When a person is in a lift accelerated upwards or downwards, do force of gravity and normal reaction on the person form action and reaction pair?
To determine whether the force of gravity and the normal reaction on a person in an accelerating lift form an action-reaction pair, we can analyze the forces involved.
1. Identify the Forces Acting on the Person:
- When a person is in a lift, two main forces act on them:
- The force of gravity (weight) acting downwards, which is given by Fg=mg, where m is the mass of the person and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- The normal reaction force N exerted by the floor of the lift acting upwards.
2. Consider the Scenario When the Lift Accelerates Upwards:
- When the lift accelerates upwards with an acceleration a, the net force acting on the person can be expressed using Newton's second law:
Fnet=N−mg=ma
- Rearranging this equation gives:
N=ma+mg=m(a+g)
- Here, the normal reaction N is greater than the gravitational force mg.
3. Consider the Scenario When the Lift Accelerates Downwards:
- When the lift accelerates downwards with an acceleration a, the net force acting on the person is:
Fnet=N−mg=−ma
- Rearranging this gives:
N=mg−ma=m(g−a)
- In this case, the normal reaction N is less than the gravitational force mg.
4. Determine if the Forces Form Action-Reaction Pairs:
- According to Newton's third law, action-reaction pairs are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
- The force of gravity mg acts downwards, while the normal reaction N acts upwards. However, they are not equal in magnitude when the lift is accelerating (either upwards or downwards).
- Therefore, the force of gravity and the normal reaction do not form an action-reaction pair because they do not satisfy the condition of being equal and opposite.
Conclusion:
The force of gravity and the normal reaction on a person in a lift that is accelerating upwards or downwards do not form an action-reaction pair.
---
- When a person is in a lift, two main forces act on them:
- The force of gravity (weight) acting downwards, which is given by Fg=mg, where m is the mass of the person and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- The normal reaction force N exerted by the floor of the lift acting upwards.
- When the lift accelerates upwards with an acceleration a, the net force acting on the person can be expressed using Newton's second law:
Fnet=N−mg=ma
- Rearranging this equation gives:
N=ma+mg=m(a+g)
- Here, the normal reaction N is greater than the gravitational force mg.
- When the lift accelerates downwards with an acceleration a, the net force acting on the person is:
Fnet=N−mg=−ma
- Rearranging this gives:
N=mg−ma=m(g−a)
- In this case, the normal reaction N is less than the gravitational force mg.
- According to Newton's third law, action-reaction pairs are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
- The force of gravity mg acts downwards, while the normal reaction N acts upwards. However, they are not equal in magnitude when the lift is accelerating (either upwards or downwards).
- Therefore, the force of gravity and the normal reaction do not form an action-reaction pair because they do not satisfy the condition of being equal and opposite.
The force of gravity and the normal reaction on a person in a lift that is accelerating upwards or downwards do not form an action-reaction pair.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:NUMERICAL EXERCISE ( LEVEL-1)
Explore 16 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:NUMERICAL EXERCISE ( LEVEL-2)
Explore 13 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
Explore 7 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL-II PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 10 Videos
- LOGIC GATESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LOGIC GATESExercise:Exercise (Very Short Answer)
Explore 7 Videos
Similar Questions
Due to the application of a force on a body of mass 100 kg that is initially at rest, the body moves with an acceleration of 20ms−2 in the direction of the force. Find the magnitude of the force.
View SolutionA block A of mass 6kg is applied on a frictionless table. A thread tied to it passes over a frictionless pulley and carries a body B of mass 4kg at the other end. Find the acceleration of the system and tension in the thread (given g=10ms−2)
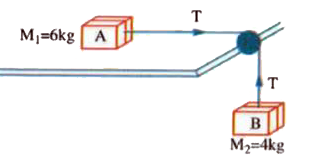
View SolutionState the Newton's laws of motion. What is the SI unit of force ?
