Suppose the acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface is 10ms−2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0ms−2. A passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship with a constant velocity. Neglect all other object in sky. Which part of figure best represent the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time?
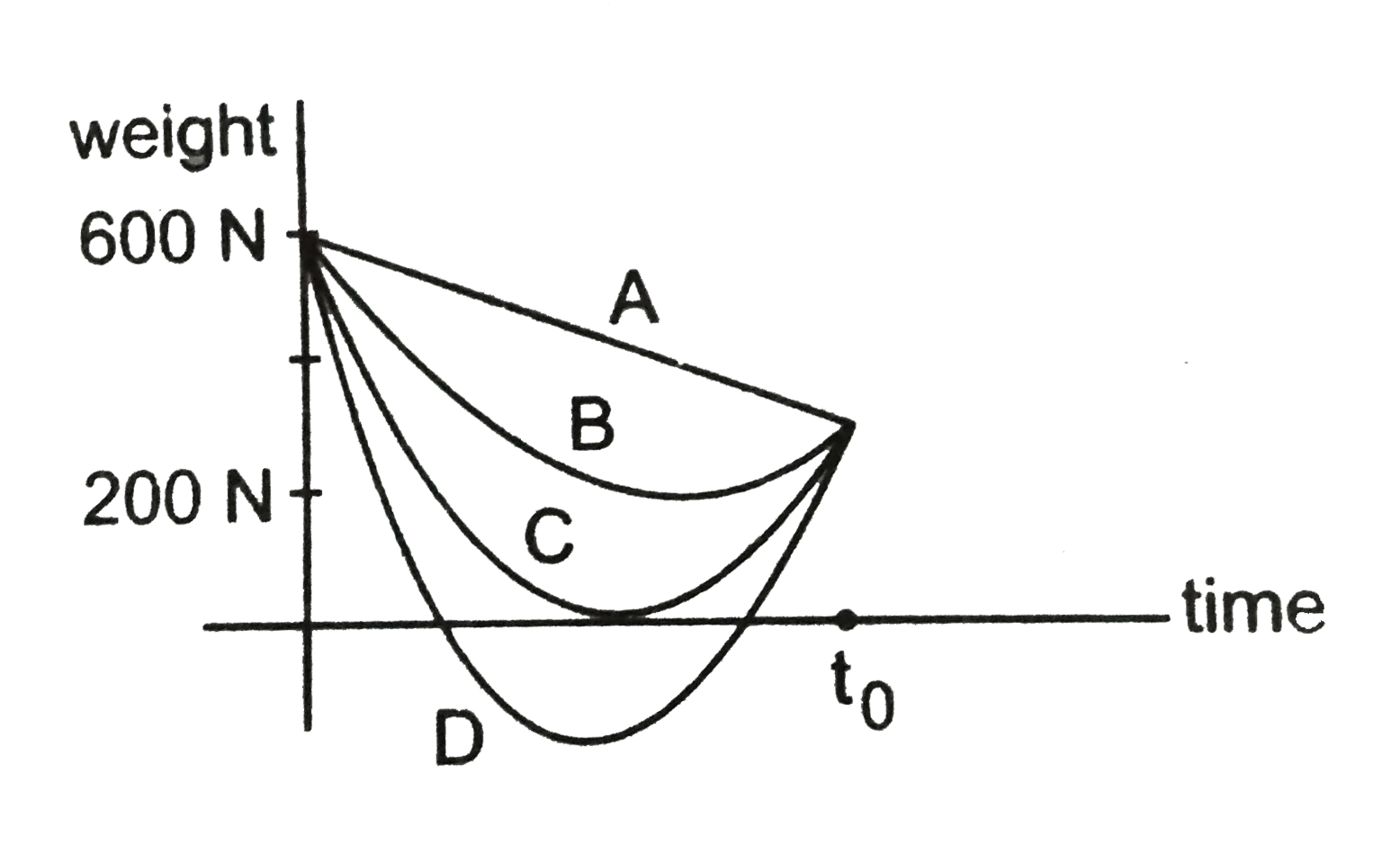
A
B
C
D
The correct Answer is:C
Step by step video solution for Suppose the acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface is 10ms^-2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0ms^-2. A passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship with a constant velocity. Neglect all other object in sky. Which part of figure best represent the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time? by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- GRAVITATIONBook:ALLENChapter:GRAVITATIONExercise:EXERCISE 2
Explore 26 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBook:ALLENChapter:GRAVITATIONExercise:EXERCISE 3
Explore 11 Videos
- GRAVITATIONBook:ALLENChapter:GRAVITATIONExercise:BOX-4
Explore 14 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:ALLENChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:subjective
Explore 14 Videos
- KINEMATICS-2DBook:ALLENChapter:KINEMATICS-2DExercise:Exercise (O-2)
Explore 46 Videos
Similar Questions
Two satellites of earth, S1andS2 , are moving in the same orbit. The mass of S1 is four times the mass of S2 . Which one of the following statements is true ?
