A glass sphere of diameter 50 cm and μ=1.5 has a small air bubble. Looking from outside the diameter, the bubble appears to be at a distance 10 cm the surface. Find the apparent position of the bubble when it is viewed from the diametrically opposite position.
real image, at the pole of 2 nd face
real image, at the pole of 1st face
virtual image, at the pole of 1st face
virtual image, at the centre of the sphere
The correct Answer is:C
To solve the problem, we need to find the apparent position of the air bubble when viewed from the diametrically opposite position of the glass sphere. We will use the lens maker's formula and the concept of refraction to find the position.
1. Identify Given Values:
- Diameter of the glass sphere (D) = 50 cm
- Radius of the sphere (R) = D/2 = 25 cm
- Refractive index of glass (μ) = 1.5
- Apparent distance of the bubble from the surface (v1) = 10 cm
2. Determine the Object Distance:
- The object (air bubble) is inside the sphere. The distance from the center of the sphere to the bubble can be calculated as:
u=R−v1=25 cm−10 cm=15 cm
- Here, u is taken as negative because the object is inside the sphere.
3. Use the Lens Formula:
The lens formula is given by:
1f=1v−1u
where:
- f = focal length
- v = image distance (which we need to find)
- u = object distance
4. Calculate the Focal Length:
The focal length (f) for a spherical interface can be calculated using the formula:
f=R2(μ−1)
Substituting the values:
f=25 cm2(1.5−1)=25 cm2×0.5=25 cm1=25 cm
5. Apply the Lens Formula:
Now we can apply the lens formula:
125=1v−1−15
Rearranging gives:
1v=125−115
Finding a common denominator (75):
1v=375−575=−275
Thus:
v=−752=−37.5 cm
6. Interpret the Result:
The negative sign indicates that the image is virtual and located on the same side as the object (inside the sphere). The apparent position of the bubble when viewed from the diametrically opposite position is 37.5 cm from the center of the sphere.
Final Result:
The apparent position of the bubble when viewed from the diametrically opposite position is 37.5 cm from the center of the sphere.
- Diameter of the glass sphere (D) = 50 cm
- Radius of the sphere (R) = D/2 = 25 cm
- Refractive index of glass (μ) = 1.5
- Apparent distance of the bubble from the surface (v1) = 10 cm
- The object (air bubble) is inside the sphere. The distance from the center of the sphere to the bubble can be calculated as:
u=R−v1=25 cm−10 cm=15 cm
- Here, u is taken as negative because the object is inside the sphere.
The lens formula is given by:
1f=1v−1u
where:
- f = focal length
- v = image distance (which we need to find)
- u = object distance
The focal length (f) for a spherical interface can be calculated using the formula:
f=R2(μ−1)
Substituting the values:
f=25 cm2(1.5−1)=25 cm2×0.5=25 cm1=25 cm
Now we can apply the lens formula:
125=1v−1−15
Rearranging gives:
1v=125−115
Finding a common denominator (75):
1v=375−575=−275
Thus:
v=−752=−37.5 cm
The negative sign indicates that the image is virtual and located on the same side as the object (inside the sphere). The apparent position of the bubble when viewed from the diametrically opposite position is 37.5 cm from the center of the sphere.
