A body of mass 5kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity of ¯¯¯U=(30i+40j)m/s. A constant force of F=(−ˆi−5ˆj)N acts on the body . Find the time in which they- component of the velocity becomes zero .
To solve the problem step-by-step, we will follow the physics principles of motion under constant acceleration.
Step 1: Identify Given Information
- Mass of the body, m=5kg
- Initial velocity, u=30^i+40^jm/s
- Force acting on the body, F=−^i−5^jN
Step 2: Calculate the Components of Initial Velocity
From the initial velocity:
- ux=30m/s (x-component)
- uy=40m/s (y-component)
Step 3: Determine the Force Components
The force acting on the body has components:
- Fx=−1N (x-component)
- Fy=−5N (y-component)
Step 4: Calculate the Acceleration
Using Newton's second law, F=ma:
- For the y-component:
ay=Fym=−5N5kg=−1m/s2
Step 5: Use the Equation of Motion for the y-component
We need to find the time t when the y-component of the velocity becomes zero. The equation of motion is:
vy=uy+ayt
Setting vy=0:
0=40m/s+(−1m/s2)t
Step 6: Solve for Time t
Rearranging the equation gives:
1m/s2⋅t=40m/s
t=40m/s1m/s2=40s
Final Answer
The time in which the y-component of the velocity becomes zero is t=40s.
---
- Mass of the body, m=5kg
- Initial velocity, u=30^i+40^jm/s
- Force acting on the body, F=−^i−5^jN
From the initial velocity:
- ux=30m/s (x-component)
- uy=40m/s (y-component)
The force acting on the body has components:
- Fx=−1N (x-component)
- Fy=−5N (y-component)
Using Newton's second law, F=ma:
- For the y-component:
ay=Fym=−5N5kg=−1m/s2
We need to find the time t when the y-component of the velocity becomes zero. The equation of motion is:
vy=uy+ayt
Setting vy=0:
0=40m/s+(−1m/s2)t
Rearranging the equation gives:
1m/s2⋅t=40m/s
t=40m/s1m/s2=40s
The time in which the y-component of the velocity becomes zero is t=40s.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 5 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
Explore 7 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL-II PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 10 Videos
- LOGIC GATESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LOGIC GATESExercise:Exercise (Very Short Answer)
Explore 7 Videos
Similar Questions
State Newton's third law of motion.
View SolutionState the Newton's laws of motion. What is the SI unit of force ?
View SolutionA light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). The refractive indices in Region I, II, III, and IV are n0,n0/2,n0/6andn0/8 , respectively. The angle of incidence θ for which the beam just misses entering Region IV is
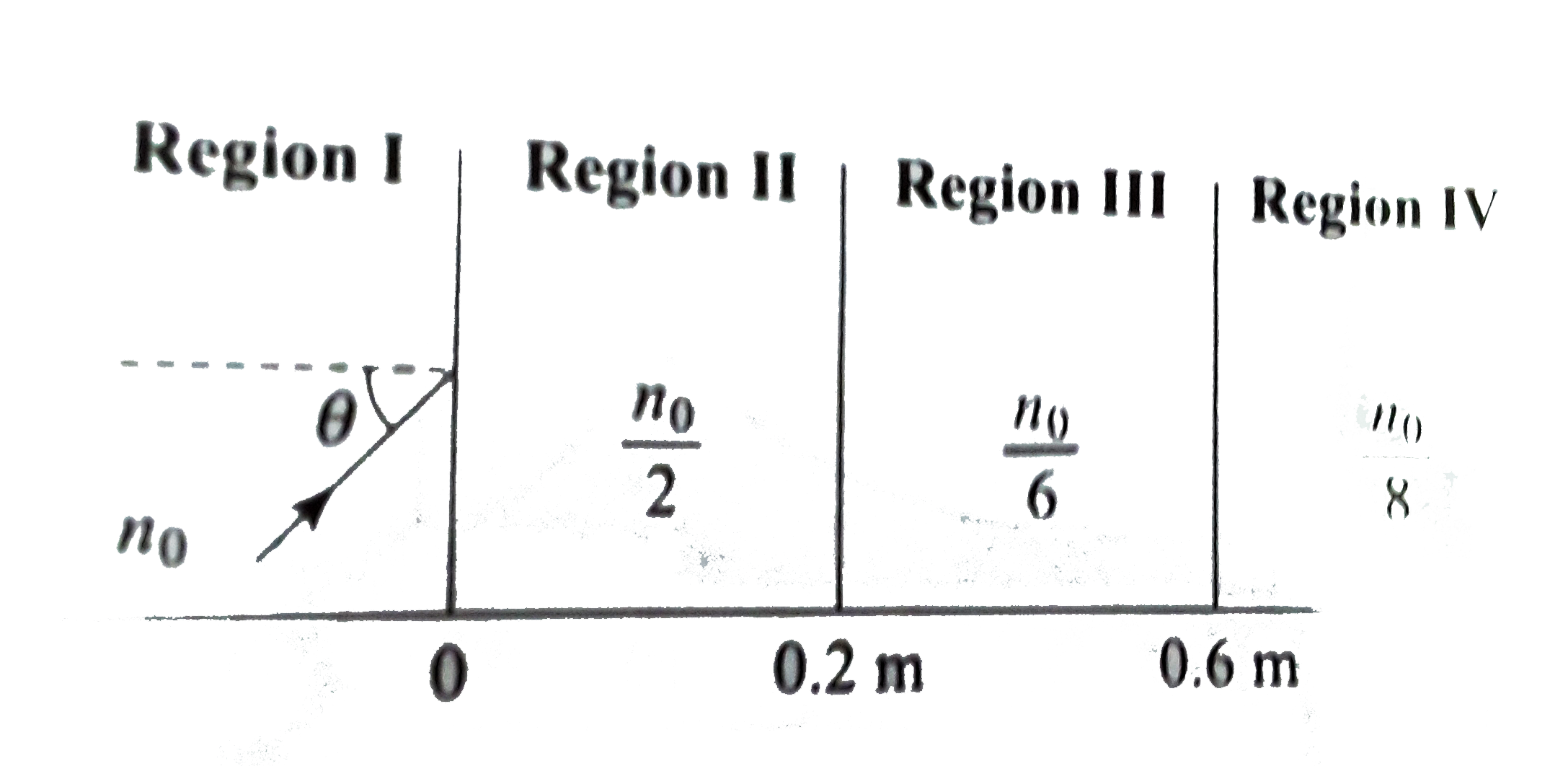
View Solution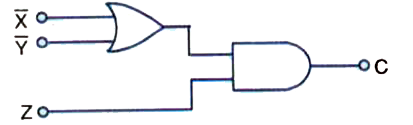