View SolutionThe change in the value of acceleration of earth toward sun, when the moon coomes from the position of solar eclipse to the position on the other side of earth in line with sun is :
(mass of moon =7.36×1022 kg, orbital radius of moon =3.8×108 m.)
View SolutionThe mean radius of the earth's orbit round the sun is 1.5×1011 . The mean radius of the orbit of mercury round the sun is 6×1010m. The mercury will rotate around the sun in
View SolutionA prism of refractive index n1 & another prism of reactive index n2 are stuck together without a gap as shown in the figure.The angle of the prisms are as shown. n1&n2depend onλ,the wavelength of light according to n1=1.20+10.8×104λ2&n2=1.45+1.80×104λ2 where λ is in nm.
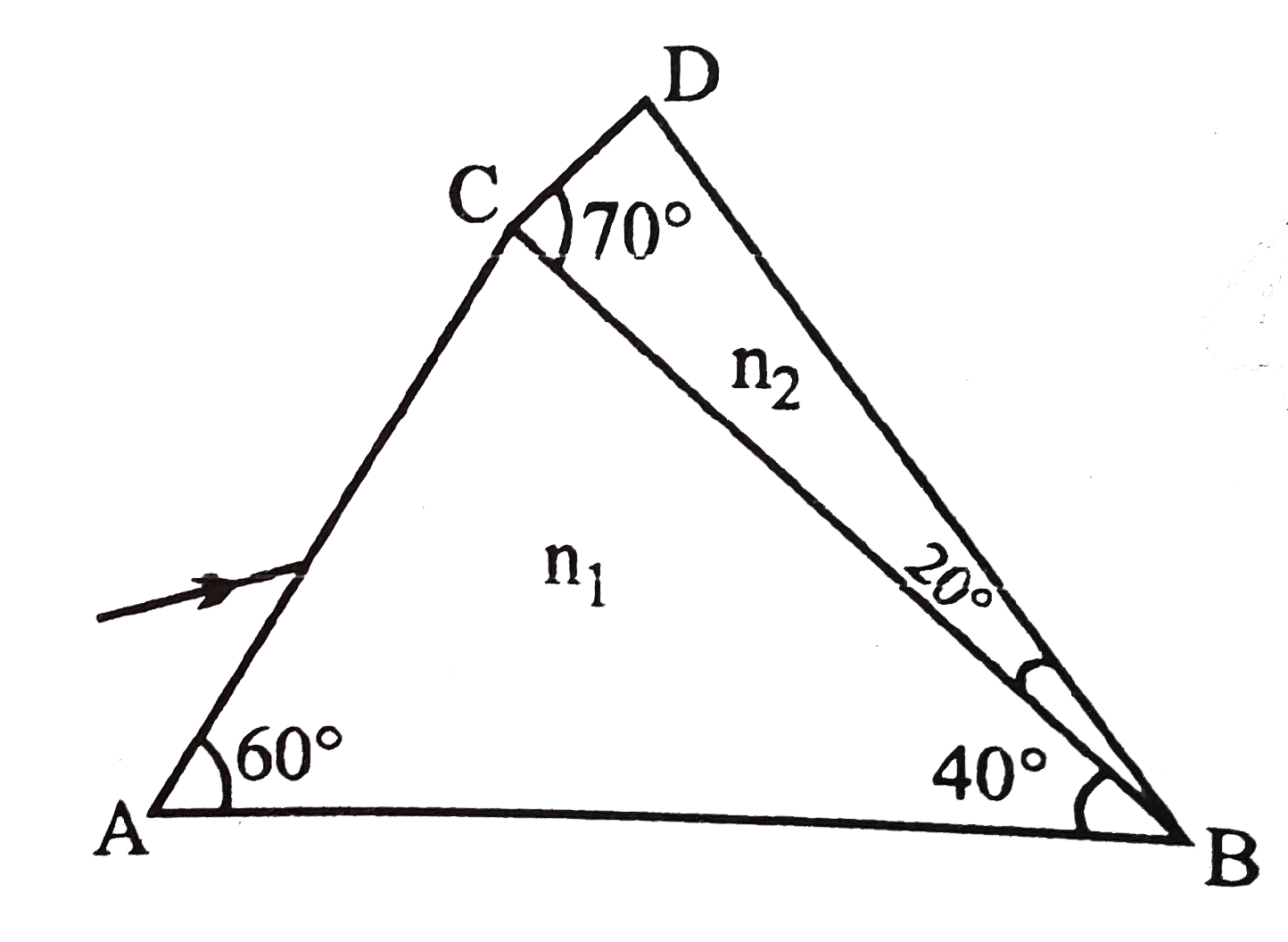
(i)Calculate the wavelength λ0for which rays incident at any angle on the interfaceBCpass through without bending at that interface.
