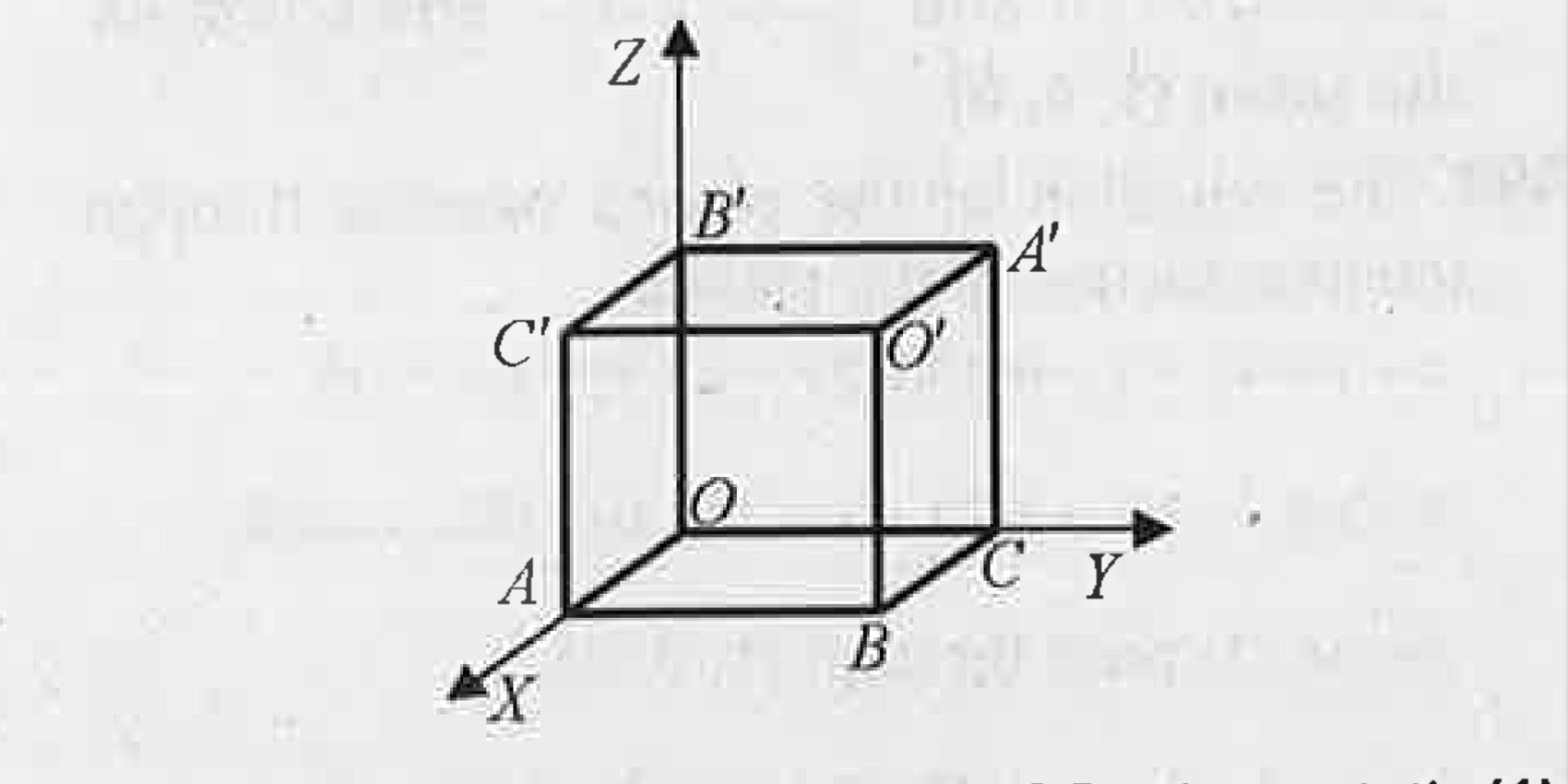
A cube in the first octant has sides OP, OQ and OR of length 1, along the z-axis, y-axis and z-axis, respectively, where O(0, 0, 0) is the origin. Let the centre of the cube be at S(12.12,12) and T be the vertex of the cube opposite to the origin O such that S lies on the diagonal OT. If →p=−→SP,→q=−−→SQ,→r=−−→SR and →t=−→ST, then the value of ∣∣(→p×→q)×(→r×→t)∣∣ is:
The correct Answer is:50
টপার এই প্রশ্নগুলো সমাধান করেছে
সম্পর্কিত প্রশ্ন
The sum of rational terms in the binomial expansion of (√2+5√3)10 is
View SolutionIf x=(√3+1)2n+1, then [x] is
[Note: Where [x] is greatest integer function'
View SolutionConsider the cube in the first octant with sides OP,OQ and OR of length 1, along the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis, respectively, where O(0,0,0) is the origin. Let S(12,12,12) be the centre of the cube and T be the vertex of the cube opposite to the origin O such that S lies on the diagonal OT. If →p=−→SP,→q=−−→SQ,→r=−−→SR and →t=−→ST then the value of ∣∣(→p×→q)×(→r×(→t)∣is
View SolutionConsider a pyramid OPQRS located in the first octant (x≥0,y≥0,z≥0) with O as origin, and OP and OR along the x-axis and the y-axis,respectively. The base OPQR of the pyramid is asqu are with OP=3. The point S is directly above the mid-point T of diagonal OQ such that TS=3.Then
View SolutionvecP,vecQ,vecR,vecS are vector of equal magnitude. If vecP+vecQ-vecR=0 angle between vecP and vecQ is theta_(1) .If vecP+vecQ-vecS=0 angle between vecP and vecS is theta_(2) .The ratio of theta_(1) to theta_(2) is
View Solution→p,→q,→ be vectors such that →q.→r=0 and →p.→q≠0. Let α is real constant such that →x.→p=α,→x×→q=→r, then →x−λ1→q=λ2(→p×→r) where
View SolutionConsider a pyamid OPQRS locaated in the first octant (x≥0,y≤0,z≤0) with O as origin , and OP an OR along the x-axis and y-axis respectively. The base OPQR of the pyramid is a square with OP=3 . The point S is directly above the mid-point T of the diagonal OQ such that TS=3 , Then , the angle between OQ and OS, is
View SolutionConsider a pyramid OPQRS located in the first octant (x≥0,y≥0,z≥0) with O as origin and OP and OR along the X-axis and the Y-axis , respectively. The base OPQRS of the pyramid is a square with OP=3. The point S is directly above the mid point T of diagonal OQ such that TS=3. Then,
