Four similar prisms of angle of prism are arranged. Which of the following arrangements give no net angular deviation?

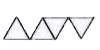


The correct Answer is:B
To solve the problem of determining which arrangement of four similar prisms results in no net angular deviation, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Understand the Concept of Angular Deviation
The angular deviation (δ) produced by a prism is the angle by which light is deviated from its original path when it passes through the prism. For a single prism, the deviation can be calculated using the formula:
δ=(n−1)A
where n is the refractive index of the prism material and A is the angle of the prism.
Step 2: Analyze the Arrangements
We need to evaluate the four arrangements of prisms provided in the question. The goal is to find an arrangement where the total deviation (sum of deviations from all prisms) equals zero.
Step 3: Set Up the Condition for No Net Deviation
For no net angular deviation, the sum of the deviations from the prisms must equal zero:
δ1+δ2+δ3+δ4=0
This can also be expressed as:
δ1+δ2=−(δ3+δ4)
This means that the deviations caused by the first two prisms must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the deviations caused by the last two prisms.
Step 4: Evaluate Each Arrangement
Let’s consider each arrangement (A, B, C, D) and analyze the deviations:
- Arrangement A: All prisms arranged in the same direction. This will result in a cumulative deviation and will not yield zero net deviation.
- Arrangement B: The first two prisms cause a deviation in one direction, while the last two prisms cause an equal deviation in the opposite direction. This arrangement satisfies the condition for no net deviation.
- Arrangement C: Similar to Arrangement A, all prisms in the same direction, leading to a net deviation.
- Arrangement D: The arrangement might have prisms that do not cancel out the deviations properly, resulting in a net deviation.
Step 5: Conclusion
After analyzing the arrangements, we find that Arrangement B is the only configuration that results in no net angular deviation.
Final Answer
The arrangement that gives no net angular deviation is Arrangement B.
---
The angular deviation (δ) produced by a prism is the angle by which light is deviated from its original path when it passes through the prism. For a single prism, the deviation can be calculated using the formula:
δ=(n−1)A
where n is the refractive index of the prism material and A is the angle of the prism.
We need to evaluate the four arrangements of prisms provided in the question. The goal is to find an arrangement where the total deviation (sum of deviations from all prisms) equals zero.
For no net angular deviation, the sum of the deviations from the prisms must equal zero:
δ1+δ2+δ3+δ4=0
This can also be expressed as:
δ1+δ2=−(δ3+δ4)
This means that the deviations caused by the first two prisms must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the deviations caused by the last two prisms.
Let’s consider each arrangement (A, B, C, D) and analyze the deviations:
- Arrangement A: All prisms arranged in the same direction. This will result in a cumulative deviation and will not yield zero net deviation.
- Arrangement B: The first two prisms cause a deviation in one direction, while the last two prisms cause an equal deviation in the opposite direction. This arrangement satisfies the condition for no net deviation.
- Arrangement C: Similar to Arrangement A, all prisms in the same direction, leading to a net deviation.
- Arrangement D: The arrangement might have prisms that do not cancel out the deviations properly, resulting in a net deviation.
After analyzing the arrangements, we find that Arrangement B is the only configuration that results in no net angular deviation.
The arrangement that gives no net angular deviation is Arrangement B.
टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE II LEVEL -II (ADVANCED) MORE THAN ONE CORRECT TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 7 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE II LEVEL -II (ADVANCED) LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 9 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:GEOMETRICAL OPTICSExercise:LECTURE SHEET (EXERCISE II LEVEL -I (MAIN) STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 17 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELEMENTS OF VECTORSExercise:QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
Explore 10 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:LAWS OF MOTIONExercise:PRACTICE EXERCISE
Explore 106 Videos
समान प्रश्न
A ray of light is incident normally on one face of 30∘−60∘−90∘ prism of refractive index 5/3 immersed in water of refractive index 4/3 as shown in figure .
_E01_076_Q01.png)
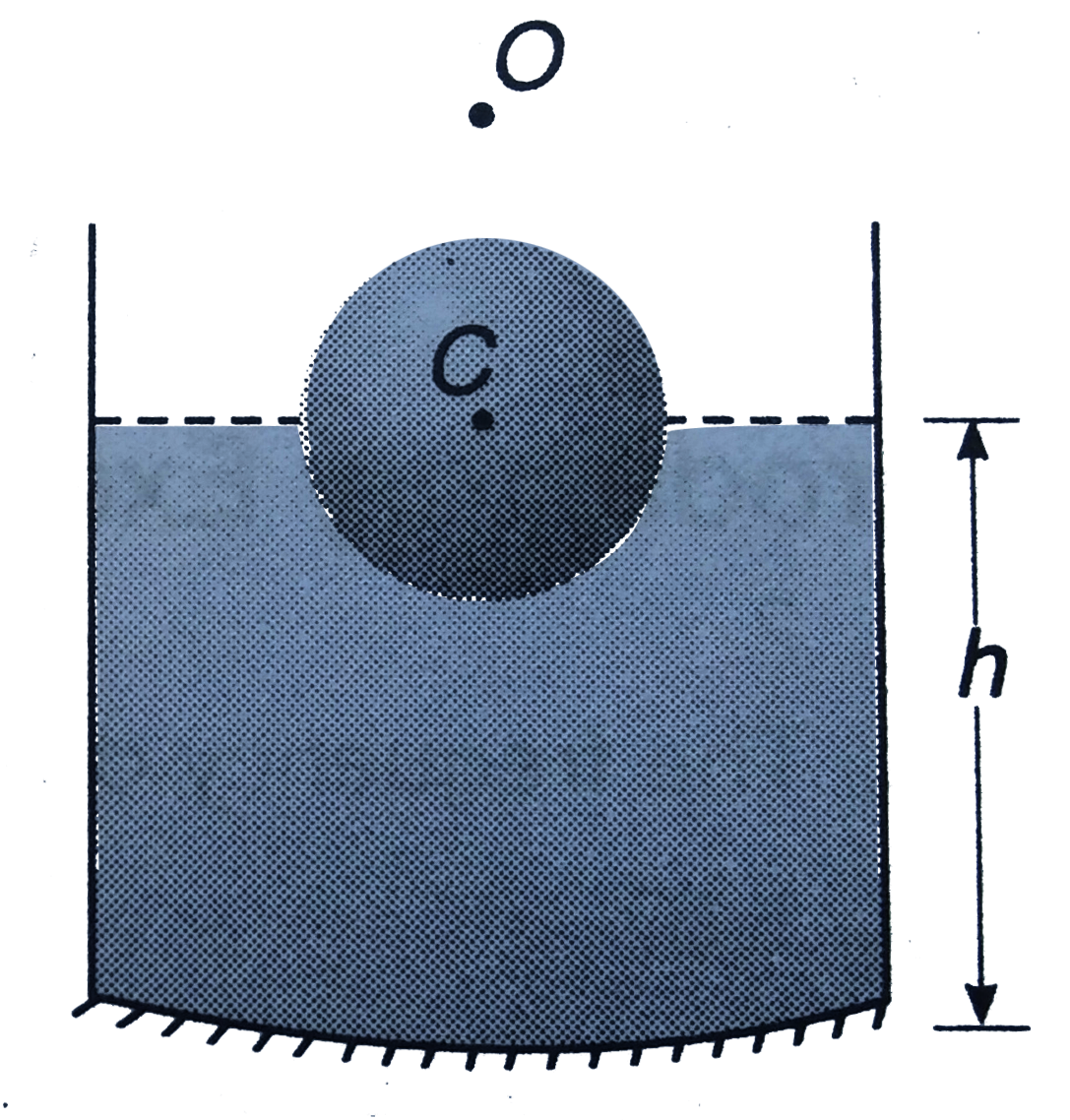
View SolutionA transparent solid sphere of radius 2cm and density ρ floats in a transparent liquid of density 2ρ kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with radius of curvature 8cm and is silvered to make it concave mirror as shown in the figure. When an object is placed at a distance of 10cm directly above the centre of the sphere C, its final image coincides with it. Find h (as shown in the figure ), the height of the liquid surface in the beaker from the apex of the bottom. Consider the paraxial rays only. The refractive index of the sphere is 3/2 and that of the liquid is 4/3.
View SolutionAbsolute refractive index of a medium is X. Refractive index of same medium w.r.t to air is Y and absolute refractive index to air is Z. Then the relation between them is
View SolutionFind the components of a vector A=2ˆi+3ˆj along the directions of ˆi+ˆjandˆi−ˆj.
View SolutionA force of 50 N acts on a body of mass 10 kg at rest. Its velocity after 5 seconds if the same force acts, is
View SolutionAngle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of prism A of an equilateral glass prism. The angle of incidence at which minimum deviation will be obtained is
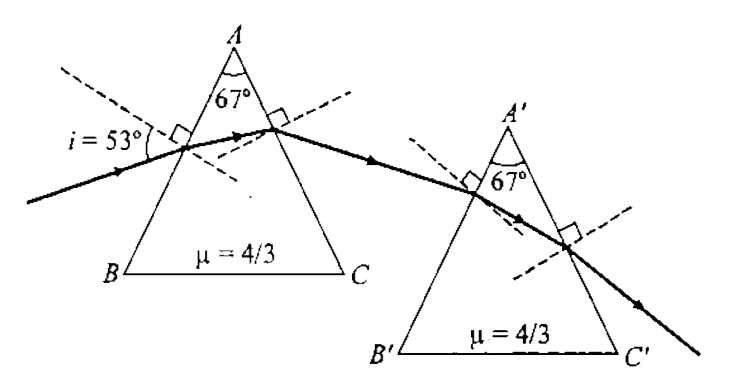
View SolutionA ray is incident on the first prism at an angle of incidence 53∘ as shown in the figure. The angle between side CA and B'A' for the net deviation by both the prisms to be double of the deviation produced by the first prism, will be:
View SolutionAngle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle prism A of an equilateral glass prism. The angle incidence at which minimum deviation will be obtained is
View SolutionA prism is found to give a minimum deviation of 51∘. The same prism gives a deviation of 62∘48' for two values of the angles of incidence 40∘6' and 82∘42'. Determine the refracting angle of the prism and the refractive index of the prism material.
View SolutionA ray is incident on the first prism at an angle of incidence of 53∘ as shown in the figure . The angle between side CA and B'A' for the net deviation by both the prisms to be double of the deviation produced by the first prism , will be
_E01_086_Q01.png)
View SolutionA prism of angle4∘ gives a deviation of 2.4∘. The refractive index of the material of the prism is
View SolutionCan two prisms be arranged to get dispersion without deviation?
View SolutionFour similar prisms of same material having same angle of prism are arranged. Which among the four of the arrangements shown in the following figures gives no not angular deviation ?
View SolutionFour similar prisms of angle of prism are arranged. Which of the following arrangements give no net angular deviation?
View Solutionएक छोटे कोण का प्रिज्म (μ=1.62)4.8∘ का विचलन देता है। प्रिज्म का कोण होगा -
View SolutionA prism of refractive index μ = 1.5 and prisim angle 15∘ is arranged with another prism ( refractive index μ2 = 1.75. If this combination gives the dispersion without deviation, the what should be the prism angle of second prism ?
View Solution
