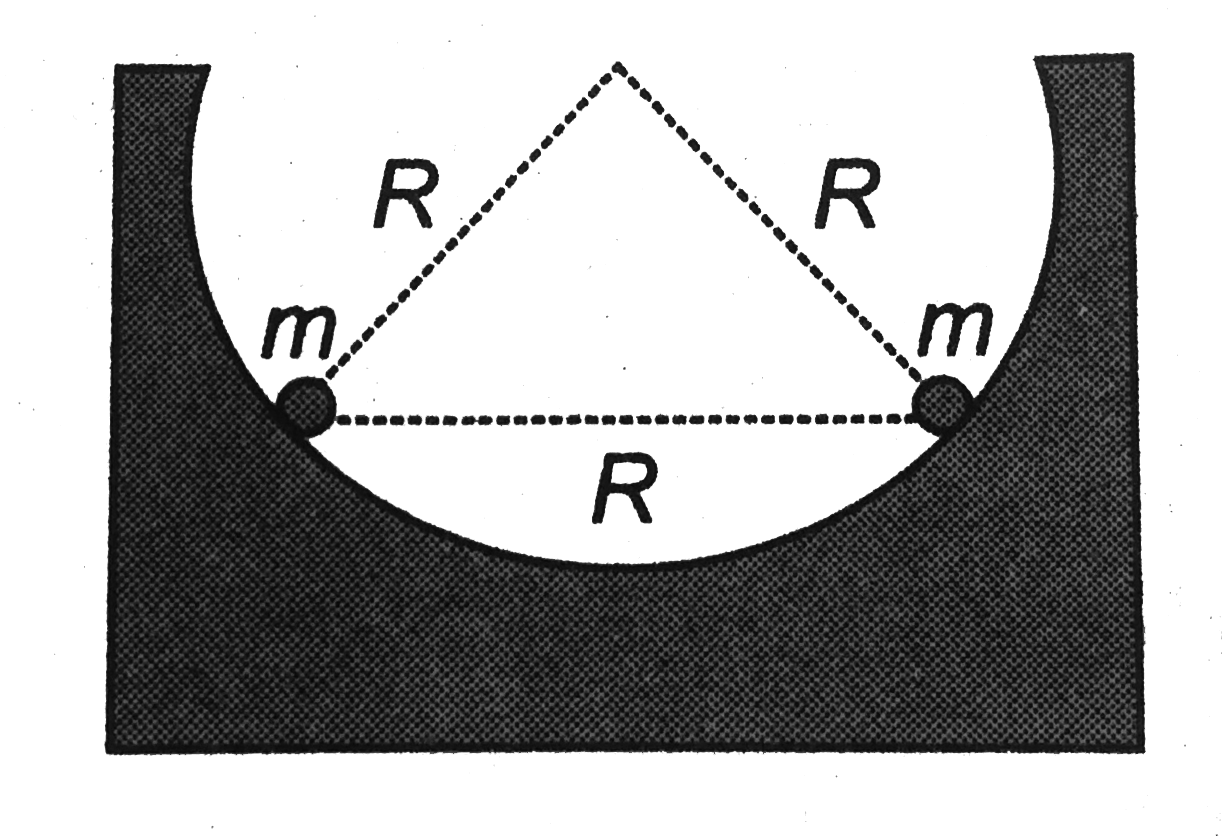
Two identical beads each have a mass m and charge q. When placed in a hemispherical bowl of radius R with frictionless, non-conducting walls, the beads move, and at equilibrium they area distance R apart (figure). Determine the charge on each bead.
The correct Answer is:A, B, C, D

Using Lami's theorem we have
mgsin(90∘+30∘)=mgsin(90∘+60∘)
∴F=mg√3or14πε0(q)(q)R2=mg√3
∴Q=√πε0mgR2√3
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
A capacitor of 2μF is charged as shown in the figure. When the switch S is turned to position 2, the percentage of its stored energy dissipated is

View SolutionA little charged bead is inside the hollow frictionless sphere manufactured from the insulting material. Sphere has a daimeter of 50 cm. The mass of the bead is 90mg, its charge is 0.5μC. What minimum charge must carry an object at the bottom of the sphere to keep hold the charged bead at the vertax of the sphere in stable equilibrium ?
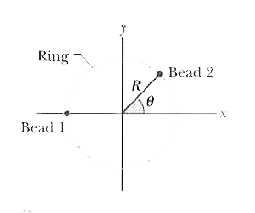
View SolutionFigure shows a distance ring of radius R = 43.0 cm. Two small charged beads are on the ring : Bead 1 of charge +20.0μC is fixed in place at the left side , bead 2 of charge +6.00μC can be moved along the ring. The two beads produce a net electric field of magnitude e at the center of the ring. At what (a) positive and (b) negative value of angle θ should bead 2 be positioned such that E=2.00×105N/C ?
View SolutionTwo identical beads each have a mass m and charge q. When placed in a hemispherical bowl of radius R with frictionless, non-conducting walls, the beads move, and at equilibrium they area distance R apart (figure). Determine the charge on each bead.

