the equilibrium constant for (1)/(2) N_(2)(g) + (1)/(2)O_(2)(g)hArrNO(g) will be:
View SolutionConsider the following equilibrium
N2O4(g)⇔2NO2(g)
Then the select the correct graph , which shows the variation in concentratins of N2O4 Against concentrations of N2O_(4):
View SolutionAt 800 K in a sealed vessel for the equilibrium N_(2)(g) + O_(2) (g) hArr 2NO(g), the equilibrium concentrations of N_(2) (g), O_(2)(g) and NO(g) are respectively 0.36xx10^(-3) M, 4.41 xx 10^(-3) M and 1.4 xx 10^(-3) M. Calculate the value of K_(c) for the reaction NO(g) hArr 1//2 N_(2)(g) +1//2 O_(2) (g) at 800 K is :
View SolutionIf the equilibrium constant for
N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g) is K , the equilibrium
constant for 12N2(g)+12O2(g)⇔NO(g) will be
View SolutionAt the equilibrium of the reaction , N_(2)O_(4)(g)rArr2NO_(2)(g) , the observed molar mass of N_(2)O_(4) is 77.70 g . The percentage dissociation of N_(2)O_(4) is :-
View SolutionIf the equilibrium constant for
N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g) is K , the equilibrium
constant for 12N2(g)+12O2(g)⇔NO(g) will be
View SolutionIf the equilibrium constant for
N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g) is K,
the equilibrium constant for
12N2(g)+12O2(g)⇔NO(g) will be :
View SolutionThe reaction N2(g)+O2(g)→2NO(g) is endothermic. The forward reaction is
View SolutionAt equilibrium, the concentrations of N2=3.0×10−3M,O2=4.2×10−3M, and NO=2.8×10−3M in a sealed vessel at 800K. What will be Kc for the reaction
N2(g)+O2(g)N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g)2NO(g)
View Solutionयदि अभिक्रिया N2(g)+O2(g)↔2NO(g) के लिए साम्य स्थिरांक K हो तो 12N2(g)+12O2(g)↔NO(g) हेतु साम्य स्थिरांक होगा-
View SolutionIf the equilibrium constant for
N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g) is K , the equilibrium
constant for 12N2(g)+12O2(g)⇔NO(g) will be
View SolutionIn the equilibrium constant for N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g) is K, the equilibrium constant for 12N2(g)+12O2(g)⇔NO(g) will be:
View SolutionIf the equilibrium constant for, N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NOg is K, the equilibrium constant for 12N2(g)+12O2(g)⇔NOg will be
View Solution