The apparent position of the bubble when viewed from the diametrically opposite position is 37.5 cm from the center of the sphere.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (MORE THAN ONE CORRECT TYPE QUESTIOS)
4 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (LINKED COMPREHENSION CORRECT TYPE QUESTIOS)
7 Videos
- GEOMETRICAL OPTICSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - GEOMETRICAL OPTICSEXERCISE - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE -I (LEVEL-II LECTURE SHEET (ADVANCED) INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS)
4 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - ELEMENTS OF VECTORSEXERCISE - QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
10 Videos
- LAWS OF MOTIONBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - LAWS OF MOTIONEXERCISE - PRACTICE EXERCISE
106 Videos
Similar Questions
A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in the figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be
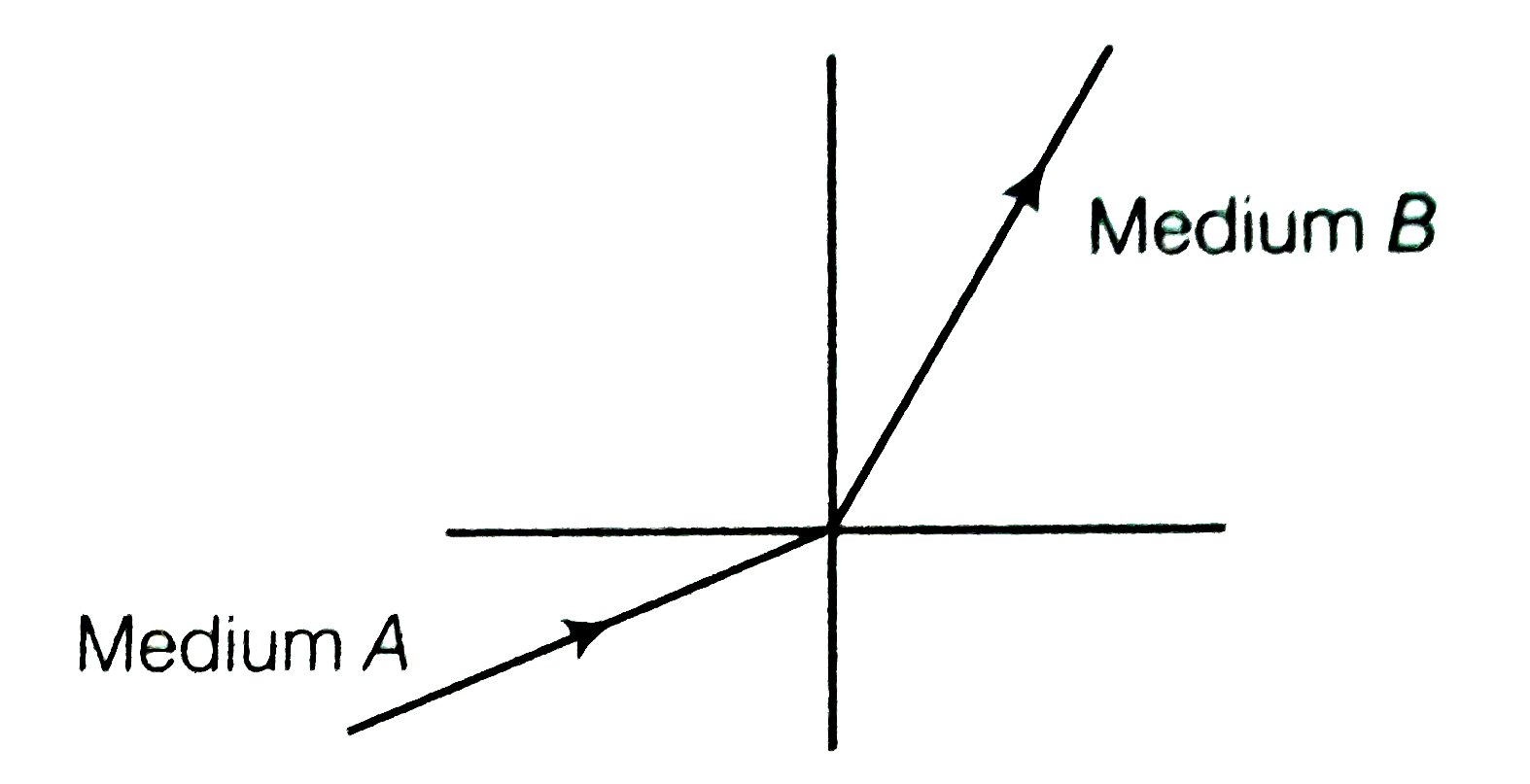
View SolutionThe refractive index of the material of the prism and liquid are 1.56 and 1.32 respectively. What will be the value of θ for the following refraction ?

View SolutionA biconvex thin lens is prepared from glass of refractive index μ2=32. The two conducting surfaces have equal radii of 20 cm each. One of the the surface is silvered from outside to make it reflecting. It is placed in a medium of refractive index μ1=53. It acts as a
View SolutionFind the components of a vector A=2ˆi+3ˆj along the directions of ˆi+ˆjandˆi−ˆj.