View SolutionA light beam is traveling from Region I to region IV (refer figure). The refractive indices in Region I, II, III, and IV are n0,n0/2,n0/6andn0/8 , respectively. The angle of incidence θ for which the beam just misses entering Region IV is
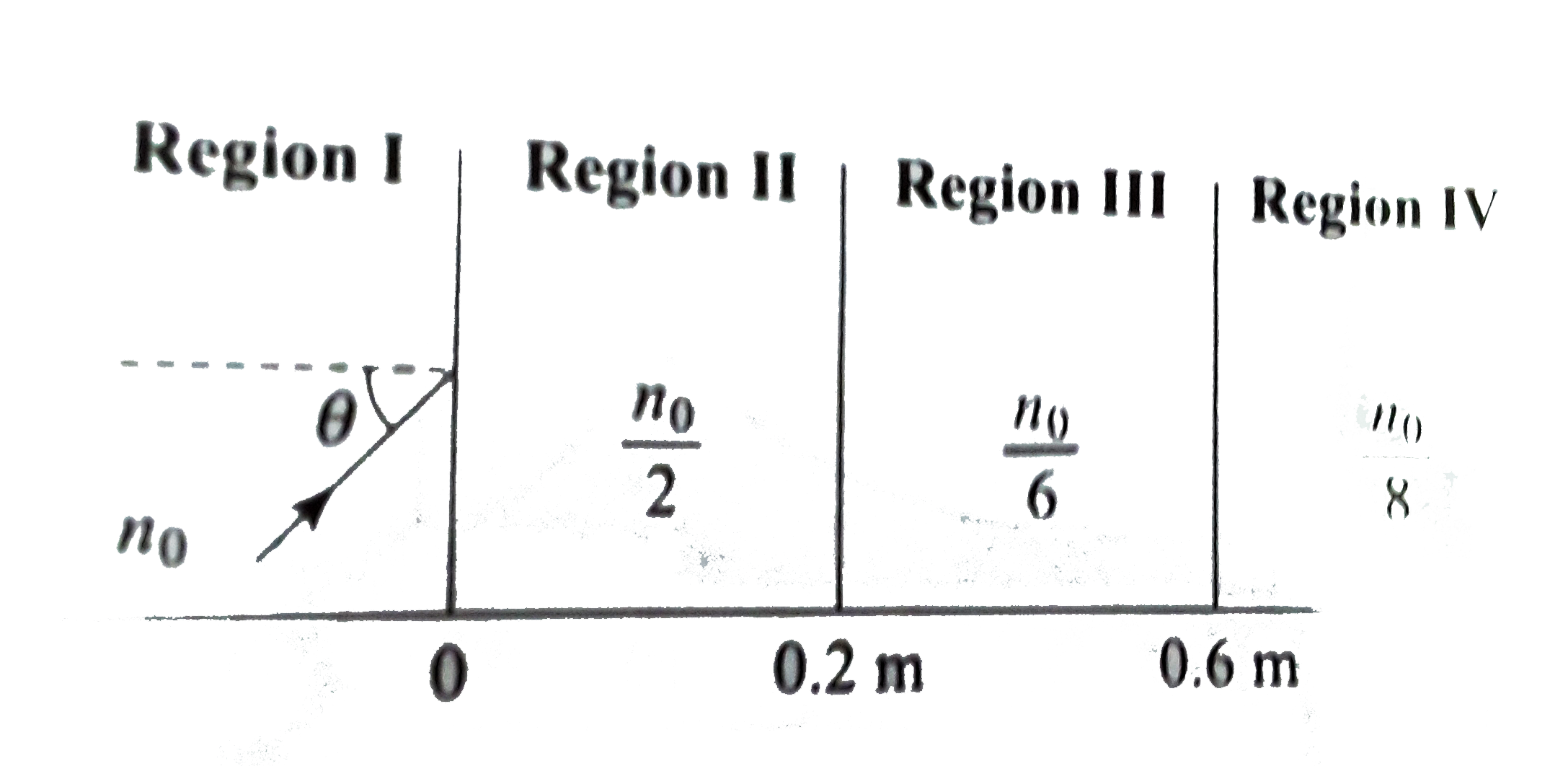
View Solution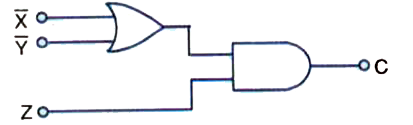
The output C in the above circuit is given by C = ---
View Solutionएक व्यक्ति लिफ्ट में खड़ा है जो a त्वरण से ऊपर जा रही हैं यदि लिफ्ट की रस्सी अचानक टूट जाती है तो लिफ्ट की सतह द्वारा प्रतिक्रिया बल है
View SolutionA person is sitting in a lift acceleration upwards, Measured weight of person will be
View SolutionA lift is accelerated upward . What is apparent weight of a person inside the lift ?
View Solutionएक व्यक्ति एक लिफ्ट के अंदर है । लिफ्ट g त्वरण से ऊपर की ओर जा रहा है । उस व्यक्ति पर फर्श की प्रतिक्रिया क्या होगी ?
View SolutionW भार का एक व्यक्ति लिफ्ट में खड़ा है । यह लिफ्ट एक समान त्वरण से ऊपर की ओर गतिमान है । व्यक्ति का आभासी भार होगा-
View Solutionस्थिर लिफ्ट में m द्रव्यमान का व्यक्ति खड़ा है लिस्ट एकाएक नीचे की ओर त्वरित हो तब व्यक्ति पर छद्म बल लगेगा
View SolutionA person of mass m is standing in a lift. Find his apparent weight when the lift is (i) moving upwards with uniform acceleration a,
View SolutionA block is placed on the horizontal surface. There are two forces acting on the block. One, the downward pull of gravity and other a normal force acting on it. Are these forces equal and opposite? Do they form action - reaction pair? Discuss with your friends.
View SolutionA block is placed on the horizontal surface. There are two forces acting on the block. One, the downward pull of gravity and other a normal force acting on it. Are these forces equal and opposite? Do they form action - reaction pair? Discuss with your friends.
View SolutionA lift is moving downward with acceleration a. A person drops a ball inside the lift. The acceleration of the ball relative to the person inside the lift and the person standing on the ground is respectively
View SolutionStatement-1: A person standing in an elevator moving from the elevator standing at rest feels more weight. Statement-2: If the acceleration of the upward lift is 'a' then the person of mass m is given the normal reaction (N) applied to lift his weight, (equal to N = m (g + a)) (where gravity causes Acceleration is g)
View Solution
