ಎಂಟು ಧಾತುಗಳ ಪರಮಾಣುಗಳಾದ A, B, C, D, E, F, G & H ಇವು ಒಂದೇ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆಯ ಇಲೆಕ್ಟ್ರಾನಿಕ್ ಕವಚಗಳನ್ನೂ ಬೇರೆ ಜೇರೆ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆಯ ಹೊರಕವಚಗಳನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿವೆ. A & G ಧಾತುಗಳು ಸೇರಿ ಅಯಾನಿಕ್ ಸಂಯುಕ್ತವನ್ನು ಉಂಟು ಮಾಡಿವೆ, ಹಾಗೆಯೇ ಆ ಸಂಯುಕ್ತವನ್ನು ಸಮುದ್ರದ ನೀರಿನಿಂದಲೂ ಪಡೆಯಬಹುದು, A & B ಧಾತುಗಳ ಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್ಗಳು ಪ್ರತ್ಯಾಮ್ಲೀಯ ಗುಣವನ್ನು, ಹಾಗೆಯೇ E & F ಧಾತುಗಳ ಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್ಗಳು ಆಮ್ಲೀಯ ಗುಣವನ್ನು, D ಧಾತುವಿನ ಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಕಡಿಮೆ ತಟಸ್ಥವಾಗಿದೆ. ಮೇಲಿನ ಮಾಹಿತಿಯನ್ನಾಧರಿಸಿ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆಗಳಿಗೆ ಉತ್ತರಿಸಿ. ಇವುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಯಾವ ಒಂದು ಧಾತುವು ಅರೆಲೋಹ ಅಥವಾ ಲೋಹಾಭವಾಗಿದೆ?
Step by step video solution for ಎಂಟು ಧಾತುಗಳ ಪರಮಾಣುಗಳಾದ A, B, C, D, E, F, G & H ಇವು ಒಂದೇ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆಯ ಇಲೆಕ್ಟ್ರಾನಿಕ್ ಕವಚಗಳನ್ನೂ ಬೇರೆ ಜೇರೆ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆಯ ಹೊರಕವಚಗಳನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿವೆ. A & G ಧಾತುಗಳು ಸೇರಿ ಅಯಾನಿಕ್ ಸಂಯುಕ್ತವನ್ನು ಉಂಟು ಮಾಡಿವೆ, ಹಾಗೆಯೇ ಆ ಸಂಯುಕ್ತವನ್ನು ಸಮುದ್ರದ ನೀರಿನಿಂದಲೂ ಪಡೆಯಬಹುದು, A & B ಧಾತುಗಳ ಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್ಗಳು ಪ್ರತ್ಯಾಮ್ಲೀಯ ಗುಣವನ್ನು, ಹಾಗೆಯೇ E & F ಧಾತುಗಳ ಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್ಗಳು ಆಮ್ಲೀಯ ಗುಣವನ್ನು, D ಧಾತುವಿನ ಆಕ್ಸೈಡ್ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಕಡಿಮೆ ತಟಸ್ಥವಾಗಿದೆ. ಮೇಲಿನ ಮಾಹಿತಿಯನ್ನಾಧರಿಸಿ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆಗಳಿಗೆ ಉತ್ತರಿಸಿ. ಇವುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಯಾವ ಒಂದು ಧಾತುವು ಅರೆಲೋಹ ಅಥವಾ ಲೋಹಾಭವಾಗಿದೆ? by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 10 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023ಟಾಪರ್ ಈ ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆಗಳನ್ನು ಪರಿಹರಿಸಿದ್ದಾರೆ
- ಆಮ್ಲ, ಪ್ರತ್ಯಾಮ್ಲಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಲವಣಗಳು - ಲವಣ, ಅವುಗಳ ಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಉಪಯೋಗಗಳುBOOK - OSWAAL PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ಆಮ್ಲ, ಪ್ರತ್ಯಾಮ್ಲಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಲವಣಗಳು - ಲವಣ, ಅವುಗಳ ಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಉಪಯೋಗಗಳುEXERCISE - EXERCISE
122 Videos
- ಕಾರ್ಬನ್ ಮತ್ತು ಅದರ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು, ಅನುರೂಪ ಶ್ರೇಣಿ ಮತ್ತು IUPAC ಹೆಸರುಗಳುBOOK - OSWAAL PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ಕಾರ್ಬನ್ ಮತ್ತು ಅದರ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು, ಅನುರೂಪ ಶ್ರೇಣಿ ಮತ್ತು IUPAC ಹೆಸರುಗಳುEXERCISE - EXAMPLE
6 Videos
ಸಮಾನ ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆಗಳು
P , Q ,R ಮತ್ತು S ದ್ರಾವಣಗಳ pH ಮೌಲ್ಯ ಕ್ರಮವಾಗಿ 7.8, 1.0,13.0 ಮತ್ತು 1.4 ಇವುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಹೆಚ್ಚಿನ H+ ಅಯಾನುಗಳ ಸಾರತೆ ಹೊಂದಿರುವ ದ್ರಾವಣವನ್ನು ತಿಳಿಸಿ ?
View Solutionಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಸಂಯುಕ್ತಗಳ ಹೆಸರನ್ನು ಬರೆಯಿರಿ.
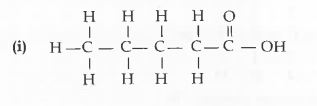
View SolutionIn Fig. 4.103, CD and GH are respectively the medians of ABC and EFG . If ABC~FEG , prove that (FIGURE) ADC~FHG (ii) CDGH=ABFE (iii) CDB~GHE
View Solutiona. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
View Solutionयदि, U={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h}, तो निम्नलिखित समुच्चयों के पूरक ज्ञात कीजिए।
A={d,e,f,g}
View SolutionIf U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h}, A = {b, d, f, h} and B = {a, d, e, h}, find the following sets.
B'
View SolutionIf U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h}, A = {b, d, f, h} and B = {a, d, e, h}, find the following sets.
(B')'
View SolutionIf U = {a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h} , find the complement of the following sets:
A= {a,b,c} , B ={d,e,f,g} , C ={a,c,eg}, D = {f,g,h,a}.
View SolutionIn Figure, CD and GH are respectively the medians of ABC and EFG . If ABC~FEG , prove that (i)ADC~FHG (ii)CDGH=ABFE (iii)CDB~GHE
View SolutionIn Figure, DEFG is a square and ∠BAC=90 . Prove that (i) A G F ~ D B G(ii)AGF~EFC (iii) D B G ~ E F C(iv)DE2=BDxEC
View SolutionABCD is a square E, F, G and H are points on AB, BC, CD and DA respectively, such that AE=BF=CG=DH. Prove that EFGH is square.
View SolutionIf U = {a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h}, find the complements of the following sets:B = {d,e,f,g}
View SolutionGiven that the universal set U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} and A = {a, b, c, d, e}, B = {a, c, e, g), C= {b, c, f, g} then determine
(A−B)−C
View SolutionGiven that the universal set U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h} and A = {a, b, c, d, e}, B = {a, c, e, g), C= {b, c, f, g} then determine
A−(B−C)
View SolutionLet A = { b,d,e,f }, B = { c,d,g,h} and C = {e,f,g,h} .Find :
A- B
View SolutionLet A = { b,d,e,f }, B = { c,d,g,h} and C = {e,f,g,h} .Find :
B-C
View Solution
