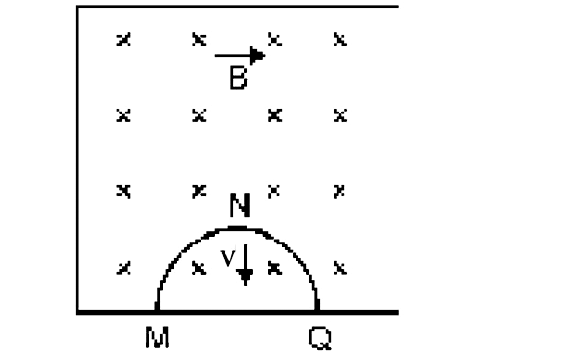
A thin semicircular conducting ring (POR) of radius r is falling with its Q B plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed is v, is

zero
Bvπr22 and P is at higher potential
πrBv and R is at higher potential
2rBv and R is at higher potential
The correct Answer is:D
Motional emf induced in the semicircular ring PQR is equivalent to the motional emf induced in the imaginary conductor PR.
i.e.,εPQR=Bvl=Bv(2r)
Therefore, potential difference developed across the ring is 2rBv with R is at higher potential.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTSBook:MTG GUIDEChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENTSExercise:CHECK YOUR NEET VITALS
Explore 25 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Book:MTG GUIDEChapter:DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Exercise:AIPMT/ NEET MCQs
Explore 30 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVESBook:MTG GUIDEChapter:ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVESExercise:AIPMT/NEET(MCQs)
Explore 15 Videos
Similar Questions
Two coils have a mutual inductance 0.005 H, The current changes in the first coil according to the equation i=imsinωt where im=10A and ω=100πrads−1. The maximum value of the emf induced in the second coil is
View SolutionWhen monochromatic radiation of intensity I falls on a metal surface, the number of photoelectrons and their maximum kinetic are N and T respectively. If the intensity of radiation is 2 I, the number of emitted electrons and their maximum kinetic energy are respectively.
View SolutionWhich of the following statement is false for the properties of electromagnetic waves?
View SolutionA thin semi-circular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane verticle in horizontal magnetic induction (→B). At the position MNQ the speed of the ring is v, and the potential difference developed across the ring is
View SolutionA thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic induction B. At the position MNQ, the speed of the ring is V and the potential difference developed across the ring is

View SolutionA thin semicircuilar conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in Fig. The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed is upsilon , is
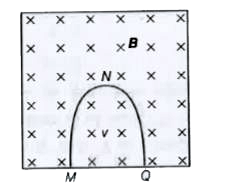
View SolutionA thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic induction B. At the position MNQ shown in the fig, the speed of the ring is V. The potential difference developed across the semicircular ring is
View Solutionr त्रिज्या की एक पतली अर्धवृत्ताकार चालक रिंग (वलय) PQR किसी क्षैतिज चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र B में गिर रही है । गिरते समय इसका समतल आरेख में दर्शाये गए अनुसार ऊर्ध्वाधर रहता है । जब गिरते हुए रिंग की चाल v है तो , इसके दो सिरों के बीच विकसित विभवान्तर है :

View Solutionr त्रिज्या की पतली अर्द्धवृत्ताकार रिंग PQR , किसी क्षैतिज चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र B में गिर रही है | गिरते समय इसका समतल , आरेख में दर्शाये गए अनुसार, ऊर्ध्वाधर रहता है | जब गिरती हुई रिंग की चाल v है तो इसके दो सिरों के बीच विकसित विभवांतर होगा -
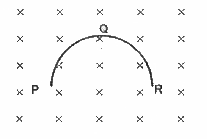
View Solutionएक अर्द्धवृत्ताकार वलय जिसकी त्रिज्या R है अपने तल के लम्बवत क्षैतिज चुम्बकीय क्षेत्र B में गिर रही है। MNQ स्थिति पर वलय की चाल है तथा वलय में विभवान्तर है
View SolutionA thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v, is
View SolutionA thin circular -conducting ring having N turns of radius R is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B . At the position MNQ the speed of ring is v the induced e.m.f developed across the ring is
View Solutionत्रिज्या R की एक पतली अर्द्धवृत्ताकार धात्विक वलय क्षैतिज चुम्बकीय प्रेरण B में इस प्रकार गिर रही है कि इसका तल ऊर्ध्वाधर रहता है। जब यह वलय MNQ की स्थिति में पहुँचती है तब इसका वेग । है। इस समय अर्द्धवृत्ताकार वलय में उत्पन्न विभवान्तर होगा

View SolutionA thin semicircular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane verticle in a horizontal magnetic inducting B . At the position MNQ , the speed of the ring is V and the potential difference developed across the ring is (1.) zero (2.) BcpiR^(2)//2 (3.) piRBV (4.) 2RBV
View SolutionA vertical conducting ring ogradius R falls vertically in a horizontal magnetic field of magnitude B . The direction of B is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. When the speed of the ring is v,
View SolutionA thin semi-circular conducting ring of radius R is falling with its plane verticle in horizontal magnetic induction (→B). At the position MNQ the speed of the ring is v, and the potential difference developed across the ring is

View Solution

