In an experiment , to study the dependence of potential difference (V) on the electric current (I) across a conductor (resistor), if the circuit is on for long time, then -select two correct options from the following:
(i) Zero error of an ammeter will be changed.
(ii) Zero error of a voltmeter will be changed .
(iii) Value of a resistance will be changed.
(iv) Resistor will be heated.
To solve the question regarding the effects of keeping a circuit on for a long time while studying the dependence of potential difference (V) on electric current (I) across a conductor (resistor), we need to analyze the options provided.
1. Understanding the Experiment:
- The experiment involves measuring the potential difference (V) and current (I) across a resistor.
2. Effects of Continuous Current:
- When the circuit is on for a long time, the resistor will conduct current continuously, which leads to the generation of heat due to the electrical energy being converted into thermal energy.
3. Analyzing the Options:
- Option (i): Zero error of an ammeter will be changed.
- This is incorrect. The zero error of an ammeter is a calibration issue and does not change with the duration the circuit is on.
- Option (ii): Zero error of a voltmeter will be changed.
- This is also incorrect for the same reason as above; the zero error of a voltmeter is a calibration issue and remains unchanged.
- Option (iii): Value of a resistance will be changed.
- This is correct. As the resistor heats up due to the continuous flow of current, its resistance changes according to the formula R=R0(1+αΔT), where α is the temperature coefficient of resistance and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- Option (iv): Resistor will be heated.
- This is correct. The continuous flow of current through the resistor will generate heat, causing the resistor to increase in temperature.
4. Final Selection:
- The two correct options are:
- (iii) Value of a resistance will be changed.
- (iv) Resistor will be heated.
Conclusion:
The correct answers are options (iii) and (iv).
---
- The experiment involves measuring the potential difference (V) and current (I) across a resistor.
- When the circuit is on for a long time, the resistor will conduct current continuously, which leads to the generation of heat due to the electrical energy being converted into thermal energy.
- Option (i): Zero error of an ammeter will be changed.
- This is incorrect. The zero error of an ammeter is a calibration issue and does not change with the duration the circuit is on.
- Option (ii): Zero error of a voltmeter will be changed.