View SolutionA force of 50 N acts on a body of mass 10 kg at rest. Its velocity after 5 seconds if the same force acts, is
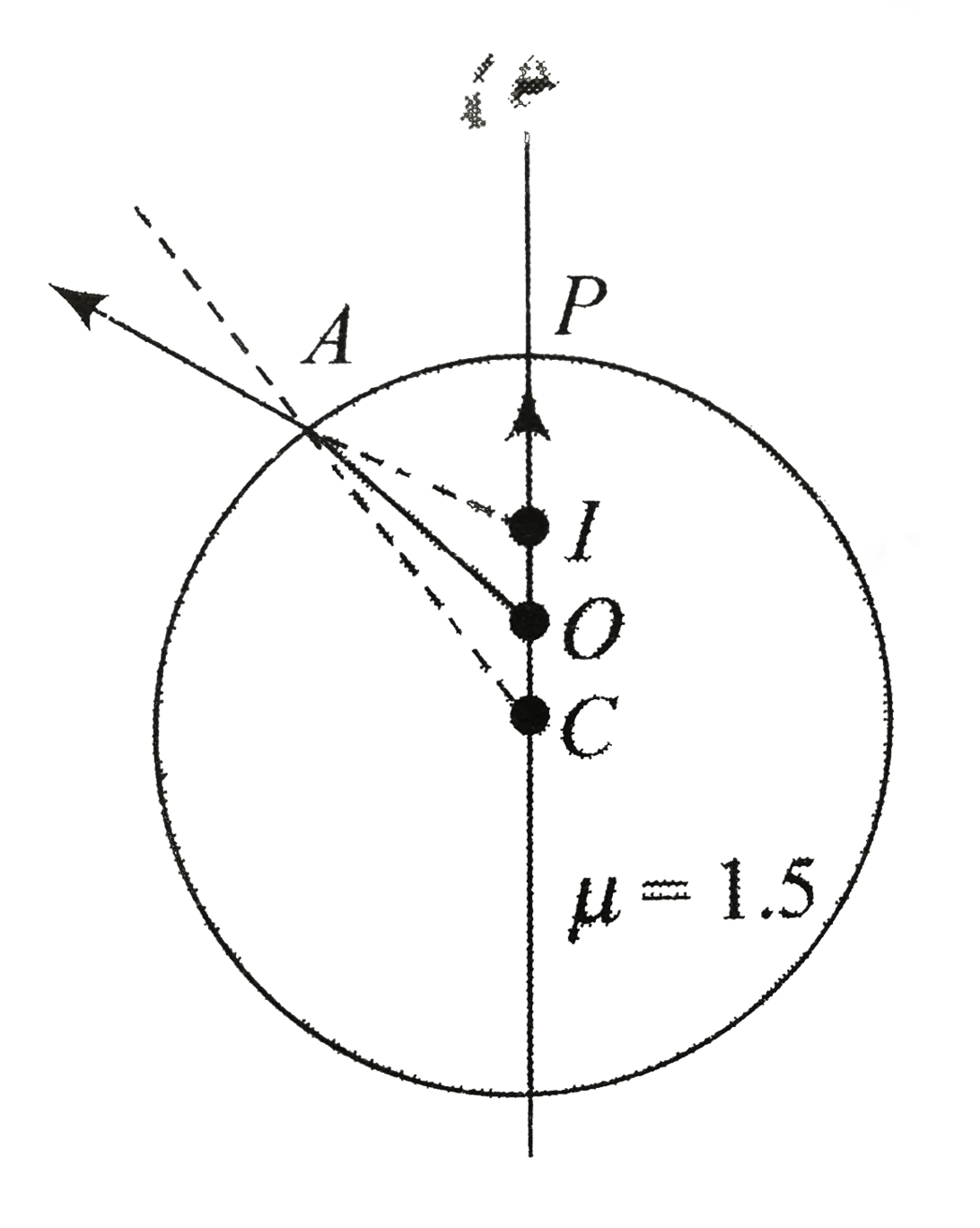
View SolutionThere is a small air bubble inside a glass sphere (μ=1.5) of radius 10 cm. The bubble is 4.0cm below the surface and is viewd normally from the outside. Find the apparent dipth of the bubble.
View SolutionA small air bubble in a glass sphere of radius 2cm appears to be 1cm from the surface when looked at, along a diameter. If the refractive index of glass is 1.5, find the true position of the air bubble.