View SolutionA particle is moving in the x-y plane. At certain instant of time, the components of its velocity and acceleration are as follows: vx=3ms−1,vy=4ms−1,ax=2ms−2anday=1ms−2. The rate of change of speed at this moment is
View SolutionSuppose the acceleratio due to gravity at thth's surface is 10ms−2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0ms−2. A passenger goes from the to the mars in a spacehip with a constant velocity. Neglect all other object in sky. Which part of figure best represent the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time?

View SolutionThe acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is 10ms−2 . The mass of the planet . Mars as compared to earth is 1/10 and radius is 1/2 . Determine the gravitational acceleration of a body on the surface on Mars .
View SolutionIf accleration due to gravity on the surface of earth is 10ms−2 and let acceleration due to gravitational acceleration at surface of another planet of our solar system be 5ms−2 An astronaut weighing 50kg on earth goes to this planet in spaceship with a constant velcity The weight of the astronaut with time of fiight is roughly given by
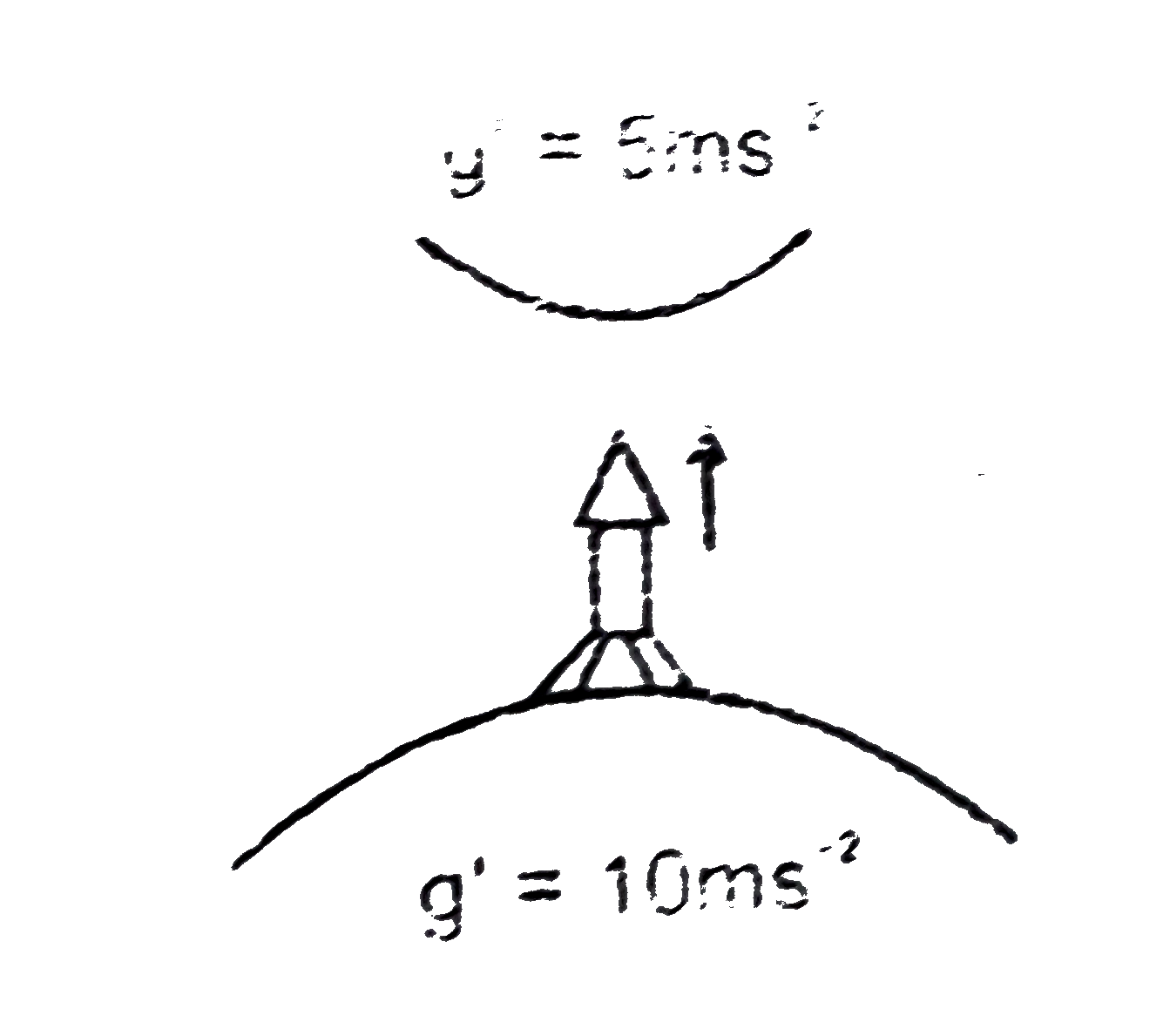 .
.
View Solutionमान ले कि पृथ्वी की सतह पर गुरूत्वीय त्वरण 10m/s2 है तथा मंगल की सतह पर इसका मान 4.0m/s2 है। एक 60kg द्रव्यमान वाला अंतरिक्ष-यात्री नियत चाल से गतिशील अंतरिक्ष - यान में पृथ्वी से मंगल की ओर जाता है। आकाश के अन्य पिंडों के प्रभाव को नगण्य मान ले। नीचे दिए गए चित्र का कौन- सा भाग अंतरिक्ष - यात्री के भार ( कुल गुरूतवीय बल) को समय के फलन के रूप में सबसे सटीक ढंग से निरूपित करता है।

View SolutionAssuming the mass of Earth to be ten times the mass of Mars, its radius to be twice the radius of Mars and the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth is 10 m//s^(2) . Then the accelration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is given by
View Solutionमाना कि पृथ्वी की सतह पर गुरूत्वीय त्वरण 10 m/स२ है मंगल की सतह पर 4.0 m/s2 है 60 kg है, मंगल पर जाता है। अंतरिक्ष में सभी वस्तुओं को नगण्य मानते हुए चित्र का कौनसा भाग यात्री के भार (कुल गुरूत्वीय बल) को समय के फलन के रूप में भली भांति दर्शाता है।