- This is also incorrect for the same reason as above; the zero error of a voltmeter is a calibration issue and remains unchanged.
- This is correct. As the resistor heats up due to the continuous flow of current, its resistance changes according to the formula R=R0(1+αΔT), where α is the temperature coefficient of resistance and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- This is correct. The continuous flow of current through the resistor will generate heat, causing the resistor to increase in temperature.
- The two correct options are:
- (iii) Value of a resistance will be changed.
- (iv) Resistor will be heated.
The correct answers are options (iii) and (iv).
Similar Questions
To study the dependence of potential difference (V) on current I across Resistor (R), Four circuit diagrams are prepared.
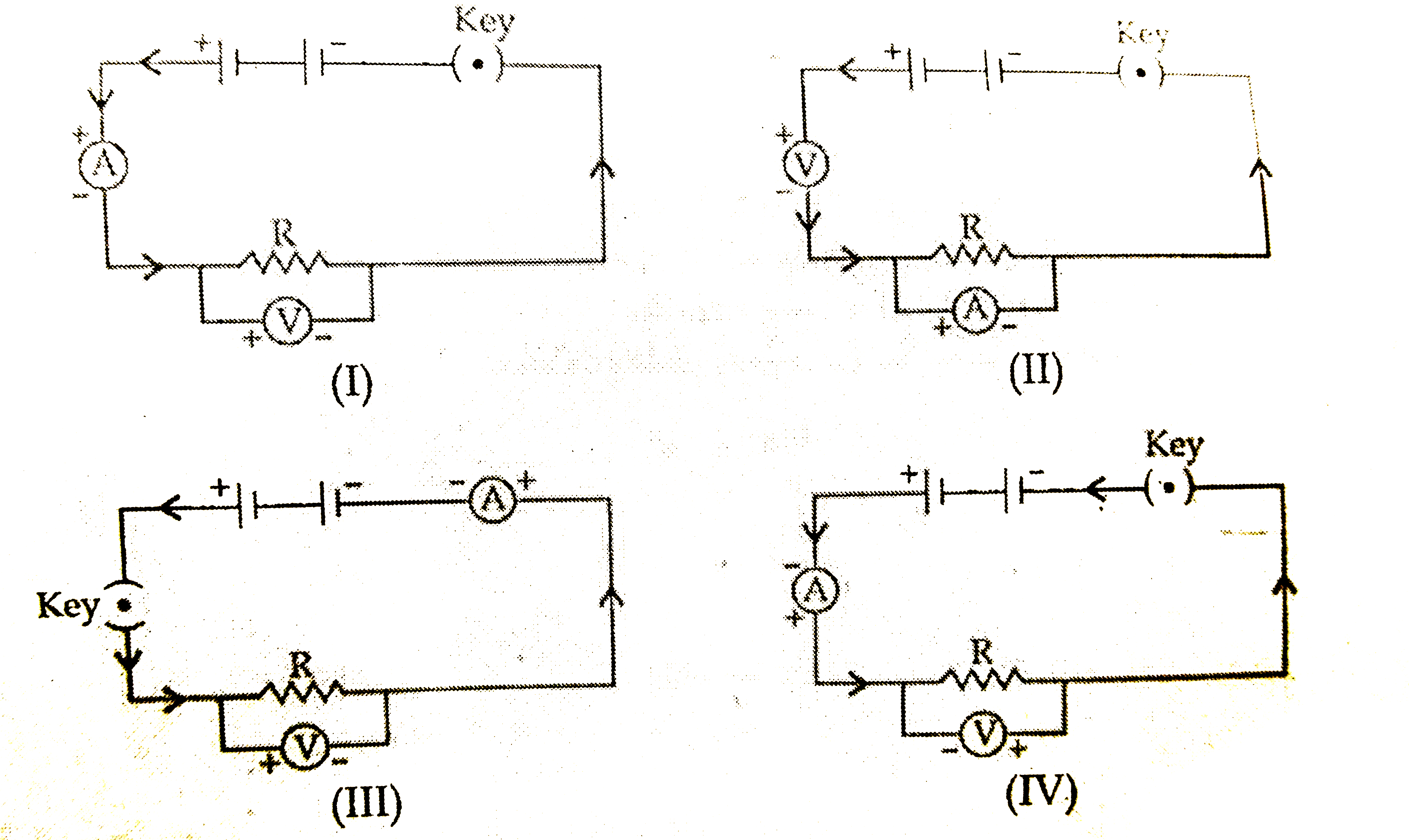
(i) Select the circuit diagrams which are correct.
(ii) Give reason for the circuit diagrams which are not correct.
View SolutionStudy the following electric circuit (i) Calculate the current flowing in the circuit and (ii) Calculate the potential difference across 10Ω resistor
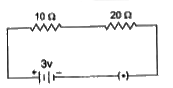
View SolutionDraw a labelled circuit diagram to study the dependence of current (I) on the potential
difference (V) across a resistor.
View SolutionTo study the dependence of potential difference (V) on current I across Resistor (R), Four circuit diagrams are prepared. (i) Select the circuit diagrams which are correct. (ii) Give reason for the circuit diagrams which are not correct.
View SolutionThe current in a conductor and the potential difference across its ends are measured by an ammeter and a voltmeter.The meters draw negligible current.The ammeter is accurate but the vlotmeter has a zero error(that is ,it does not read zero when no potential difference is applied).Calculate the zero error if the readings for two different conditions are 1.75A, 14.4Vand 2.75a, 22.4V.
View SolutionThe resistance of a metal is given by R = V//I , where V is potential difference and I is current . In a circuit , the potential difference across resistance is V = ( 8 +- 0.5) V and current in resistance , I = ( 4 +- 0.2)A . What is the value of resistance with its percentage error?
View SolutionA voltmeter and an ammeter are connected in series to an ideal cell of emfE. The voltmeter reading is V, and the ammeter readings is I. Then
(i) V<E (ii) the voltmeter resistance is V/I
(iii) the potential difference across the ammeter is E−V
(iv) Voltmeter resistance + ammeter resistance = E//I
Correct statements are
View Solution
