Explain geometrical isomerism in Co-ordination compounds giving suitable examples.Solution in Telugu
Video Solution
Text Solution
→ Geometrical isomerism arises in Co-ordination complexes due to different possible geometric arrangements of the ligands.
→ This isomerism found in complexes with Co-ordination numbers 4 and 6.
→ In a square planar complex of formula [MX2L2] the two ligands may be arranged in adjacent to each other in a cis isomer (or) opposite to each other in a trans isomer.

→ Square planar complex of type [MAB XL] shows three isomers two-cis and one trans. (A, B, X, L are unidentate ligands is square planar complex).
→ Geometrical isomerism is not possible in tetrahedral geometry.
→ In octahedral complexes of formula [MX2L4] in which two ligands X may be oriented cis or trans to each other.
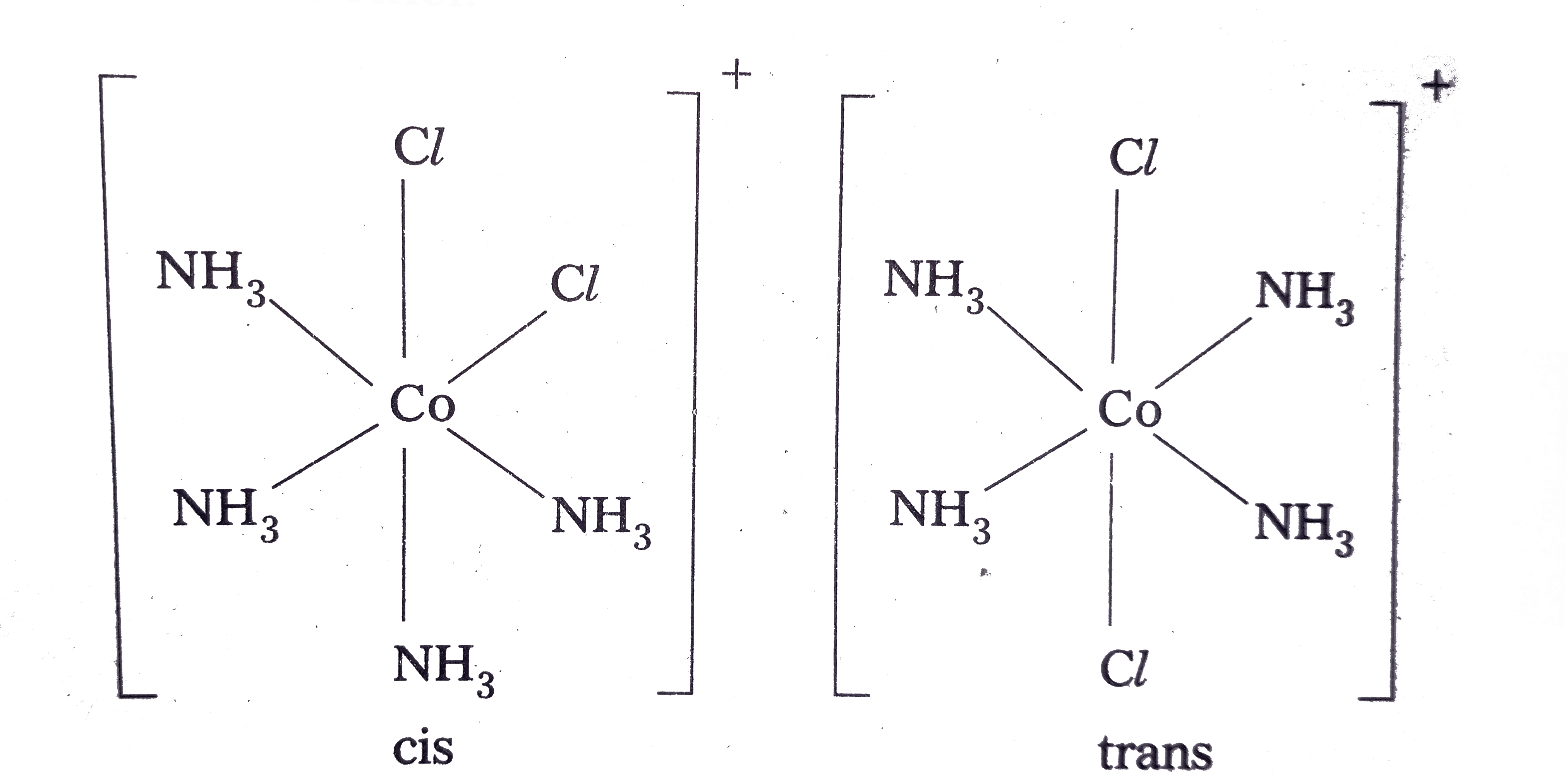
→ Another type of geometrical isomerism occurs in octahedral Co-ordination compoundsof type [Ma3b3] if three donar atoms of the same ligands occupy adjacent positions at the corners of an octahedral face then it is facial (fac) isomer. When the positions occupied are around the meridian of the octahedran then it is meridonial (mer) isomer.