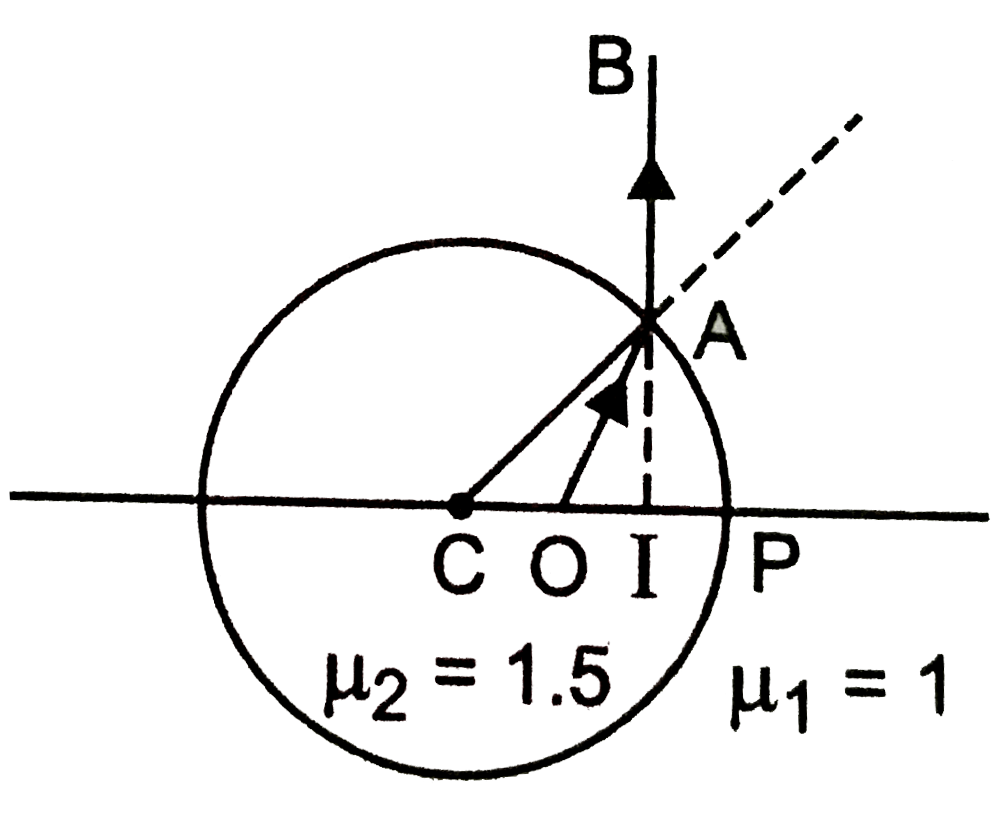 .
.
View SolutionAn air bubble in a glass sphere (μ=1.5) is situated at a distance 3cm from a convex surface of diameter 10cm. At what distance from the surface will the bubble appear ?
View SolutionAn air bubble in sphere having 4cm diameter appears of 1 cm from surface nearest to eye when looked along diameter. If nga = 1.5, the distance of bubble from refracting surface is
View SolutionAn air bubble in a glass sphere (mu = 1.5) is situated at a distance 3 cm from a convex surface of diameter 10 cm . At what distance from the surface will be the bubble appear ?
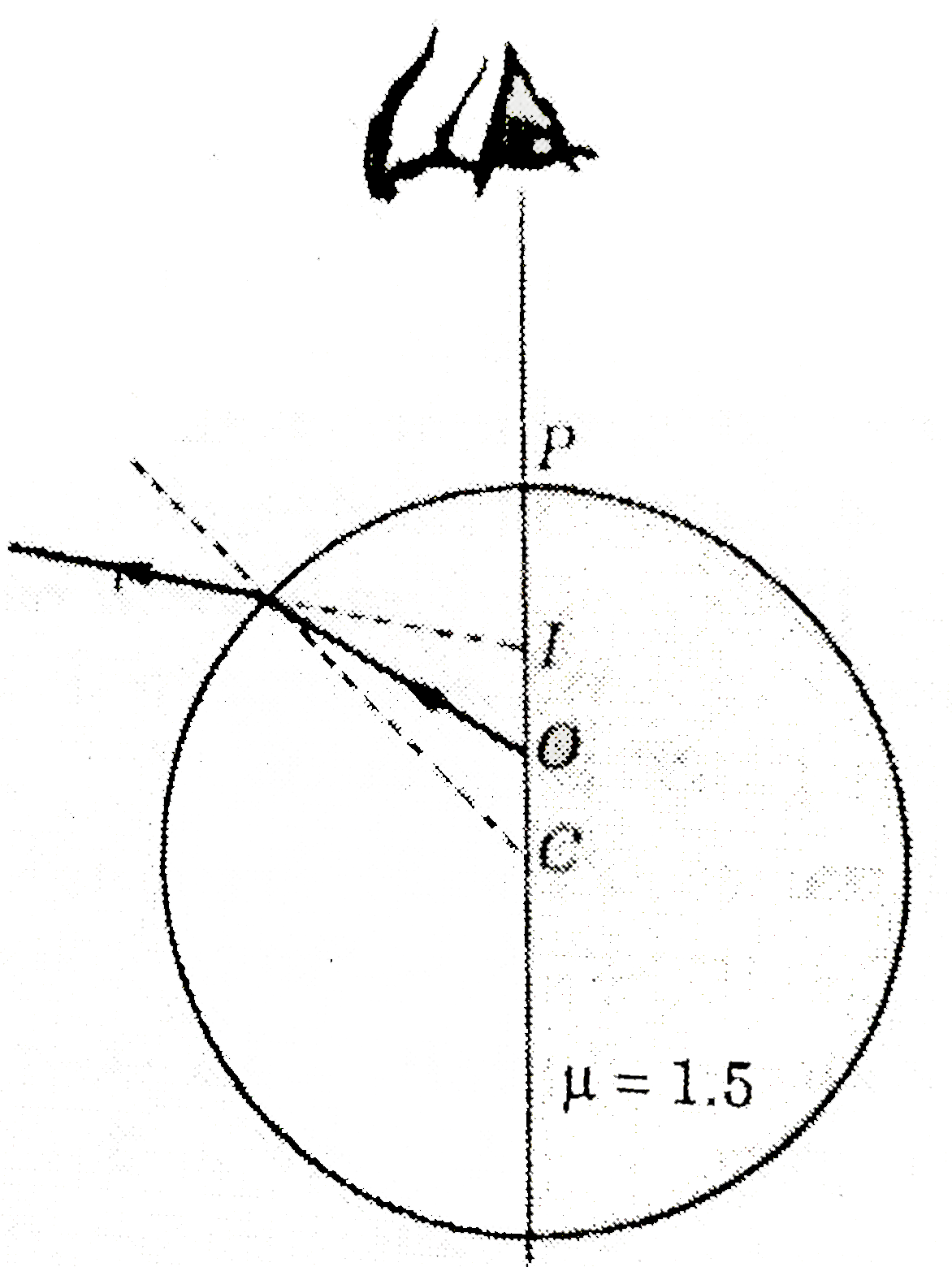
View SolutionFig shows a small air bubble inside a glass sphere (μ=1.5) of radius 10 cm. the bubble is 4.0 cm below the surface and is viewed normally from the outside. Find the apparent depth of the bubble.
View Solutionकाँच (n = 1.5) के 4.0 सेमी व्यास के एक ठोस गोले के भीतर वायु का एक बुलबुला गोले के पृष्ट से ( व्यास के अनुदिश देखने पर ) 1.0 सेमी की दूरी पर दिखाई देता हैं | गोले के भीतर बुलबुले की वास्तविक स्थिति ज्ञात कीजिए |
View Solution6 cm त्रिज्या तथा 1.5 अपवर्तनांक वाले एक काँच के गोले में हवा का एक छोटा बुलबुला, यदि इसमें से होकर गुजरनेवाले व्यास की और से देखा जाए, तो पास वाली सतह से 2 cm पर मालूम पड़ता है। बुलबुले की वास्तविक स्थिति ज्ञात करे।
View Solution6 cm व्यास और 1.5 अपवर्तनांक वाले गोले में एक छोटा वायु का बुलबुला फँसा है | व्यास के अनुदिश देखने पर बुलबुला, गोले के 1 cm अन्दर प्रतीत होता है | बुलबुले की वास्तविक स्थिति निकालें |
View SolutionThere is a small air bubble inside a glass sphere (μ=1.5) of radius 10 cm. The bubble is 4 cm below the surface and is viewed normally from the outside. The apparent depth of the bubble is
View SolutionA glass sphere of diameter 50 cm and μ=1.5 has a small air bubble. Looking from outside the diameter, the bubble appears to be at a distance 10 cm the surface. Find the apparent position of the bubble when it is viewed from the diametrically opposite position.
View Solution

