A small, electrically charged bead can slide on a circular, frictioless, insulating rod. A point - like electric dipole (→P) is fixed at the centre of the circle with the dipole.s axis lying in the plane of the circle. Intially the bead is on the plane of symmetry of the dipole, as shown in the figure. The bead is slightly displaced along ring, tangentially with intial speed very close to zero. (Ignore the effect of gravity, assuming that the electric forces are much greater than the gravitational ones).
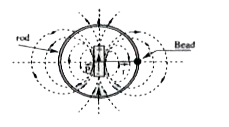
The normal force exerted by rod on the bead is (q = angle between an radius vector of bead, (considering dipole as origin)
2K|→p|θ.cosθr3
K|→p|θ.cosθr3
zero
K|→p|θ.sinθr3
The correct Answer is:C
Step by step video solution for A small, electrically charged bead can slide on a circular, frictioless, insulating rod. A point - like electric dipole (vec(P)) is fixed at the centre of the circle with the dipole.s axis lying in the plane of the circle. Intially the bead is on the plane of symmetry of the dipole, as shown in the figure. The bead is slightly displaced along ring, tangentially with intial speed very close to zero. (Ignore the effect of gravity, assuming that the electric forces are much greater than the gravitational ones). The normal force exerted by rod on the bead is (q = angle between an radius vector of bead, (considering dipole as origin) by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023टॉपर्स ने हल किए ये सवाल
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE -V ELECTRIC DIPOLE) (LEVEL -II INTEGER TYPE QUESTION)
Explore 2 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL - I (MAIN) (STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)
Explore 24 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELECTROSTATICSExercise:PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE -V ELECTRIC DIPOLE) (LEVEL -II STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION)
Explore 7 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETICSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELECTROMAGNETICSExercise:ADDITIONAL EXERCISE
Explore 13 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORSBook:AAKASH SERIESChapter:ELEMENTS OF VECTORSExercise:QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
Explore 10 Videos
समान प्रश्न
A small, electrically charged bead can slide on a circular, frictioless, insulating rod. A point - like electric dipole (→P) is fixed at the centre of the circle with the dipole.s axis lying in the plane of the circle. Intially the bead is on the plane of symmetry of the dipole, as shown in the figure. The bead is slightly displaced along ring, tangentially with intial speed very close to zero. (Ignore the effect of gravity, assuming that the electric forces are much greater than the gravitational ones).

The normal force exerted by rod on the bead is (q = angle between an radius vector of bead, (considering dipole as origin)
View SolutionFind the electric dipole moment of the system shown in figure.
View SolutionDue to an electric dipole shown in fig., the electric field intensity is parallel to dipole axis :

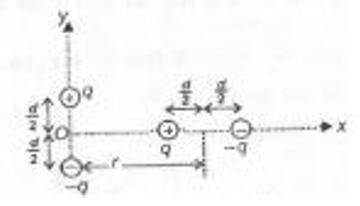
View SolutionTwo identical electric dipoles of dipole moments p are placed as shown in the figure. The electrostatic force on dipole placed along x-axis is (d << r) (14πε0 )
View SolutionAn electric dipole is placed along x-axis with its centre at origin:
View SolutionAn electric dipole is kept in the electric field produced by a point charge
View SolutionTwo short electric dipoles are placed as shown. The energy of electric interaction these dipoles will be
View SolutionA dipole of dipole moment P is kept at the centre of a ring of radius R and charge Q. If the dipole lies along the axis of the ring. Electric force on the ring due to the dipole is : (K=14πε0)
View SolutionAn electric dipole is placed in an uniform electric field with the dipole axis making an angle θ with the direction of the electric field. The orientation of the dipole for stable equilibrium is
View SolutionAn electric dipole is placed in uniform electric field as shown in the figure. The dipole is slightly rotated about its centre and released. Select the correct statement(s).
View Solution