The output C in the above circuit is given by C = ---
View SolutionA body of mass 5 kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity →u=30ˆi+40ˆjms−1. If a constant force →F=−(ˆi+5ˆj)N acts on the body, the time in which the y-component of the velocity becomes zero is
View SolutionA body of mass 5 kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity bar(u)=(30hati+40hatj)ms^(-1) .If a constant force (-6hati-5hatj)N acts on the body, the time in velocity, which the y-component of the velocity becomes zero is.
View SolutionA body of mass 5 kg statrs from the origin with an initial velocity vec(u) = (30 hat(i) + 40 hat(j)) ms^(-1) . If a constant force (-6 hat(i) - 5 hat(j))N acts on the body, the time in which they component of the velocity becomes zero is
View SolutionA body of mass 2 kg starts with an intitial-velocity 5 m/s. It the body is acted upon by a time dependent force (F) as shown in figure, then work done on the body in 20 s is
View SolutionA force of 6N acts on a body at rest and of mass 1kg. During this time, the body attains a velocity of 30m/s. The time for which the force acts on body is :
View Solution(2ˆi+ˆj−ˆk) N force is acting on a body of 10 kg mass, if the body starts from rest, then after 20 sec what will be its velocity ?
View SolutionA body of mass 5kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity →u=30ˆi+40ˆjms−1. If a constant force →F=−(ˆi+5ˆj)N acts on the body, the time in which the y-component of the velocity becomes zero is
View Solution5 The initial velocity from an object's original point of mass kg vecu=30hati+40hatj Speed starts from m / s. If a fixed force on the object vecF=-(hati+5hatj)N If applied, the time in which the y component of velocity becomes zero will be
View SolutionA body of mass 5kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity of barU= (30i+40j)m//s . A constant force of F= (-hati - 5 hatj)N acts on the body . Find the time in which they- component of the velocity becomes zero .
View SolutionA body of mass 5kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity of ¯¯¯U=(30i+40j)m/s. A constant force of F=(−ˆi−5ˆj)N acts on the body . Find the time in which they- component of the velocity becomes zero .
View SolutionA body of mass 5kg starts from origin with a velocity baru = (30hati +40hatj)ms^(-1) . If a constant force F=-(hati+5hatj)N acts on the body, then pick up the correct statements
View SolutionA body of mass 5kg starts from the origin with an initial velocity vecu = 30 hati + 40 hatj ms^(-1) . If a constant force vecF = -(hati + 5hatj) acts on the body, the time in which the y-component of the velocity becomes zero is :
View Solution