View SolutionA horizontal frictionless rod is threaded through a bead of mass m . The length of the cart is L and the radius of the bead, r , is very small in comparison with L(r lt lt L) . Initially at ( t = 0 ) the bead is at the right edge of the cart. The can is struck and as a result, it moves with velocity v_(0) towards right. When the bead collides with the cart's walls, the collisions are always completely elastic. What is the velocity of the cart just after the first collision?
View SolutionA horizontal frictionless rod is threaded through a bead of mass m . The length of the cart is L and the radius of the bead, r , is very small in comparison with L(r lt lt L) . Initially at ( t = 0 ) the bead is at the right edge of the cart. The can is struck and as a result, it moves with velocity v_(0) towards right. When the bead collides with the cart's walls, the collisions are always completely elastic. Velocity of bead just after the first collision is
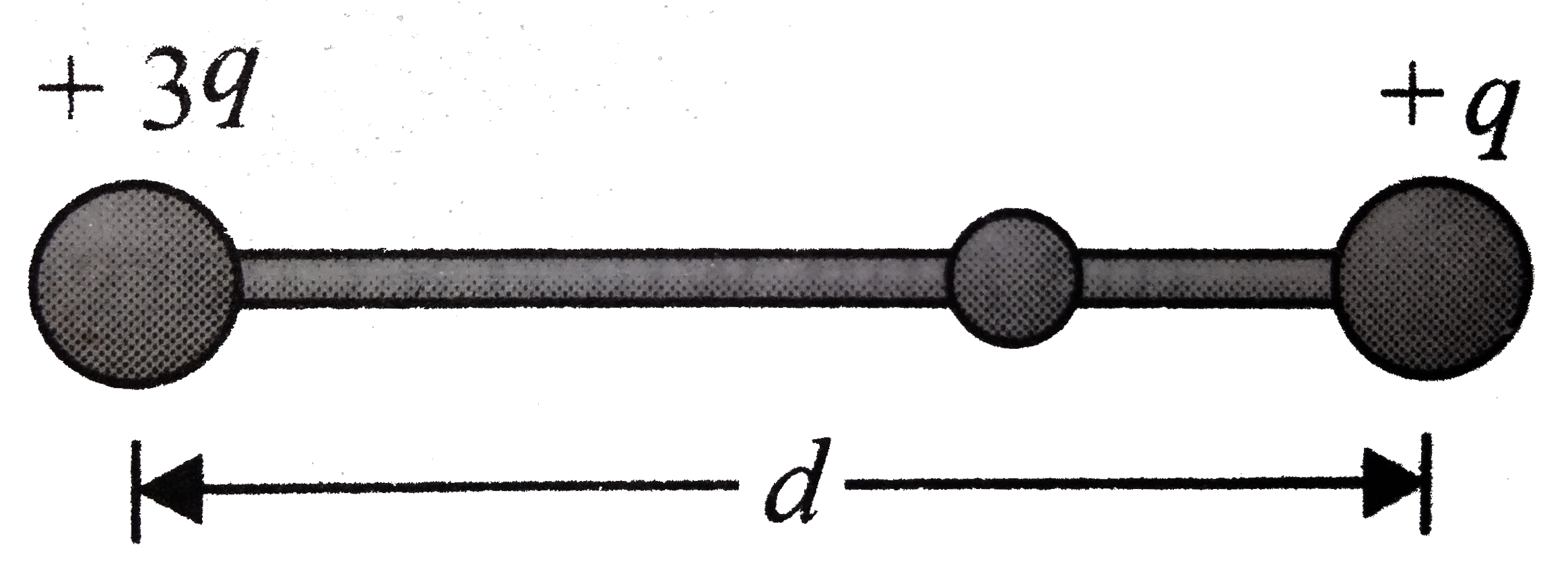
View SolutionTwo small beads having positive charges 3q and q are fixed at the opposite ends of a horizontal, insulating rod, extending from the origin to the point x=d as shown in fig. A third small charged bead is free to slide on the rod. At what position is the third bead in equilibrium? Can it be in stable equilibrium ?
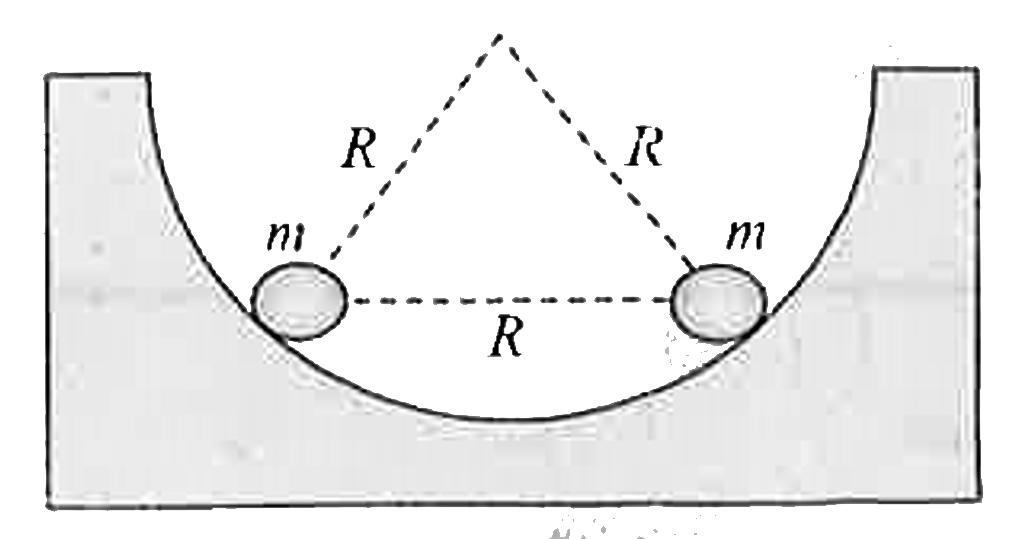
View SolutionTwo identical small balls each have a mass m and charge q. When placed in a hemispherical bowl of radius R with frictionless, nonconductive walls, the bead move, and at equilibrium the line joining the balls is horizontal and the distance between them is R (see figure). Neglect any induced charge on the hemispherical bowl. Then the charge on each bead is : (here K=14πε0)
View Solution

