A beam of light coming from infinty is passing through a biconvex lens having radius of curvature R=20cm of each surface, if focused at a certain distance from lens. Find the radius of curvature of emergent wave front from lens : (μ≤ns=1.5)
10cm
5cm
1cm
20cm
To solve the problem, we need to determine the radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront from a biconvex lens when a beam of light coming from infinity passes through it. Here are the steps to arrive at the solution:
Step 1: Understand the Lens and Given Data
We have a biconvex lens with:
- Radius of curvature of each surface, R=20cm
- Refractive index of the lens, μ=1.5
Step 2: Identify the Lens Formula
The lens formula relating the focal length F of the lens to the radii of curvature R1 and R2 is given by:
1F=(μ−1)(1R1−1R2)
Where:
- R1 is the radius of curvature of the first surface (convex, positive)
- R2 is the radius of curvature of the second surface (concave, negative)
Step 3: Assign Values to R1 and R2
For our biconvex lens:
- R1=+20cm (first surface)
- R2=−20cm (second surface)
Step 4: Substitute Values into the Lens Formula
Now substituting the values into the lens formula:
1F=(1.5−1)(120−1−20)
1F=0.5(120+120)
1F=0.5(220)=0.5(110)=0.510=120
Step 5: Calculate the Focal Length F
Now, taking the reciprocal to find F:
F=20cm
Step 6: Determine the Radius of Curvature of the Emergent Wavefront
The radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront from the lens is equal to the focal length of the lens. Therefore, the radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront is:
Remergent=F=20cm
Final Answer
The radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront from the lens is 20cm.
---
We have a biconvex lens with:
- Radius of curvature of each surface, R=20cm
- Refractive index of the lens, μ=1.5
The lens formula relating the focal length F of the lens to the radii of curvature R1 and R2 is given by:
1F=(μ−1)(1R1−1R2)
Where:
- R1 is the radius of curvature of the first surface (convex, positive)
- R2 is the radius of curvature of the second surface (concave, negative)
For our biconvex lens:
- R1=+20cm (first surface)
- R2=−20cm (second surface)
Now substituting the values into the lens formula:
1F=(1.5−1)(120−1−20)
1F=0.5(120+120)
1F=0.5(220)=0.5(110)=0.510=120
Now, taking the reciprocal to find F:
F=20cm
The radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront from the lens is equal to the focal length of the lens. Therefore, the radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront is:
Remergent=F=20cm
The radius of curvature of the emergent wavefront from the lens is 20cm.
Similar Questions
There is a glass (mu=1.5) biconvex lens of radius of curvature 5 cm and thickness of the lens is also 5 cm. An object is placed at a distance 20 cm from the front surface of lens. Locate its final image.
View Solutionएक उभयोत्तल लेंस (μ=1.5) के प्रत्येक तल की वक्रता त्रिज्या 20 सेमी है। लेंस की क्षमता है :
View Solutionयदि एक उभयोत्तल लेंस की वक्रता त्रिज्या R तथा फोकस दूरी f हैं। यदि f>r , लेंस के पदार्थ का अवर्तनांक μ हैं
View Solutionएक उभयोत्तल लेन्स के काँच का अपवर्तनांक μ=1.5 एवं इसके प्रत्येक पृष्ठ की वक्रता त्रिज्या 0.2 मीटर है लेन्स की क्षमता है
View Solution10 cm वक्रता त्रिज्या का एक समतल उत्तल लेंस (μ=1.5) की समतल सतह को रजित कर देते हैं। तो रजित करने के बाद लेंस की फोकस दूरी होगी :
View SolutionA biconvex lens (μ=1.5) has radius of curvature 20cm (both).
find its focal length.
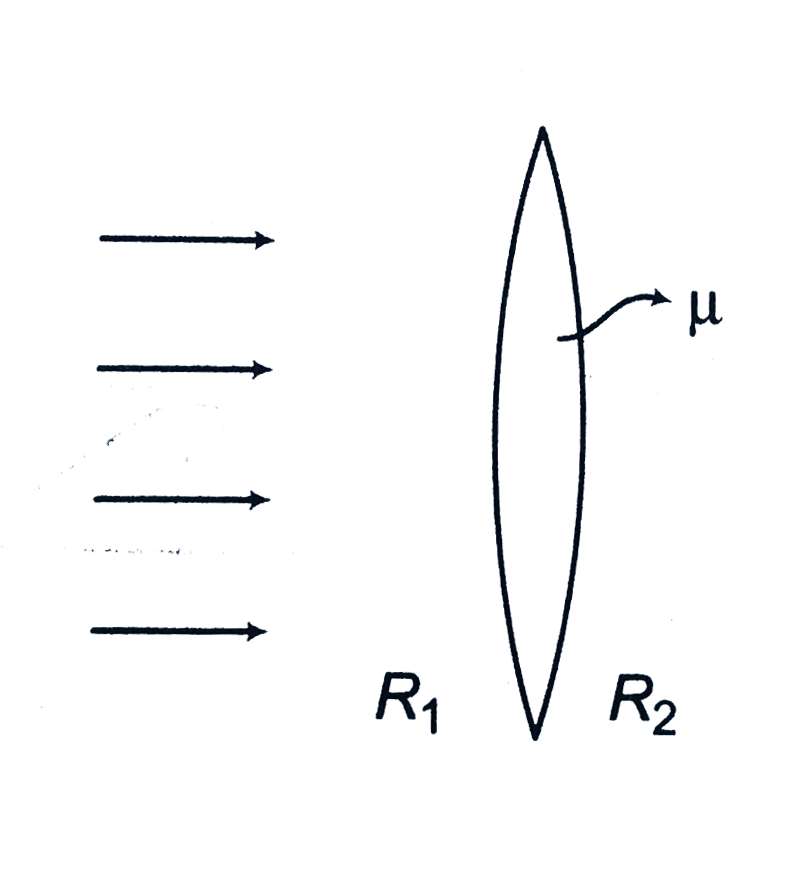
View SolutionA biconvex lens (mu=1.5) The radius of curvature of each plane is 20 cm. The capacity of the lens is
View SolutionFor the given figure, the radjus of curvature of each surface is R=16 cm . Rays of light parallel to the axis of lens from left of the lens traversing through the lens get focused at distance f from the lens. Find the value of magnitude of f . ( mu represents retive index and lens is silvered as shown) '(##CEN_KSR_PHY_JEE_C26_E01_023_Q09##)'
View Solution