View SolutionSuppose the acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface is 10ms−2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0ms−2. A passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship with a constant velocity. Neglect all other object in sky. Which part of figure best represent the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time?

View SolutionSuppose, the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth.s surface is 10m/s2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0 m/s2. A 60 kg passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship moving with a constant velocity. Neglect all other objects in the sky. Which part of figure best represents the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time.
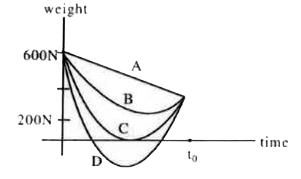
View SolutionSuppose, the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth.s surface is 10m/s2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0m/s2 . A 60 kg passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship moving with a constant velocity, Neglect all other objects in the sky. Which part of figure best represents the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time.
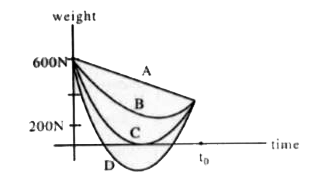
View SolutionSuppose, the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface is 10 m//s^(2) and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0 m//s^(2) . A 60 kg passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship moving with a constant velocity. Neglect all other objects in the sky. Which part of figure best represents the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time.
View SolutionSuppose, the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface is 10m/s2 and at the surface of Mars it is 4.0m/s2. A 60 kg passenger goes from the earth to the mars in a spaceship moving with a constant velocity. Neglect all other objects in the sky. Which part of figure best represents the weight (net gravitational force) of the passenger as a function of time.

View Solution