View SolutionConsider a pyramid OPQRS located in the first octant (x≥0,y≥0,z≥0) with O as origin and OP and OR along the X-axis and the Y-axis, respectively. The base OPQRS of the pyramid is a square with OP = 3. The point S is directly above the midpoint T of diagonal OQ such that TS = 3. Then,
View Solutionप्रथम अष्टांश में एक ऐसे घन पर विचार कीजिए, जिसकी भुजाओं OP, OQ और OR की लम्बाई 1 है और जो क्रमश: x-अक्ष, y-अक्ष और z-अक्ष के अनुदिश हैं, जहाँ O(0,0,0) मूलबिन्दु है | मना कि घन का केन्द्र S(12,12,12) है, शीर्ष T मूलबिन्दु O के सम्मुख वाला वह शीर्ष है कि बिन्दु S विकर्ण OT पर स्थित है | यदि →p=−→SP,→q=−−→SQ,→r=−−→SR और →t=−→ST, तब ∣∣(→p×→q)×(→r×→t)∣∣ का मान है
View Solution→P,→Q,→R,→S are vector of equal magnitude. If →P+→Q−→R=0 angle between →P and →Q is θ1 . If →P+→Q−→S=0 angle between →P and →S is θ2 . The ratio of θ1 to θ2 is
View Solutionविचार कीजिये, एक सूच्याकार (pyramid, OPQRS) जो प्रथम अष्टांशक (first octant) (x≥0,y≥0,z≥0) में स्थित है, जिसमें O मुलबिन्दु (origin) तथा OP तथा OR क्रमश: x- अक्ष है | इस सूच्याकार का आधार (base) OPQR एक वर्ग (square) है जिसमें OP = 3 है | बिन्दु S कर्ण (diagonal) OQ के मध्यबिन्दु T के ठीक ऊपर इस प्रकार है कि TS=3 है, तब
View Solutionप्रथम अष्टांश में एक ऐसे घन पर विचार कीजिए, जिसकी भुजाओं OP, OQ और OR की लम्बाई 1 है और जो क्रमश: x-अक्ष, y-अक्ष और z-अक्ष के अनुदिश हैं, जहाँ O(0,0,0) मूलबिन्दु है | मना कि घन का केन्द्र S(12,12,12) है, शीर्ष T मूलबिन्दु O के सम्मुख वाला वह शीर्ष है कि बिन्दु S विकर्ण OT पर स्थित है | यदि →p=−→SP,→q=−−→SQ,→r=−−→SR और →t=−→ST, तब ∣∣(→p×→q)×(→r×→t)∣∣ का मान है
View SolutionConsider a cube of side 'a' unit has one vertex at the origin O.
Show that the angle between the main diagonals of the above cube is cos−1(13)
View SolutionConsider a pyramid OPQRS located in the first octan (x≥0,y≥0z≥0) with O as origin, and OP and OR along the x-axis and the y-axis, respectively. The base OPQR of the pyramid is a square with OP =3. The point S is directly above the midpoint T of diagonal OQ such that TS = 3. Then
View SolutionConsider a pyramid OPQRS located in the first octant (x≥0,y≥0,z≥0) with O as origin and OP and OR along the X-axis and the Y-axis , respectively. The base OPQRS of the pyramid is a square with OP=3. The point S is directly above the mid point T of diagonal OQ such that TS=3. Then,
View Solution

