A spherical planet far out in space has a mass M0 and diameter D0. A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an accelertion due to gravity which is equal to
GMP/D2P
4GMPm/D2P
4GMP/D2P
GMPm/D2P
The correct Answer is:C
g=GMPR2P where RP=DP/2
Topper's Solved these Questions
- NEETBOOK - NEET PREVIOUS YEAR (YEARWISE + CHAPTERWISE)CHAPTER - NEETEXERCISE - MCQs
613 Videos
- NEETBOOK - NEET PREVIOUS YEAR (YEARWISE + CHAPTERWISE)CHAPTER - NEETEXERCISE - QUESTION
83 Videos
- MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONBOOK - NEET PREVIOUS YEAR (YEARWISE + CHAPTERWISE)CHAPTER - MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONEXERCISE - All Questions
47 Videos
- NEET 2020BOOK - NEET PREVIOUS YEAR (YEARWISE + CHAPTERWISE)CHAPTER - NEET 2020EXERCISE - All Questions
45 Videos
Similar Questions
Two masses as shown are suspended from a massless pulley. Calculate the acceleration of the system when masses aere left free:
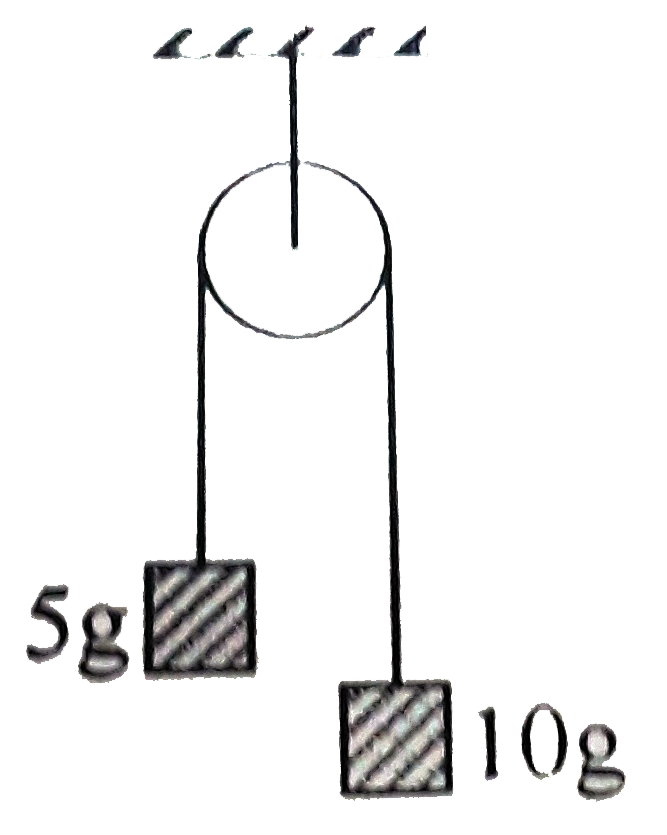
View SolutionThe mass of a .73Li nucleus is 0.042u less than the sum of the masses of all its nucleons. The binding energy per nucleon of .73Li nucleus is nearly
View SolutionThe x and y coordinates of the particle at any time are x=5t−2t2andy=10t respectively, where x and y are in meters and t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle at t=2s is:
View SolutionLight with an average flux of 20Wcm2 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence having surface area 20cm2. The energy received by the surface during time span of 1 minute is:
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M_(0) and diameter D_(0) . A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an accelertion due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M0 and diameter D0. A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an accelertion due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet has a mass Mp and diameter Dp. A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity, equal to:
View SolutionA spherical planet has a mass Mp and diameter Dp. A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity, equal to :
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M0 and diameter D0. A particle of mass .m. falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M_0 and diameter D_0 A particle of mass .m. falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M0 and diameter D0. A particle of mass 'm' falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M_(0) and diameter D_(0) . A particle of mass 'm' falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M0 and diameter D0. A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an acceleration due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M_(0) and diameter D_(0) . A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an accelertion due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M_(0) and diameter D_(0) . A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an accelertion due to gravity which is equal to
View SolutionA spherical planet far out in space has a mass M0 and diameter D0. A particle of mass m falling freely near the surface of this planet will experience an accelertion due to gravity which is equal to
View Solution

