A 1 kg mass is projected down a rough circular track (radius = 2 m) placed in vertical plane as shown. The speed of the mass at point P is 3 m/s and at point Q is 6 m/s. How much work is done on the mass between points P and Q by the force of friction? (Take g = 10 m/s2)

−7.5 J
−8.5 J
−6.5 J
−24 J
The correct Answer is:C
Step by step video solution for A 1 kg mass is projected down a rough circular track (radius = 2 m) placed in vertical plane as shown. The speed of the mass at point P is 3 m/s and at point Q is 6 m/s. How much work is done on the mass between points P and Q by the force of friction? (Take "g = 10 m/s"^2) by Physics experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 9 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- NSO QUESTION PAPER 2018 SET B Book:SCIENCE OLYMPIAD FOUNDATION Chapter:NSO QUESTION PAPER 2018 SET B Exercise:ACHIEVERS SECTION
Explore 4 Videos
- NSO QUESTION PAPER 2018 SET ABook:SCIENCE OLYMPIAD FOUNDATION Chapter:NSO QUESTION PAPER 2018 SET AExercise:ACHIEVERS SECTION
Explore 4 Videos
- NSO QUESTION PAPER 2019 SET ABook:SCIENCE OLYMPIAD FOUNDATION Chapter:NSO QUESTION PAPER 2019 SET AExercise:ACHIEVERS SECTION
Explore 2 Videos
Similar Questions
Read the given passage and fill in the blanks by selecting an appropriate option.
The velocity-time graphs of a car and a scooter are shown in the figure. The difference between the distance travelled by the car and the scooter in first 15 s is __(i)__ and the time at which the car will catch up with the scooter is ___(ii)___ . At time t = 10 s, acceleration of car is ___(iii)___ while velocity of scooter is (iv).
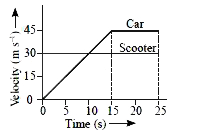
View SolutionRefer to the given graph which shows a variable force acting on a particle of mass 2 kg and fill in the blanks by selecting an appropriate option.
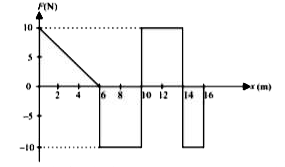
If the initial kinetic energy (at x = 0) of the particle is 25 J, then the kinetic energy of the particle at the end of 6 m and 16 m is (i) –––––– and (ii) ––––––– respectively. The momentum of the particle at the end of 10 m and 14 m is (iii) –––––––– and (iv) ––––––––– respectively.
View SolutionRead the given passage and answer the following questions.
A small block of mass M = 1 kg moves on a frictionless surface of an inclined plane, as shown in the figure. The angle of the incline suddenly changes from 60∘ to 30∘ at point Q. The block is initially at rest at point P. Assume that there is no loss of energy for collisions between the block and the incline. (Take g = 10 m s−2)
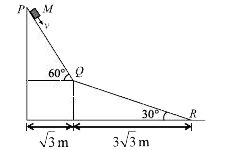
The speed of the block at point Q immediately before it strikes the second incline is
View SolutionA 1kg mass is projected down a rough circule track (redius=2.0m) placed in vertical plane as shown. The speed of the mass at point A is 3m/s and at point B, it is 6.0m/s. How much is work is done on the mass between A and B by the force of friction?

