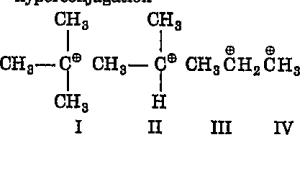
(i) The stability of carbocation is explain by delocalised structure of hyperconjugation.
(ii) The stability of carbocation is explain by drawing the resonance structure.
(iii) Hyperconjugation effect is (+) or (-)
(iv) Mesomeric effect is (+) or (-)
Text Solution
(i−T),(ii−F),(iii−F),(iv−T)
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Stability of alkyl carbocations can be explained by
Ainductive effect onlyBhyperconjugation onlyCboth inductive effect and hyperconjugationDelectromeric effect onlyStability of alkyl carbocations can be explained by
Ainductive effect onlyBhyperconjugation onlyCboth inductive effect and hyperconjugationDelectromeric effect only
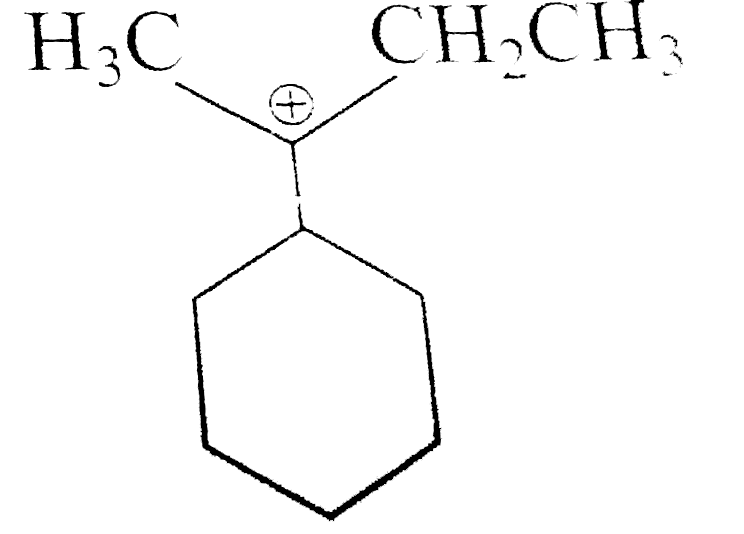
The total number of contributing structures showing hyperconjugation (involving C−H bonds) for the following carbocation is

View SolutionThe total number of contributing structures showing hyperconjugation (involving C−H bonds) for the following carbocation is:
View SolutionWhat is the effect of introducing an alkyl group on the stability of carbocation?
View SolutionWhat is the effect of introducing an alkyl group on the stability of carbocation?
View SolutionThe total number of contributing structures showing hyperconjugation (involving C−H bonds) for the following carbocation is:

View SolutionExplain the
Hyperconjugation effect is also termed as 'no bond resonance'.
View Solution