(A): According to Laplace the propagation of sound in air is an adiabatic process.
(B): Pressure has no effect on velocity of sound in a gas as long as temperature remains constant.
(C): The velocity of sound in air changes by 0.61 m/s when temperature changes by 1∘C
All are true
A,B are only true
B are true
A,C are only true
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the question, we need to evaluate the three statements regarding the propagation of sound in air. Let's analyze each statement step by step.
Statement A:
According to Laplace, the propagation of sound in air is an adiabatic process.
1. Understanding Adiabatic Process: An adiabatic process is one in which no heat is exchanged with the surroundings. In the context of sound propagation, this means that the temperature of the medium changes during the compression and rarefaction of sound waves.
2. Laplace's Assumption: Laplace proposed that sound waves in air propagate as an adiabatic process, where the temperature increases during compression and decreases during rarefaction, but the total heat remains constant.
3. Conclusion: This statement is true because Laplace's theory correctly describes sound propagation as an adiabatic process.
Statement B:
Pressure has no effect on the velocity of sound in a gas as long as temperature remains constant.
1. Velocity of Sound Formula: The velocity of sound v in a gas is given by the formula:
v=√γPρ
where γ is the ratio of specific heats, P is the pressure, and ρ is the density of the gas.
2. Ideal Gas Law: According to the ideal gas law PV=nRT, we can express density ρ as ρ=mV, which implies that pressure and density are related.
3. Effect of Pressure: If temperature is constant, any increase in pressure will increase density proportionally, thus maintaining the ratio Pρ constant. Therefore, pressure does not affect the velocity of sound in an isothermal process.
4. Conclusion: This statement is true because, under constant temperature, pressure does not affect the velocity of sound.
Statement C:
The velocity of sound in air changes by 0.61 m/s when temperature changes by 1°C.
1. Temperature and Velocity Relationship: The velocity of sound is directly proportional to the square root of the absolute temperature (in Kelvin):
v∝√T
2. Standard Values: At 0°C (273 K), the velocity of sound is approximately 330 m/s.
3. Calculating Change: If the temperature increases by 1°C (from 273 K to 274 K):
vnew=vold×√TnewTold=330×√274273
4. Calculating the Result: After performing the calculation:
vnew≈330.61m/s
The change in velocity is:
Δv=vnew−vold=330.61−330=0.61m/s
5. Conclusion: This statement is true as the velocity of sound indeed changes by 0.61 m/s for a temperature change of 1°C.
Final Conclusion:
All three statements (A, B, and C) are true.
---
According to Laplace, the propagation of sound in air is an adiabatic process.
2. Laplace's Assumption: Laplace proposed that sound waves in air propagate as an adiabatic process, where the temperature increases during compression and decreases during rarefaction, but the total heat remains constant.
Pressure has no effect on the velocity of sound in a gas as long as temperature remains constant.
v=√γPρ
where γ is the ratio of specific heats, P is the pressure, and ρ is the density of the gas.
The velocity of sound in air changes by 0.61 m/s when temperature changes by 1°C.
v∝√T
vnew=vold×√TnewTold=330×√274273
vnew≈330.61m/s
The change in velocity is:
Δv=vnew−vold=330.61−330=0.61m/s
All three statements (A, B, and C) are true.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- WAVESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:WAVESExercise:EXERCISE-IA (Matching )
Explore 4 Videos
- WAVESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:WAVESExercise:EXERCISE-IB (Assertion (A) & Reason (R) Type Questions)
Explore 72 Videos
- WAVESBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:WAVESExercise:EXERCISE-IA (Theoretical questions :)
Explore 85 Videos
- WAVE OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:WAVE OPTICSExercise:PROBLEMS (LEVEL - II)
Explore 33 Videos
- WAVES OPTICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:WAVES OPTICSExercise:EXERCISE -III (POLARISITION)
Explore 10 Videos
Similar Questions
Match the following
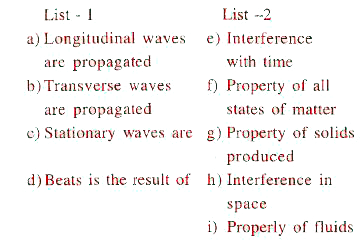
View Solution(A): In a mechanical progressive wave, energy is transferred from one point to the other.
(R): In a mechanical progressive wave energy transfer takes place because of the coupling through elastic forces between neighbouring oscillating particles of the medium.
View SolutionTransverse waves are possible in solids only because
View SolutionIn Young's double-slit experiment, the y-coordinate of central maxima and 10th maxima are 2 cm and 5 cm, respectively, When the YDSE apparatus is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.5, the corresponding y-coordinates will be
View SolutionA ray of light is incident on the surface of a glass plate of refractive index √3 at the polarising angle . The angle of incidence and angle of refraction of the ray is
View SolutionThe velocity of sound in air at 20^(@)C is 340ms^(-1) . Keeping the temperature constant, what will be the velocity of sound in air when the pressure of the gas is doubled?
View SolutionThe velocity of sound in air at 27∘C is 330 m/s. the velocity of sound when the temperature of the gas is raised to 227∘C is
View SolutionAt room temperature (27^(@)C) the velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s. the increase in velocity of sound when temperature is increased by 1^(@)C is
View Solutionकिसी गैस में ध्वनि की चाल पर ताप के प्रभाव की विवेचना कीजिए 1∘C ताप बढ़ाने पर वायु में ध्वनि की चाल में कितना परिवर्तन होगा ?
View Solutionस्थिर ताप पर वायुदाब में परिवर्तन कर देने पर ध्वनि की चाल पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ता है?
View SolutionThe velocity of sound in air when temperature is halved and pressure doubled will be
(The velocity of sound in air at NTP is 330 m/s)
View SolutionWhich of the following statements are incorrect? A) Changes in air temperature have no effect on the speed of sound. B) Changes in air pressure have no effect on the speed of sound. C) Changes in air pressure have effect on the speed of sound. D) The speed of sound in water is lower than in air
View SolutionVelocity of sound in air at NTP is 332 m/s. What will be the velocity, when pressure is doubled and temperature is kept constant?
View SolutionThe velocity of sound in air at 20∘C is 340ms−1. Keeping the temperature constant, what will be the velocity of sound in air when the pressure of the gas is doubled?
View Solutionकथन : वायु में ध्वनि का वेग घटता है यदि नियत ताप पर वायु का दाब घटता है।
न्यूटन द्वारा संशोधित लाप्लास के सूत्र के अनुसार वायु में ध्वनि का वेग V=√γPρ है।
View Solution(A): According to Laplace the propagation of sound in air is an adiabatic process. (B): Pressure has no effect on velocity of sound in a gas as long as temperature remains constant. (C): The velocity of sound in air changes by 0.61 m/s when temperature changes by 1^(@)C
View Solution