View SolutionA ball is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 5m/sec from point P as shown Q is a point 10m vertically below the point P. Then the speed of ball at point Q will be : (take g=10m/s2 and neglect air resistance)
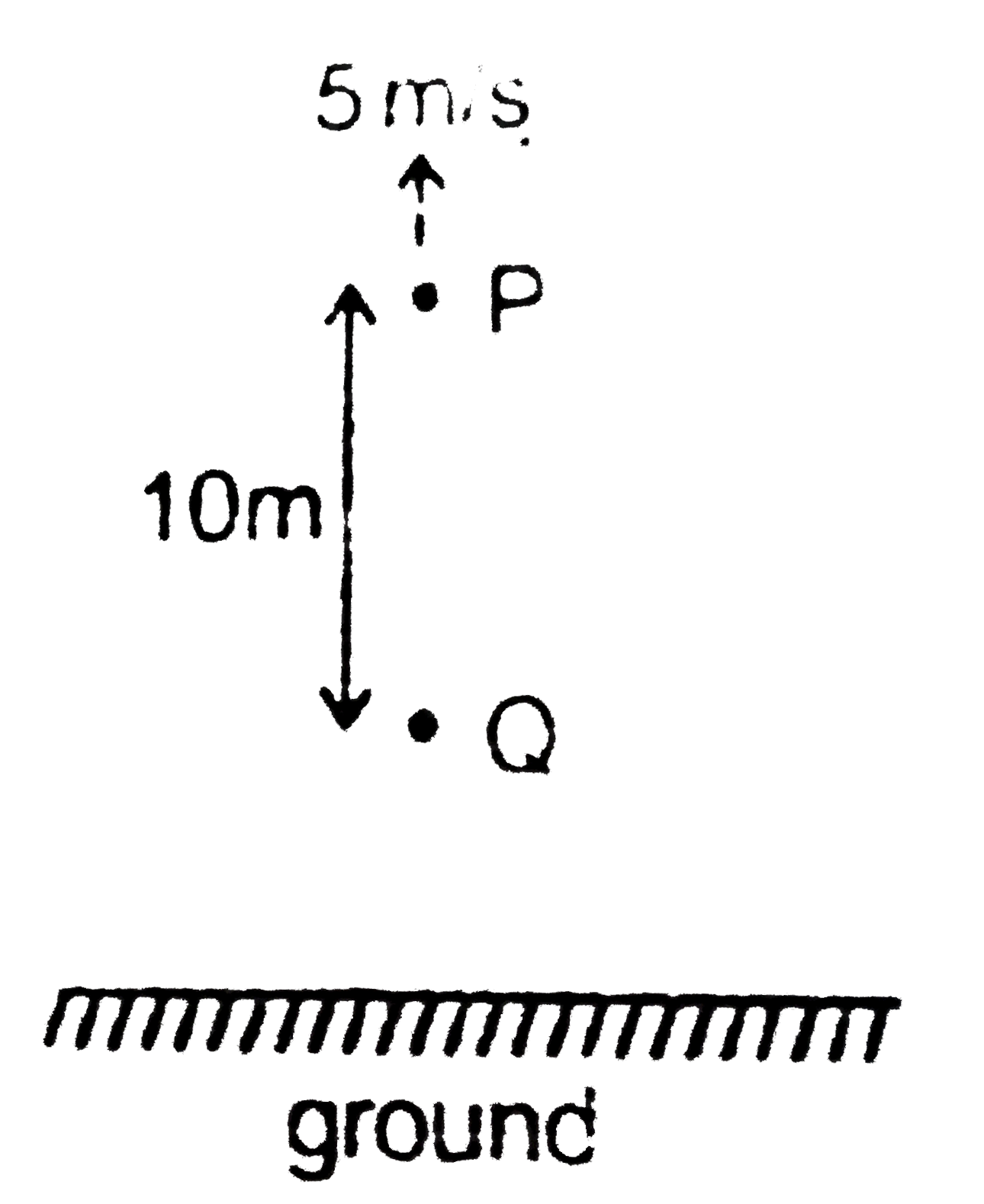
View SolutionA block of mass 1 kg slides down a vertical curved track that is one quadrant of a circle of radius 1m. Its speed ast the the bottom si 2m/s. The work done by frictional force is :
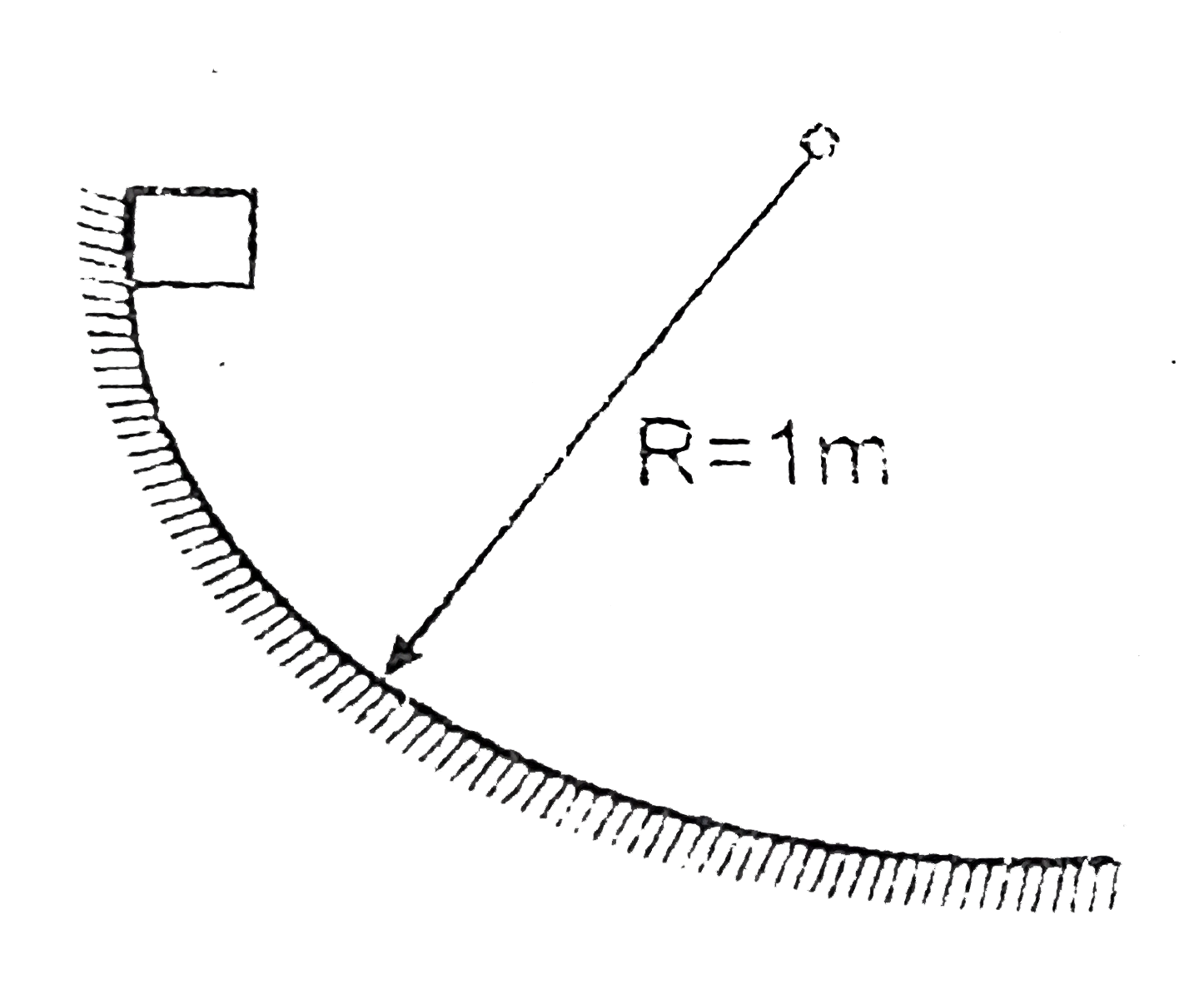
View SolutionTwo particles P and Q have mass 1 kg and 2 kg respectively. They are projected along a vertical line with velocity u_(p) = 20 m/s and u_(Q) = 5 m/s when separation between them was 60 m. P was projected vertically up while Q was projected vertically down. Calculate the maximum height attained by the centre of mass of the system of two particles, measured from the initial position of P. Assume that the particles do not collide and that the ground is far below their point of projection [g = 10 m//s^(2)]
