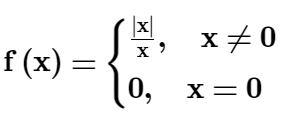If the function f(x) satisfies limx→1f(x)−2x2−1=π, evaluate limX→1f(x).
Video Solution
Text Solution
According to the problem,
limx→1f(x)−2x2−1=π
Now, limX→1[f(x)−2]=limX→1[f(x)−2x2−1.(x2−1)]
=limx→1f(x)−2x2−1.limx→1(x2−1)
=π×0=0
⇒limx→1f(x)=2
|
Topper's Solved these Questions
- LIMITS AND DERIVATIVESBOOK - NAGEEN PRAKASHANCHAPTER - LIMITS AND DERIVATIVESEXERCISE - EX -13.2
11 Videos
- LIMITS AND DERIVATIVESBOOK - NAGEEN PRAKASHANCHAPTER - LIMITS AND DERIVATIVESEXERCISE - Miscellaneous Exercise
30 Videos
- LIMITS AND DERIVATIVESBOOK - NAGEEN PRAKASHANCHAPTER - LIMITS AND DERIVATIVESEXERCISE - EX-13H
9 Videos
- INTRODUCTION OF THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRYBOOK - NAGEEN PRAKASHANCHAPTER - INTRODUCTION OF THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRYEXERCISE - Miscellaneous Exercise
6 Videos
- LINEAR INEQUALITIESBOOK - NAGEEN PRAKASHANCHAPTER - LINEAR INEQUALITIESEXERCISE - MISCELLANEOUS EXERCISE
14 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
If the function f(x) satisfies limx→1f(x)−2x2−1=π, then limx→1f(x) is equal to
A1B2C0D3limx→1xm−1xn−1 is equal to
A1BmnC−mnDm2n2If a differentiable function f(x) satisfies
limx→−1f(x)+1x2−1=32
Then what is limx→−1f(x) equal to ?A−32B−1C0D1