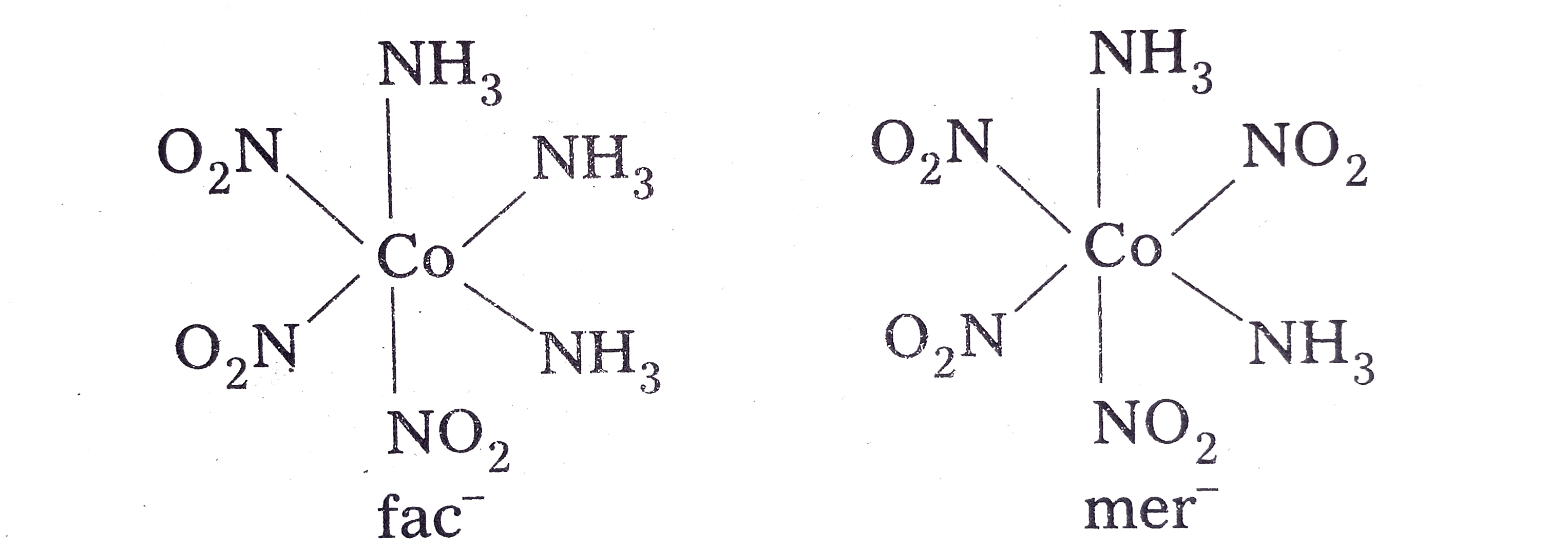
The facial (fac) and meridonial (mer) isomers of [Co(NH3)3(NO2)3]
|
Similar Questions
Explain about the geometrical isomerism of octahedral complexes with suitable example.
View SolutionIllustrate the following with an example : 'Coordination isomerism.'
View SolutionDefine linkage isomerism of.co-ordination compounds. Give an example.
View Solution(a) What is coordination isomerism? Give an example.
View SolutionExplain optical isomerism or Geometrical isomerism with example.
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is found in co-ordination compounds having co-ordination number:
View SolutionGeometrical isomerism is found in co-ordination compounds having co-ordination number:
View SolutionExplain geometrical isomerism with the help of suitable example.
View Solution