View SolutionIn the diagram shown in figure wedge of mass M is stationary. Block of mass m=2 kg is slipping down. Force of friction on the wedge from ground is (g=10m/s2)
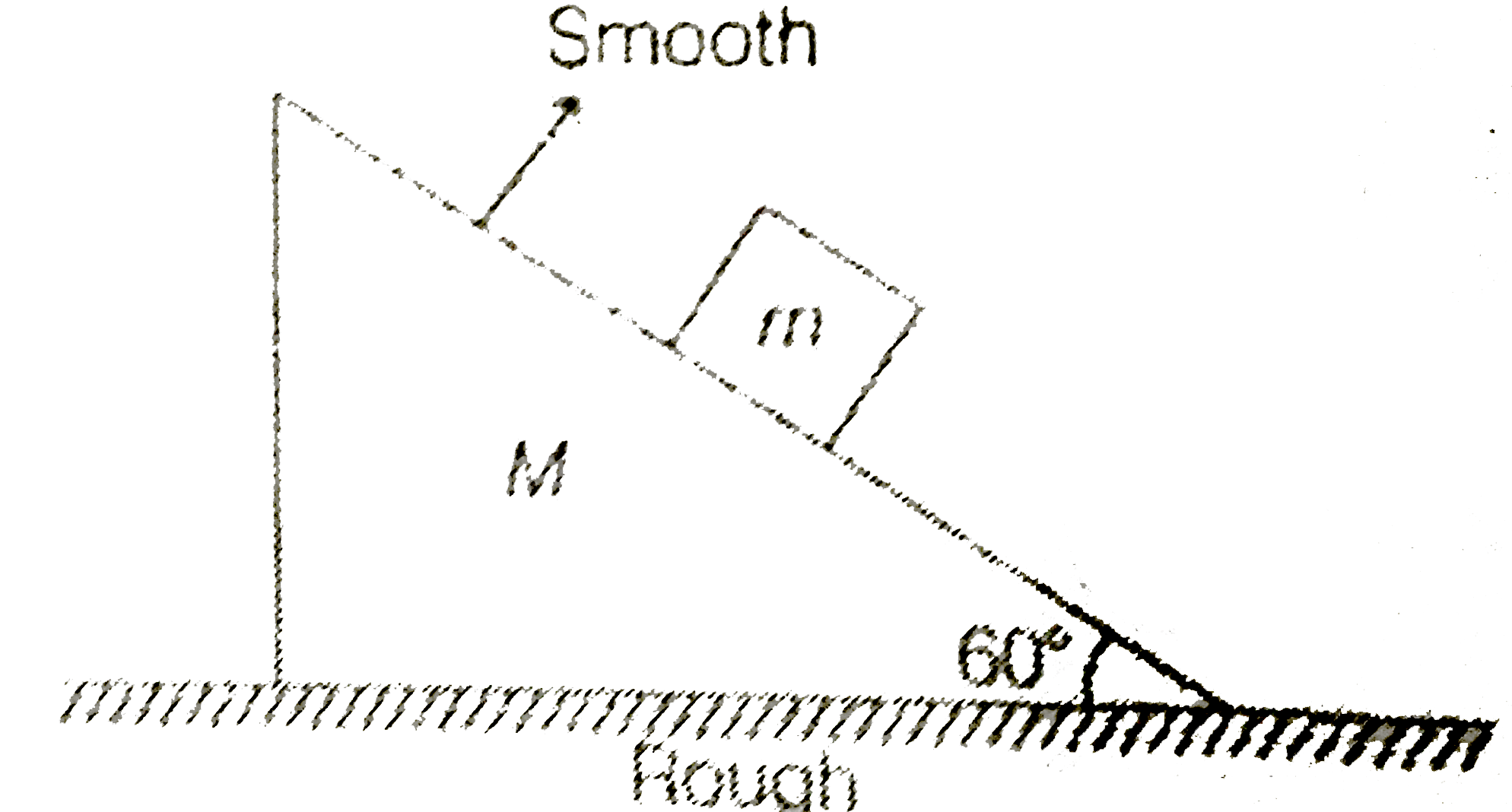
View Solution5.0 kg द्रव्यमान की एक वस्तु को ऊर्ध्वाधरत: पृथ्वी से 2.4 m की ऊँचाई तक उठाने में कितना कार्य करना पड़ेगा ? (g=10 m/s2)
View Solution50 kg द्रव्यमान की एक वस्तु 10 मी/से के वेग से चल रही है | वस्तु का वेग 20 मी/से तक बढ़ाने के लिए कितना कार्य करना होगा ?
View SolutionA block of mass 1 kg slides down a vertical curved track that is one quadrant of a circle of radius 1m. Its speed ast the the bottom si 2m/s. The work done by frictional force is :

View SolutionP and Q run on a circular track of 100 m speed of P is 250 m/s and that of Q is 400 m/s at how many points on a circular track will they meet if they start fromn the same point simultaneously in the same direction?
View SolutionA body of mass 1 kg falls from rest through a distance of 200 m and acquires a speed of 50 m/s. Work done against friction of air is (Take g=10m/s2)
View SolutionIn the diagram shown in figure wedge of mass M is stationary. Block of mass m=2 kg is slipping down. Force of friction on the wedge from ground is (g=10 m//s^(2))
View Solution5kg द्रव्यमान का एक पिण्ड स्थिर अवस्था से 20 m की उर्ध्वाधर दूरी तक गिरता है, और 10 m/s का वेग प्राप्त होता है। वायु प्रतिरोध द्वारा पिण्ड पर कितना कार्य किया गया है? (g=10m/s2)
View SolutionP and Q run on a circular track of 100 m speed of P is 250 m/s and that of Q is 400 m/s at how many points on a circular track will they meet if they start fromn the same point simultaneously in the same direction?
View Solution
