The following results are obtained in several dihybrid test crosses in an organism considering three genes loci Aa,Bb and Cc.
a. In test cross with AaBb the number of recombinants and parental combinations are 50 and 950 respectively.
b. In TC with AaCc the number of Rc and PC are 75 and 425 respectively.
c. In TC with BbCc the number of RC and PC are 160 and 640 respectively.
basing on the above result identify the gene loci of the three genes /prepare a genetic map of the three genes.
To solve the problem of determining the gene loci of three genes (A, B, and C) based on the results of several dihybrid test crosses, we will follow these steps:
Step 1: Analyze the Test Cross Results
We have three test crosses with the following results:
1. Test Cross with AaBb:
- Recombinants (RC) = 50
- Parental Combinations (PC) = 950
- Total = 50 + 950 = 1000
2. Test Cross with AaCc:
- Recombinants (RC) = 75
- Parental Combinations (PC) = 425
- Total = 75 + 425 = 500
3. Test Cross with BbCc:
- Recombinants (RC) = 160
- Parental Combinations (PC) = 640
- Total = 160 + 640 = 800
Step 2: Calculate the Recombination Frequencies
We will calculate the recombination frequency (RF) for each test cross using the formula:
\( \text{Recombination Frequency (RF)} = \frac{\text{Number of Recombinants}}{\text{Total Offspring}} \times 100 \)
1. For AaBb:
\(
RF = \frac{50}{1000} \times 100 = 5\%
\)
2. For AaCc:
\(
RF = \frac{75}{500} \times 100 = 15\%
\)
3. For BbCc:
\(
RF = \frac{160}{800} \times 100 = 20\%
\)
Step 3: Determine Gene Order
The recombination frequencies suggest the relative distances between the genes. The smaller the RF, the closer the genes are likely to be located on the chromosome.
- From the results:
- A and B are 5 map units apart (from AaBb).
- A and C are 15 map units apart (from AaCc).
- B and C are 20 map units apart (from BbCc).
Step 4: Construct the Genetic Map
Based on the recombination frequencies:
- Place A and B close together since they have the smallest RF (5 map units).
- Place C further away from A and B since it has the largest RF with B (20 map units).
The genetic map can be represented as:
A−−−−5m.u.−−−−B−−−−15m.u.−−−−C
Final Genetic Map Summary
- A is located at 0 m.u.
- B is at 5 m.u.
- C is at 20 m.u.
We have three test crosses with the following results:
1. Test Cross with AaBb:
- Recombinants (RC) = 50
- Parental Combinations (PC) = 950
- Total = 50 + 950 = 1000
- Recombinants (RC) = 75
- Parental Combinations (PC) = 425
- Total = 75 + 425 = 500
- Recombinants (RC) = 160
- Parental Combinations (PC) = 640
- Total = 160 + 640 = 800
We will calculate the recombination frequency (RF) for each test cross using the formula:
\( \text{Recombination Frequency (RF)} = \frac{\text{Number of Recombinants}}{\text{Total Offspring}} \times 100 \)
\(
RF = \frac{50}{1000} \times 100 = 5\%
\)
\(
RF = \frac{75}{500} \times 100 = 15\%
\)
\(
RF = \frac{160}{800} \times 100 = 20\%
\)
The recombination frequencies suggest the relative distances between the genes. The smaller the RF, the closer the genes are likely to be located on the chromosome.
- A and B are 5 map units apart (from AaBb).
- A and C are 15 map units apart (from AaCc).
- B and C are 20 map units apart (from BbCc).
Based on the recombination frequencies:
- Place A and B close together since they have the smallest RF (5 map units).
- Place C further away from A and B since it has the largest RF with B (20 map units).
A−−−−5m.u.−−−−B−−−−15m.u.−−−−C
- A is located at 0 m.u.
- B is at 5 m.u.
- C is at 20 m.u.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATIONExercise:EXERCISE-I
Explore 152 Videos
- PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATIONBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE AND VARIATIONExercise:EXERCISE-I (Sex determination & Genetic Disorders)
Explore 44 Videos
- PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES Book:AAKASH SERIESChapter:PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES Exercise:Exercise - III (Previous AIPMT/NEET Questions)
Explore 26 Videos
- RESPIRATION IN PLANTSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:RESPIRATION IN PLANTSExercise:Exercise - III
Explore 9 Videos
Similar Questions
The process of transmision of parental characters to the offspring is
View SolutionChromosomal disorders are caused due to
View SolutionDNA fragments are
View SolutionWhich statement is wrong for Kreb's cycle?
View SolutionArrange the follwing in decreasing order based on the results obtained in the F2 progeny of dihybrid cross
(a) Total number of parental genotype
(b) Total number of recombinant genotypes
( c) Total phenotypes
(d) Total genotypes
View SolutionA pair of genes are linked if their recombination frequency in test cross is
View SolutionA test cross of Aa Bb Cc produces how many phenotypes?
View SolutionTwo linked genes and b show 20% recombination the individuals of a hybrid cross between ++/++ X ab/ab shall show gametes:
View SolutionIn an experiment, AaBb obtained in the (F1) generation was test crossed. In the progeny , genotype Aabb and aaBb were more frequent than AaBb and aabb. Then the genotype of the parents should be
View SolutionThe percentage proportion of homozygous parents in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross is ……….the percentage proportion of homozygous parents in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross
View SolutionThe figure shows the experiment of T.H Morgan on the linkage. If in cross-I, genes are tightly linked and in cross-II, genes are loosely linked then what will be the percentage of recombination produced in cross-I and cross-II respectively?
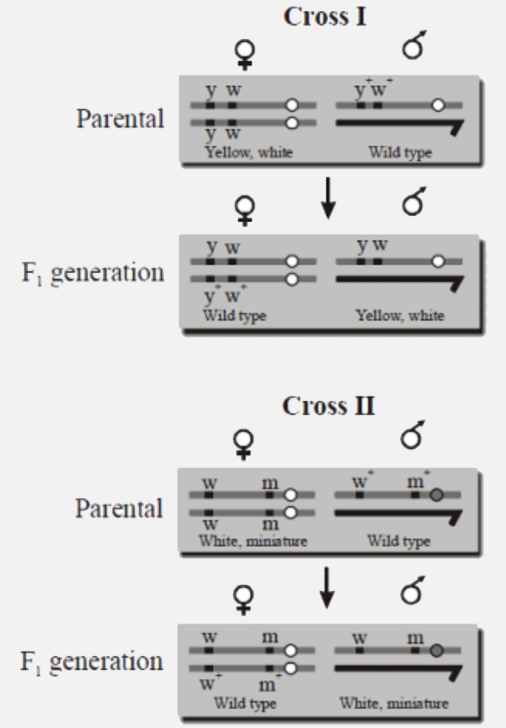
View SolutionIn a dihybrid test cross,if the parental types exceed the recombination types among the resultant progeny, it is due to
View SolutionGive the phenotypic ratio of (a) Dihybrid cross (b) Dihybrid test cross
View SolutionThe percentage of a recombinants in the F2 of a typical dihybrid cross is
View SolutionDihybrid test cross ratio with 82% parental type and 18% recombinants type shows that genes have
View SolutionHow many different types of gametes can be formed by F1 progeny , resulting from the following cross ? ∀BBC×aa :
View Solution
