Gemmae are present in:
Some Gymnosperms
Some Liverworts
Mosses
Pteridophytes
To determine where gemmae are present, we need to analyze the characteristics of the groups mentioned in the question: Gymnosperms, Liverworts, Mosses, and Pteridophytes.
1. Understanding Gemmae:
- Gemmae are asexual reproductive structures found in certain plants. They are typically small, multicellular, and can develop into new individuals.
2. Identifying Plant Groups:
- Gymnosperms: These are seed-producing plants that bear naked seeds. They do not produce gemmae.
- Liverworts: These are non-vascular plants that belong to the group of Bryophytes. They reproduce asexually through structures called gemmae, which are formed in specialized cups on the thallus.
- Mosses: Also part of Bryophytes, mosses primarily reproduce through spores rather than gemmae, although some mosses can produce gemmae.
- Pteridophytes: This group includes ferns and does not typically produce gemmae; they reproduce via spores.
3. Conclusion:
- Among the four groups, gemmae are primarily associated with Liverworts. While some mosses may produce them, the most definitive presence of gemmae is in liverworts.
Final Answer:
Gemmae are present in Liverworts.
- Gemmae are asexual reproductive structures found in certain plants. They are typically small, multicellular, and can develop into new individuals.
- Gymnosperms: These are seed-producing plants that bear naked seeds. They do not produce gemmae.
- Liverworts: These are non-vascular plants that belong to the group of Bryophytes. They reproduce asexually through structures called gemmae, which are formed in specialized cups on the thallus.
- Mosses: Also part of Bryophytes, mosses primarily reproduce through spores rather than gemmae, although some mosses can produce gemmae.
- Pteridophytes: This group includes ferns and does not typically produce gemmae; they reproduce via spores.
- Among the four groups, gemmae are primarily associated with Liverworts. While some mosses may produce them, the most definitive presence of gemmae is in liverworts.
Gemmae are present in Liverworts.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
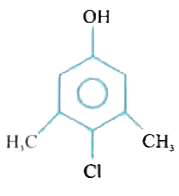 is present in ADettolBPenicillinCDyesDAntifertility drug
is present in ADettolBPenicillinCDyesDAntifertility drugThe number of atoms present in 1 g of hydrogen gas is the same as are present in
A4 g of HeliumB32 g of OxygenC7 g of NitrogenD24 g of CarbonAssertion : Gemmae are green, unicellular, asexual buds, which develop in small receptacles called gemma cups located on the thalli
Reason : In liverwords, spores germinate to form free-living sporophyte.AIf both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertionBIf both assertion and reason are true and but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertionCIf assertion is true but reason is falseDIf both assertion and reason are false
Johnston's organ present in mosquitoes, are to detect vibration. They are present in
View Solution
The oxidation state of the metal present in A is the same as that of the metal present in
View SolutionGemmae are the specialised structures produced in liverworts. These are
View SolutionGemmae are the specialised structures produced in liverworts. These are
View SolutionGemmae are vegetative repreoductive structures found in
View Solution

