In PQR , right-angled at Q, PQ=3cm and PR=6cm . Determine ∠P and ∠R .
30∘
45∘
60∘
90∘
Step by step video solution for In P Q R , right-angled at Q ,\ P Q=3c m and P R=6c m . Determine /_P and /_R . by Maths experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 10 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Book:OSWAL PUBLICATIONChapter:INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Exercise:NCERT CORNER (Textbook Questions) (Exercise - 8.1)
Explore 18 Videos
- INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Book:OSWAL PUBLICATIONChapter:INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Exercise:NCERT CORNER (Textbook Questions) (Exercise - 8.2)
Explore 15 Videos
- INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Book:OSWAL PUBLICATIONChapter:INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY AND TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Exercise:SELF ASSESSMENT - 2 (I. Objective Type Questions)(IV.Long Answer Type Questions - II)
Explore 3 Videos
- INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY Book:OSWAL PUBLICATIONChapter:INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY Exercise:Self - Assessment
Explore 15 Videos
- LINES (IN TWO - DIMENSIONS)Book:OSWAL PUBLICATIONChapter:LINES (IN TWO - DIMENSIONS)Exercise:BOARD CORNER (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION)
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
In ΔABC , right - angled at B , AB = 24 cm , BC = 7 cm .
sinA,cosA
View SolutionEvalulate the following :
sin60∘cos30∘+sin30∘cos60∘
View SolutionProve that tan2Atan2A−1+cosec2Asec2A−cosec2A=11−2cos2A
View SolutionIn ΔABC right - angled at c, AB = 29 units BC = 21 units and ∠ABC=θ Determine the value of
cos2θ+sin2θand
View SolutionIf a≠b≠c,prove that(a,a2),(b,b2),(0,0) will not be collinear.
View SolutionIn ΔPQR,right-angled at Q (see figure), PQ = 3 cm and PR = 6 cm. Determine ∠QPRand ∠PRQ
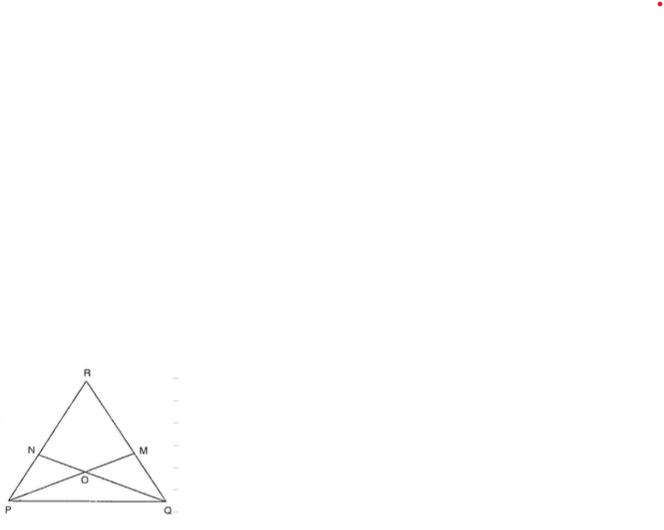
View SolutionIn Figure, ∠QPR=∠PQR and M and N are respectively on sides QR and PR of PQR such that QM=PN . Prove that OP=OQ, where O is the point of intersection of PM and QN.
View SolutionIn ABC , P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that PQBC . If AP=4cm, PB=6cm and PQ=3cm , determine BC .
View SolutionIn ΔPQR,right angled at Q, PR+QR=25cm and PQ=5cm. Determine the values of sinP,cosP and tanP.
View SolutionIn PQR, QM⊥PR and PR2−PQ2=QR2 . Prove that QM2=PM×MR
View SolutionIn Figure, ∠QPR=∠PQR and M and N are respectively on sides QR and PR of PQR such that QM=PN . Prove that OP=OQ, where O is the point of intersection of PM and QN.
View SolutionIn PQR, QM⊥PR and PR2−PQ2=QR2 . Prove that QM2=PM×MR
View SolutionIn ABC , P and Q are points on sides AB and AC respectively such that PQ∣∣BC . If AP=4cm, PB=6cm and PQ=3cm , determine BC .
View SolutionIn △OPQ right angled at P, OP=7cm , OQ−PQ=1cm . Determine the values of sinQ and cosQ .
View SolutionIn ΔPQR,right angled at Q, PR+QR=25cm and PQ=5cm. Determine the values of sinP,cosP and tanP.
View SolutionIn △PQR , right angled at Q, PQ=4cm and RQ=3cm . Find the values of sinP , sinR , secP and secR .
View Solution